The Great Escape, ‘pathetic’ collaborators and the British men who fought for Hitler
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.
The atmosphere inside the prisoner-of-war camp was electric.
Packed into a wooden theatre were several hundred Allied prisoners of war watched over by their German guards. Suddenly, heads turned and a hush fell. Two men, dressed in the uniform of the dreaded Waffen-SS, entered the room and walked down the aisle.
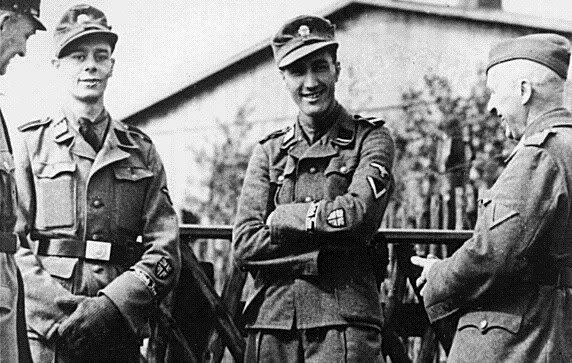
Some noticed that there was something strange about their SS uniforms. On the men’s left sleeves had been sewn Union Flag shields. There were three lions from the Royal Standard on their right collar tabs and the words “British Free Corps” had been stitched on their left cuffs.
The two men mounted the stage and one of them started to speak in perfect English. The POWs listened in dumbstruck silence as it became clear that they were both British and were exhorting them to join the German cause.
The younger of the two repeated the words from the flimsy recruiting leaflet in his hand and said: “In order to fight the menace of Jewish Communism, we ask you to join the British Free Corps and take up arms with Germany in our fight against the common enemy.”
His words were soon drowned out by jeers. Before long, the guards escorted the two British SS men out of the theatre trying to shield them from punches and the odd projectile. The prisoners were stunned. Many were tempted to tear up the leaflets but others advised against it, suggesting that with the shortage of lavatory paper they could be put to better use.
It was the spring of 1944, and the Germans were so desperate to find soldiers to fight on the Eastern Front they had launched a campaign to recruit from the ranks of Allied POWs. This camp in northern Germany was no exception. Although many of the prisoners had endured the hardships of camp life since Dunkirk, it seemed inconceivable that they would fight for the hated Nazis, and even more so as part of the SS. Yet some of them did.
This weekend, as we commemorate the 80th anniversary of the Great Escape – the mass breakout from the Stalag Luft III camp in 1944 – we should remember that the story of the POW experience is not all the stuff of patriotic guts and glory. The recent revelation made by the National Archives that Desmond Plunkett, one of the Great Escapers, suspected that the breakout was compromised by two treacherous Englishmen, is proof that the prisoners were well aware that collaborators and traitors were among them.
And while we rightly remember the heroism and sacrifice of those on the Great Escape, immortalised by Steve McQueen, Richard Attenborough et al in the 1963 war film, we should also realise that escaping was a minority activity, as only a third of prisoners took part in escape plans.
Uncomfortable though it is to consider, most were happy to sit out the war behind the safety of the barbed wire. And at a number of camps, it was known that some prisoners deliberately informed their German captors of forthcoming escape attempts in order to keep camp life quiet, and to avoid any collective punishments when escapes were mounted. According to Will Butler, the head of military records at the National Archives, “There is evidence across the war of the Nazis putting in ‘stooges’, placing them in prisoner-of-war camps to gather intelligence to stop escape attempts.”
However, the real villains were undoubtedly those prisoners of war who went the whole hog and decided to join the enemy by enlisting in the Waffen-SS. So who were these men who joined this mysterious unit called the British Free Corps (BFC)?
The POWs would have been surprised to find that its members had been born into decent, middle-class families, and had been educated at grammar or private schools in places such as London, Harrogate and Edinburgh. They were men with quintessentially British names such as Nightingale, Pleasants, Purdy and Cooper.
For the most part, BFC members were either fascists or simpletons, pathetic individuals for whom concepts such as decency held little currency. Of all of them, the example of Thomas Cooper serves well to illustrate the treacherous journey these renegades took.

Educated at the prestigious Latymer Upper School, in west London, Cooper was remembered by his headmaster as being “a clever boy who was interested in modern languages”. Although his mother was German, he had been born and brought up in England, and he left school after matriculation at the age of 17.
But his applications to join the police, the Navy and the Air Force were all turned down because of the “nationality question”. Deeply frustrated, Cooper decided to join Sir Oswald Mosley’s Blackshirt movement in 1938, and he was soon blaming the Jews for his lack of success in the job market. In the spring of 1939, he went to Germany to find employment. Despite his fluency in German, he could find only occasional work as a farm labourer or English teacher. With the outbreak of war, Cooper found himself joining the German army. His application was noticed by a senior SS officer who invited him to join the elite SS fighting force in early 1940.
By his own account Cooper performed admirably, but it was an excellence of the most horrific and criminal sort. He would later tell his fellow British traitors that he had shot 200 Poles and 80 Jews during a single day in Warsaw. He also boasted that he had thrown women from the top storeys of buildings as well as butchering young children and babies “as they would only grow into big Jews”. Cooper was promoted to sergeant and soon saw action on the Russian Front. But in February 1943, he was badly wounded by shrapnel in both legs and was sent back to Germany for treatment.
His injuries won him the Silver Wound Badge, making him the only Englishman to win a German combat decoration during the war. Cooper was, therefore, a natural choice to help the Germans set up a unit of British volunteers.
Hitler had personally approved the plan, and on December 28 1942 sent out the following order: “The Führer is in agreement with the establishment of an English legion (former members of the English Fascist Party or those with similar ideology) - therefore quality, not quantity.” Hitler stipulated that the unit, then called The Legion of St George, should reach platoon strength (around 30 men) before going into action against the Russians.
According to Adrian Weale, the author of Renegades, a history of the BFC, the Nazis considered that “a British Regiment or Brigade on the Eastern Front would be a useful addition, with the extra impact of a propaganda value out of all proportion to its size”.
One of Cooper’s jobs was to “butter up” potential recruits from the ranks of British POWs. A special POW camp had been set up at Genshagen, just outside Berlin, where the conditions were luxurious compared to other camps. Cooper’s mission was to recruit a minimum of 30 men needed to form the unit.

Those who joined came from a variety of backgrounds. There were former Blackshirts such as Francis McLardy, a Liverpudlian pharmacist and a sergeant in the Royal Army Medical Corps. Then there were the chancers such as former professional strongman Eric Pleasants from Norfolk, who wanted to escape incarceration. There were also those who were in it for the availability of women, such as Private John Eric Wilson of No 3 Commando, who was “sexually obsessed” according to other members of the unit.
Many came from middle-class backgrounds and knew exactly what they were doing although, clearly, others were simple men such as Kenneth Berry, who had left school at 13 and was under the impression that the British approved of the unit. In all, 57 British and Commonwealth citizens joined the BFC between 1943 and 1945. However, at any one time, there were never more than 20 members of the unit and, as a result of Hitler’s strict insistence of its required strength, the unit never saw any direct action.
When not touring POW camps on recruitment drives, much of the men’s time was spent with other non-German SS men in the town of Hildesheim, where they learnt German and trained in SS lore. In their spare time, women and alcohol were priorities and discipline was often a problem. Local women regarded British SS men as quite a catch. For such pathetic and largely unattractive men such as them, the sexual surfeit was often too much.
In Britain, authorities were aware of the BFC. Details were found in letters home from scornful POWs whom they had failed to recruit. Other letters, written in code, contained more specific information that was passed on by MI9, the secret intelligence agency that was responsible for escape attempts by Allied POWs.
At the end of the war, members of the unit were rounded up and taken home for trial. Naturally, most lied and claimed that they had joined the BFC in order to spy on the Germans. Yet the sentences meted out to these traitors were surprisingly lenient. Although Thomas Cooper was sentenced to death, this was commuted to life imprisonment and he was released from jail as early as January 1953. It is believed that he went to live in Japan, although he returned to Britain and died here in the mid-1980s. Francis McLardy received a 15-year sentence, and Kenneth Berry got a mere nine months. Some Commonwealth citizens received only fines, others were not proceeded against at all.
Moreover, it appears that members of the BFC reintegrated themselves into British society with little difficulty after they had served their prison sentences. Some, such as Eric Pleasants, went to live near their childhood homes. Alfred Minchin, a BFC lance corporal, spent the remainder of his years living in Weston-super-Mare - a town that is, coincidentally, twinned with the BFC’s hometown of Hildesheim.
Ironically, the UK government’s obsession with secrecy meant that these traitors could live in peaceful anonymity. Some never even told their wives that they were once one of Hitler’s Englishmen.
Some chapters in Britain’s wartime history have been kept quiet, like looting during the Blitz and strikes on armaments lines. But, as well as celebrating the valour of so many prisoners of war, and especially those murdered for taking part in the Great Escape, we should remember that there are some who are the very opposite of heroes.
Guy Walters is the author of ‘The Real Great Escape’ (Bantam, £12.99)

