Treating Painful Scalp Pimples
When a hair follicle gets clogged, a pimple forms
Soumen Hazra / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Susan Bard, MD
An occasional painful scalp pimple can form due to a clogged pore or inflamed hair follicle, but multiple or chronic painful scalp pimples may signal a different problem.
Acne cosmetica on the scalp is caused by oil-containing hair products. The condition usually clears up within a few weeks of discontinuing the use of the product.
Scalp folliculitis, also known as acne necrotica miliaris or Propionibacterium folliculitis, is an inflammatory condition that causes small pustules (pimples that contain a yellowish fluid). They often occur on the frontal hairline, can be itchy or sore, and often become crusted.
Acne keloidalis nuchae (AKN) is a skin condition that causes bumps on the back of the neck and scalp that are often mistaken for razor bumps or acne. Left untreated, AKN can cause raised scars and hair loss.
This article will discuss these causes of scalp pimples, other possible causes, how these conditions are treated, and what to do if they don't go away.
Soumen Hazra / Getty Images
How Do Scalp Pimples Feel and Look?
Acne cosmetica causes whiteheads and papules (small, flesh-colored bumps) along the hairline, forehead, or back of the head.
Folliculitis starts with an area near a strand of hair that becomes red and may itch, burn, or be tender. A pustule can then form in the hair follicle that may drain pus or blood.
AKN can begin with an itch on the back of the neck or scalp, followed by a rash of small, firm, dome-shaped bumps. Infection can occur when these bumps are scratched or combed, leading to pus-filled bumps. Bumps may also bleed.
Without treatment, the bumps can join together to cause a large, raised scar that can be painful.
Causes of Scalp Pimples
Acne cosmetica, scalp folliculitis, and acne keloidalis nuchae are both conditions that can cause pimple-like bumps on the scalp.
Acne Cosmetica
Acne cosmetica is acne that is caused by products that are applied to the skin. Acne cosmetica on the scalp is caused by hair care products, usually that contain oils. These may include:
Shampoos
Conditioners
Pomade
Styling gels
Waxes
Pastes
Sprays
Shaving creams
Aftershave
The oil from these products can clog pores and lead to acne.
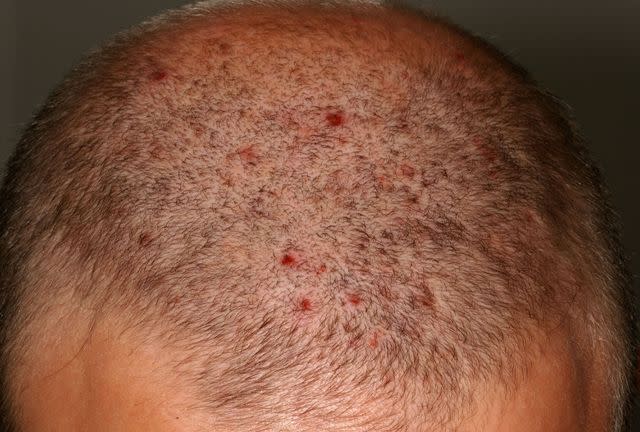
Scalp Folliculitis
Scalp folliculitis occurs when hair follicles (the openings in the skin that hold the hair root) on the scalp become clogged, causing infection.
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet and © Raimo Suhonen www.dermnetnz.org 2023.
Folliculitis is believed to be an inflammatory response to microorganisms in the hair follicle, such as:
Bacteria
Parasites, such as mites
Folliculitis can also occur after an injury to the hair follicle or irritation, including from:
Hair styling
Using chemical products on the scalp
Pulling hair too tight
Shaving
Ingrown hairs
A 2014 study found that chronic scalp folliculitis may be associated with acne vulgaris (the common form of acne).
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
AKN causes acne-like breakouts on the back of the neck or head due to long-term inflammation inside the hair follicles. This inflammation weakens the hair follicles, which can cause hairs to penetrate and burrow into the skin (ingrown hairs).
AKN is most common in Black males and generally begins between ages 14 and 25. Without treatment, AKN can cause scars to cover the hair follicle, which can lead to permanent hair loss.
Abscesses (swollen, pus-containing areas under the skin) can develop and may grow together to form sinus tracts (tunnels under the skin). Abscesses and sinus tracts can leak foul-smelling fluid.
The exact reason that the inflammation develops is not known, but possible risk factors incluide:
Having a chronic, mild infection
Taking some medications, such as the immunosuppressant medication cyclosporine, or certain antiepileptic medications like carbamazepine or phenytoin
Having a close relative who has AKN
Causes of irritation on the back of the neck or scalp may include:
Frequent, close-shave haircuts
Jewelry around the neck
A shirt with a collar
Caps, hard hats, helmets, and other head coverings
Skinfolds that rub against each other
When Could Scalp Pimples Be Something Else?
Less common forms of scalp folliculitis include:
Acne necrotica
Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens
Folliculitis decalvans
Acne Necrotica
Acne necrotica, also called acne varioliformis or acne frontalis, is a more severe form of scalp folliculitis. It causes larger follicular spots that become inflamed, develop blackened crusts, and leave permanent scars. It can affect the scalp, face, and other areas.
Perifolliculitis Capitis Abscedens et Suffodiens
Another severe form of scalp folliculitis is perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens, also called dissecting cellulitis/folliculitis, or perifolliculitis capitis. This rare condition causes large nodules and cysts that contain pus alongside smaller follicular papules (raised spots) and pustules.
Folliculitis Decalvans
Folliculitis decalvans causes inflammation and hair loss on the scalp. The exact cause isn't known, but it may be caused by a reaction to the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
Folliculitis decalvans may cause red, itchy, swollen, and/or painful areas on the scalp that can scab and crust. Pus-filled spots can also occur. Folliculitis decalvans is very rare.
Scalp Pimples and Hair Loss
Without proper treatment, AKN can cause scarring that leads to hair loss. The scars can also cause ingrown hairs or tufted hairs (several hairs growing out of one hair follicle) to occur near the edge of the scars.
Folliculitis decalvans can also cause hair loss due to scarring. It can also cause "corn stalking" (grouped hairs growing within a patch of hair loss).
To Pop or Not to Pop Scalp Pimples?
While it's tempting to pop pustules, it's best to leave them be or leave it to a healthcare provider like a dermatologist.
Popping pimples and blemishes can lead to problems such as:
Scarring
Pain
Development and spread of infection
Increased inflammation
Self-Care to Get Rid of Scalp Pimples
Acne cosmetica typically clears up within six weeks of discontinuing the product that is causing it. Make sure to also wash the residue of the product from anything your head touched, such as bedding, hats, and other headgear.
If you aren't sure which product is causing your symptoms, check the labels and stop using any products whose labels don't have one or more of the following claims:
Oil-free
Non-acnegenic (won't cause acne)
Noncomedogenic (won't clog pores)
Along with medication, self-care can help folliculitis to heal. Home care for scalp folliculitis may include:
Wash your hair with normal shampoo or an anti-dandruff shampoo containing antifungal agents like ketoconazole or ciclopirox.
Avoid shaving the scalp or use an electric razor.
If a clean shave is needed, use shaving cream/gel and shave in the direction the hair grows.
Apply a warm, moist cloth on the area for five to 10 minutes, three to six times daily, to help relieve itching or pain.
Avoid styling hair too tightly.
AKN needs medical treatment and cannot be treated effectively with self-care alone. Self-care may help when used alongside medical treatment. This may include:
Avoid getting haircuts that shave the back of the head or neck.
Avoid wearing clothing and jewelry that rubs the back of the head or neck.
Keep the back of the head and neck cool, dry, and sweat-free.
Wash the back of your head and neck with antimicrobial cleanser, such as those that contain benzoyl peroxide or chlorhexidine.
Avoid using pomade or hair grease.
Use a cool compress, such as a washcloth that is damp with cool water, on the skin for 10 minutes to help relieve itch.
Be careful not to rub roughly or scratch the skin on the back of your head or neck.
Avoid products sold as permanent remedies for bumps on the back of the neck or pimples on your scalp, as they can contain harmful substances (such as acids) and cause chemical burns.
Lifestyle Habits to Support a Healthy Scalp
To help maintain a healthy scalp and hair:
Wash your hair regularly.
Remove dirt, oil, and residue with soap and clean, running water.
Use shampoo and conditioner that work for your hair type.
Brush your hair regularly to break apart buildup and prevent tangles.
Avoid sharing objects like combs, towels, and other personal items.
Wash your hands regularly to avoid spreading infections like ringworm (a fungal infection).
The Next Step: Scalp Pimples That Won’t Go Away
Scalp folliculitis may need to be treated with medication.
Topical medications may include:
Antibiotics, such as fusidic acid gel, clindamycin solution, erythromycin solution
Mild steroid lotions or creams
Oral medications may include:
Antihistamines
Antibiotics, such as long-term tetracycline
Isotretinoin (a retinoid medication used to treat acne)
AKN does not currently have a cure, but symptoms can be managed, and treatment can help prevent the condition from worsening.
Medical treatment for AKN may include:
Washing with an antimicrobial cleanser and shampoo, or tar shampoo
Using a medicated product, such as ones that contain alpha hydroxy acid or a retinoid, to soften coarse hairs
Topical medications, such as corticosteroids and/or retinoids
Corticosteroid injections
Topical or oral antibiotics
Surgery to remove scarring
Draining abscesses and sinus tracts, then treating the infection with medication
When to Call a Healthcare Provider
Contact a healthcare provider if you have:
New, persistent, or worsening symptoms
A sore nodule that is getting bigger
A temperature of 101 degrees F (38.3 degrees C) or higher
Sores that continue to spread 48 hours after treatment
Signs of infection, such as pain, swelling, redness, or warmth
Red streaks leading from the affected area
Pus draining from the area
Summary
Scalp folliculitis, acne keloidalis nuchae, and acne cosmetica are three conditions that can cause pimple-like bumps on the scalp. Acne cosmetica on the scalp is caused by hair products that contain oil. The condition usually clears up within a few weeks of stopping the use of the product.
Scalp folliculitis is caused by blocked, injured, or irritated hair follicles. It can be treated with self-care, such as washing the hair with shampoo, avoiding shaving the head, and applying a warm, moist cloth. Treatment may also include medications such as antibiotics, mild steroids, antihistamines, or isotretinoin.
AKN requires medical treatment, such as using medicated products, topical or oral medications (including corticosteroids, retinoids, or antibiotics), and surgery.

