What Are Those Bumps on My Tongue?
Medically reviewed by Edmund Khoo, DDS
Tongue bumps come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on what is causing the bumps. There are many different types of conditions that affect the tongue, including ones that cause the tongue to change color or texture.
Small bumps on the tongue may be caused by common injury or irritation, while bumps that get bigger or worse over time may signal an underlying health condition.
This article discusses potential causes of tongue bumps, what they look like, and when it’s time to contact a healthcare provider.

LaylaBird / Getty Images
What Do Tongue Bumps Look Like?
There are many types of bumps (papillae) on the tongue, each with its own purpose. One such bump, fungiform papillae bumps are located on the sides and top of the tongue, mostly at the tip. Fungiform papillae play an important role—they contain taste buds and temperature receptors. You usually wouldn’t notice fungiform papillae because they’re pink and flat and blend in with the tongue.
However, certain conditions can cause noticeable bumps on the tongue. For example, strawberry tongue—bumps on the tongue that look like strawberry seeds—is one condition in which you would notice the papillae.
What Can Cause Tongue Bumps?
The causes of tongue bumps vary greatly, from simple injury to more serious health conditions. Some bumps are characteristic of a certain condition but are always best diagnosed by a healthcare provider.
Tongue Injuries
Injury to the tongue, such as from accidentally biting the tongue or burning it from a hot drink or food, can cause sores or bumps on the tongue. The injured part of the tongue may be swollen and painful for a few days but will heal on its own.
Lie Bumps (Transient Lingual Papillitis)
When one or more fungiform papillae become inflamed, it’s called transient lingual papillitis, also known as “lie bumps.” When the papillae are inflamed (papillitis) due to irritation or injury, they become more noticeable. The bumps are usually painful.
Besides irritation of the fungiform papillae, other possible causes of transient lingual papillitis are:
Gastrointestinal (digestive system) issues
Stress
Fluctuating hormones
Certain foods
The classic form of transient lingual papillitis is one red or white bump on the tongue that’s raised and painful. The bump usually goes away in a day or two but may show up again.
Sometimes, many bumps develop with a tingling or burning sensation and may stay for a few hours or days, though this is less common.
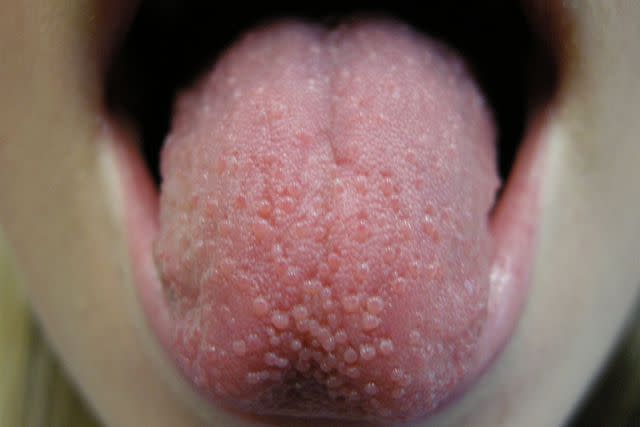
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet dermnetnz.org 2023.
Canker Sores (Aphthous Ulcers)
Canker sores are open sores that appear in the mouth, including on the tongue. A canker sore starts out as a red bump or spot that turns into an open sore. Other symptoms of a canker sore include:
Small in size
Yellow or white in the center
Gray when they heal
Painful
Canker sores can show up for a variety of reasons, including:
Being stressed
Injuring your mouth, such as biting your tongue
Using toothpaste or mouthwash with sodium lauryl sulfate
Smoking
Not getting enough iron, vitamin B12, or folic acid (vitamin B9)
Having an immune system problem
Canker sore pain usually goes away within 10 days, though it can take up to three weeks for them to heal completely and longer for large canker sores.
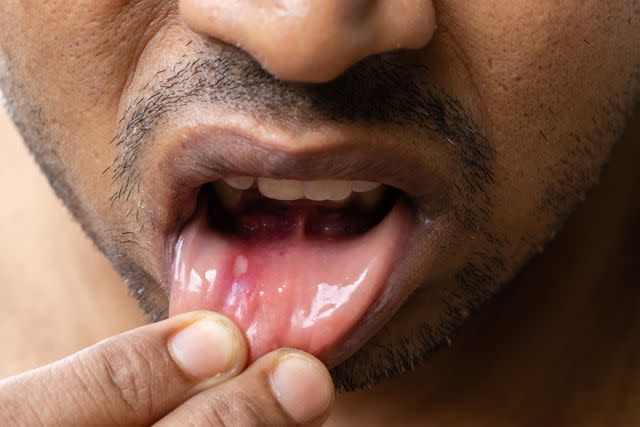
Soumen Hazra / Getty Images
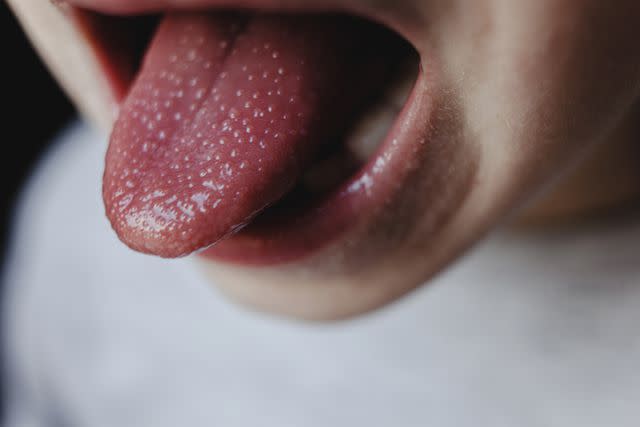
Oral Herpes
Oral herpes is when there are painful blisters (also called fever blisters or cold sores) on the gums, lips, or mouth due to a herpes simplex virus infection. Oral herpes lesions can also occur on the tongue.
Blisters or bumps from oral herpes are filled with fluid and will start to leak fluid, then crust over and heal over the course of four to six days. The blisters themselves and the fluid in them are contagious.
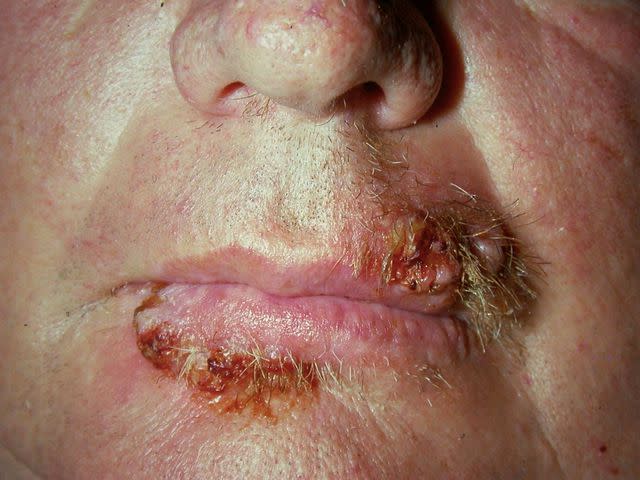
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet dermnetnz.org 2023
Allergies
Certain food allergies can affect the mouth and tongue. Oral allergy syndrome is a type of allergic reaction that can happen when you eat certain raw fruits or vegetables. The most common symptoms of oral allergy syndrome include swelling and itching of the tongue, lips, or throat. If the papillae become irritated, you may notice bumps.
Oral allergy syndrome is common among people with pollen allergies. The immune system mistakes certain proteins in some raw fruits and vegetables for pollen proteins, triggering an allergic reaction.
Infections
Bacterial infections can also cause bumps or sores on your tongue. Other types of tongue infections can cause changes on the tongue. For example, thrush, a yeast infection of the mouth, can cause white, velvetlike sores on the tongue and mouth.
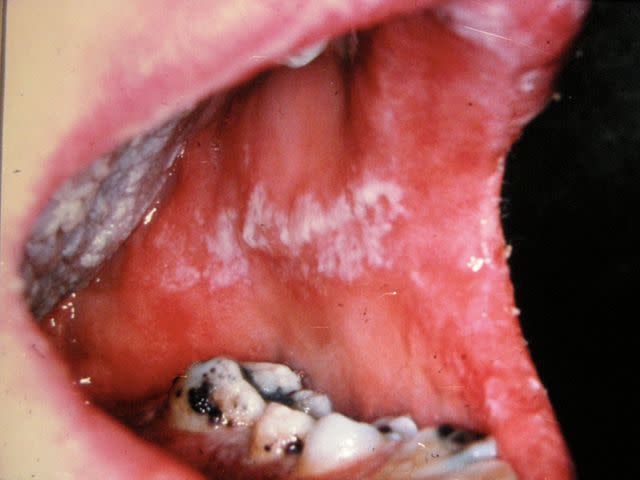
Reproduced with permission from ©DermNet NZ www.dermnetnz.org 2022
Squamous Papilloma
Squamous cell papilloma is a noncancerous growth. It can appear on different tissues in the body, where squamous cells are found. which includes the mouth and tongue. Squamous cell papilloma that affects the mouth is commonly found on the tongue.
Squamous cell papilloma usually appears as a single soft mass on a stalk or stem with fingerlike projections.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that, in the beginning stages of the infection, can cause sores on the inside of the mouth. This is called oral syphilis, which is usually transmitted by oral sex with someone with a syphilis infection. Syphilis lesions can appear on the inner lips and tongue. Syphilis is curable.
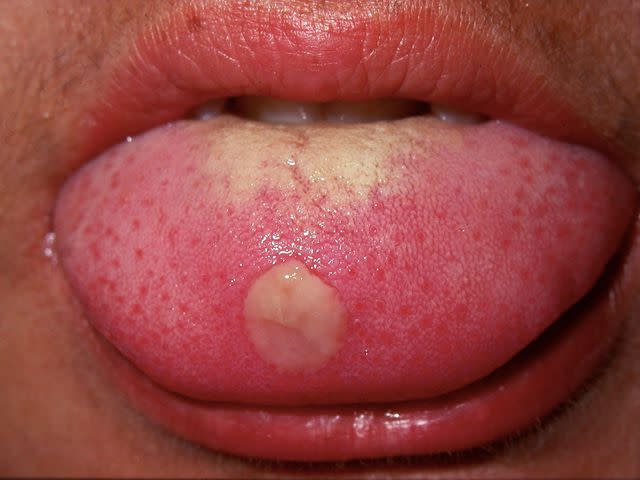
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet dermnetnz.org 2023
Scarlet Fever
Scarlet fever is a bacterial infection caused by group A Streptococcus (group A strep), the same bacteria that cause strep throat. Symptoms of scarlet fever include changes in the mouth, including the tongue. At first, the tongue may look white at first and then become red and bumpy.

Pawel Wewiorski / Getty Images
Glossitis
Glossitis is when the tongue becomes inflamed and looks swollen. Glossitis can cause the normal bumps on the tongue to disappear, giving the tongue a smooth appearance.
Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is a type of head and neck cancer. Cancer cells can develop from the squamous cells in the mouth, including the tongue. One of the symptoms of tongue cancer, specifically, is a lump on the side of the tongue that is gray-pink or red, touches the teeth, and bleeds easily if it's touched or bitten.
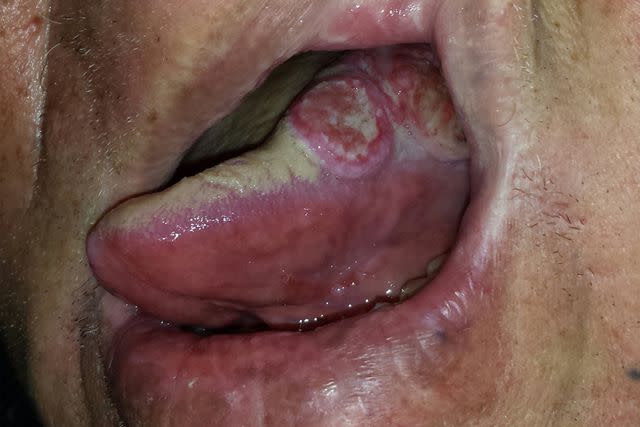
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet dermnetnz.org 2023.
Traumatic Fibroma
Traumatic fibroma, also known as oral irritation fibroma, is a harmless scar-like reaction to ongoing irritation in the mouth. It appears as a firm, smooth bump, usually the same color as the mouth or slightly darker if it has been bleeding.
Traumatic fibroma commonly is found on the side of the tongue and results from irritation, such as from a tooth with a rough texture, dentures, or other oral gear.
Lymphoepithelial Cysts
Lymphoepithelial cysts are small bumps that can occur on the tongue or floor of the mouth. Lymphoepithelial cysts are small, yellowish or white in color, and usually not painful. They are rare. The cause of lymphoepithelial cysts isn’t well-known, though they are generally harmless and stay away once removed.
How Tongue Bumps are Diagnosed
Diagnosing bumps on the tongue will likely involve a physical exam by a healthcare provider. The provider will look inside your mouth and at your tongue to check for bumps or other symptoms. Some characteristic bumps, like strawberry tongue, may be diagnosed from a physical exam alone.
A dentist may also perform oral exams during a regular checkup to look for lumps on your tongue or lips. They may also feel for bumps on your face and neck.
Since some tongue bumps are symptoms of other conditions, like syphilis or oral herpes, a healthcare provider may run some tests to confirm a diagnosis.
Treatment and Home Remedies for Tongue Bumps
Treatment for tongue bumps depends on the cause of the bumps. Some tongue bumps will go away on their own. For example, if a bump appears after biting or burning your tongue with hot food or liquid, it will heal on its own after a few days.
Taking extra care to not irritate the bump further, such as not eating or drinking extremely hot food or beverages, can help prevent further pain.
Other tongue bumps may need help from medications or other therapies to get rid of them or keep them from returning. For example, lymphoepithelial cysts are usually surgically removed. Bumps caused by health conditions like syphilis will require treatment of the underlying condition.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
If you have a bump (or bumps) on the tongue that gets worse or doesn’t go away on its own, contact a healthcare provider for a diagnosis and treatment plan. For example, a bump on the side of your tongue that touches your teeth and bleeds easily, or a red or white patch on the tongue that doesn’t go away warrants medical attention.
Some tongue bumps may indicate a more serious underlying condition, so it’s best to seek medical advice for persistent or severe bumps.
Summary
Tongue bumps can be caused by a variety of reasons, from something as simple as biting or burning your tongue to a health condition that requires medical attention. If a bump on your tongue doesn’t go away on its own, contact a healthcare provider to diagnose the bump and set you up on a treatment plan if necessary.
Read the original article on Verywell Health.

