Why You Might Have White Spots on Your Skin

Hiraman / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by William Truswell, MD
White spots on the skin can happen for a variety of reasons. From sun exposure to a fungal infection to a skin condition, there are many things that can cause areas of your skin to become lighter.
While they're not typically a cause for alarm, you still may want to have a healthcare provider examine your white spots so they can determine what is causing the skin discoloration. Depending on the underlying cause, there may be ways to minimize the appearance of the white spots on your skin or resolve any other bothersome symptoms the underlying condition may be causing.
What Causes White Spots on Skin?
Noticing white spots on the skin doesn't automatically mean there's a skin disorder at play. Sometimes, other factors can cause the areas of lighter skin. Here are some reasons you might develop white spots on your skin.
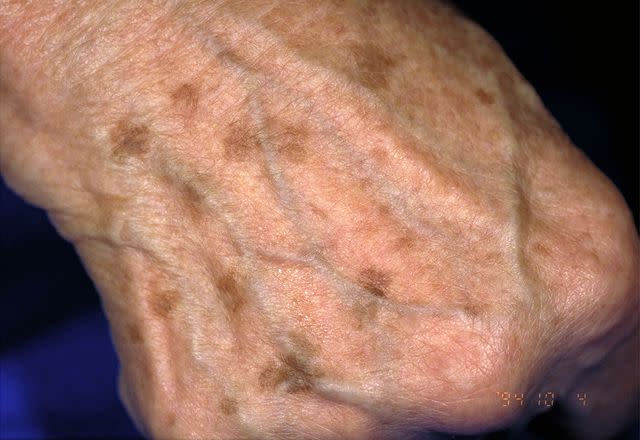
Sunspots
Dermnet
While the term sunspots may conjure up the image of darker spots or freckle-like marks, it's also possible for sunspots to appear as white or lighter spots on the skin.
Medically known as idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, these harmless white spots develop when there's a decrease in melanin (the pigment cells that give your skin, eyes, and hair their color) in the skin. Experts think this happens as a result of repeated sun exposure rather than another factor like aging.
Not surprisingly, these white spots typically show on areas that see the most sun, such as the shins, arms, back, and face. They're small like freckles—usually less than 1/8 of an inch—and seem to run in families.
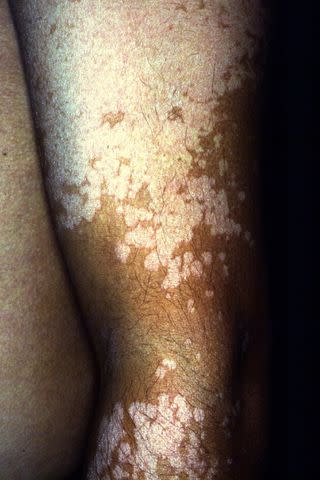
Tinea Versicolor
Dermnet
Tinea versicolor happens when there’s an overgrowth of a naturally occurring yeast on the skin. This fungal infection on the skin transforms into a rash that can eventually look like white or light spots.
The white spots that can appear with tinea versicolor are often found on the back, upper arms, chest, neck, and underarms. This type of fungal infection is not considered to be contagious.
Tinea versicolor is fairly common among teenagers and young adults as well as people who live in warmer climates. If you have the infection, you may also experience symptoms like mild itching, mild swelling, and increased sweating.
Pityriasis Alba
Pityriasis alba is a skin condition that causes small, round patches of skin to lose their color. It may feel like a rash and be itchy for some people.
These white spots typically develop on the face, arms, and upper torso. They may last for several months or more than a year, but they aren't permanent.
Experts aren't sure what causes pityriasis alba, but it's thought to be linked to eczema. It's most common in children and adolescents.
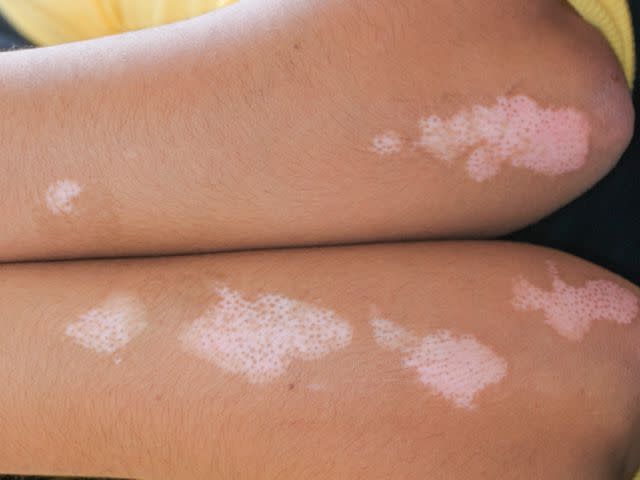
Vitiligo

Dermnet
Vitiligo is an autoimmune condition that causes patches of the skin to lose color, resulting in white spots. This condition develops when the immune system mistakenly attacks pigmentation cells in the body.
Vitiligo spots and patches typically start on the face, arms, hands, and feet. From there, the spots and patches can grow or more patches can develop on other places on your body. At first, the patches may be pink. The affected skin turns white once the vitiligo is no longer active.
Some people may notice other symptoms of vitiligo, like itchiness, increased risk of sunburn, hearing changes, and eye or hair color lightening.
While vitiligo can run in families, it may also be triggered by factors like a bad sunburn, skin injury, or skin exposure to strong chemicals.
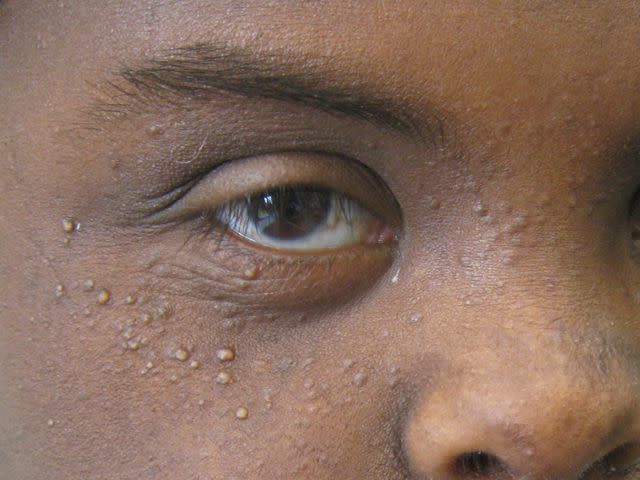
Milia

Dermnet
Milia are white, tiny, harmless bumps that develop when dead skin cells (keratin) get caught under the surface of the skin.
Most commonly, milia appear on the face—like across the cheeks, nose, and chin—but they can also occur on parts of the body that have been injured. Adults can get them, but they're pretty common in newborn babies.
Steroid-induced Hypopigmentation
Getting a corticosteroid injection or applying a steroid topically can sometimes cause white spots to appear in the area injection site or application area.
While these spots (or single spot) will often look irregularly shaped, they will look pretty well-defined. They can take a while to show up and may resolve themselves after a few months.
How to Get Rid of White Spots on Skin
Depending on the cause, you may or may not be able to get rid of the white spots on your skin. For spots that can go away, sometimes they clear up on their own. Other times, you might need treatment. Sometimes you might not need treatment for medical reasons but instead want to make the spots less noticeable for cosmetic purposes.
Sunspots: Sunspots don't necessarily need to be treated, but if their appearance is bothersome for you, a healthcare provider may recommend a topical cream like tretinoin (a retinoid). A dermabrasion procedure might be able to help smooth out the area, too.
Pityriasis alba: Pityriasis alba white spots tend to heal on their own, though topical steroids, certain moisturizers, or laser treatments may help reduce their appearance if needed.
Tinea versicolor: For a fungal infection like tinea versicolor, an over-the-counter antifungal topical product may be suggested. Some cases may require a prescription antifungal medication, either applied to the skin or taken orally.
Vitiligo: There’s currently no cure for vitiligo, but there are a variety of treatments available that can help restore skin color—and potentially reduce the chances of white spots spreading to other parts of the body. Treatment options for vitligo often include topical medications, lasers, phototherapy (light therapy), and cosmetic cover-ups. Skin grafting procedures may be used in severe cases.
Milia: Milia do not need to be treated in children or babies and commonly go away on their own within weeks without treatment. But in adults, stubborn milia can be removed by a healthcare provider, if that's preferred by the patient.
Steroid-induced hypopigmentation: White spots caused by steroid injection or application can also resolve on their own.
When Should You Be Concerned About White Spots on Your Skin?
White spots on the skin are not typically a cause for concern. But because they can appear for a variety of reasons, it's a good idea to have a healthcare provider look at any areas of skin that have experienced a change in color. This way, you can get an accurate diagnosis and treatment, if necessary.
In general, check with a healthcare provider if you're noticing unusual spots on the skin that:
Have changed in color
Haven't gone away or keep reappearing
Spread to other parts of the body
Cause additional symptoms like itchiness or pain
How to Prevent White Spots on the Skin
There’s no way to prevent a skin condition like vitiligo. But you can do your part to keep your skin healthy and protected from some factors like the suny's rays, chemical exposure, and other potential irritants.
For overall skin health, experts typically recommend:
Applying sunscreen or wearing protective clothing while being in the sun
Taking precautions at workplaces where chemicals are involved
Asking your healthcare provider whether you should schedule regular skin screenings
Keeping hands washed often with soap and water
Using warm (not hot) water and gentle products during your skincare routine
A Quick Review
White spots on the skin can develop as a result of sun exposure, a fungal infection, or a steroid that was injected or applied topically. The white spots may also be from an underlying skin condition, such as pityriasis alba, vitiligo, or milia. While many white spots are usually harmless and may resolve on their own, it's a good idea to get the area examined by a healthcare provider for an official diagnosis and treatment, if needed.
For more Health.com news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.com.

