Signs and Symptoms of Upper Respiratory Infection
Medically reviewed by Rochelle Collins, DO
An upper respiratory infection (URI) is a group of infections that affects any part of your upper airways, including the nose, sinuses, throat (pharynx), and voice box (larynx). Common types of upper respiratory infections include the common cold, influenza (flu), sinusitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, and tonsillitis. These infections can cause of variety of symptoms, including sneezing, runny nose, sore throat, cough, congestion, low-grade fever, and headache.
Symptoms usually begin mildly, gradually worsening over a few days before reaching their peak. Most people start to feel better within a week, though some may have lingering symptoms for up to three weeks.

Design by Health
Common URI Symptoms
Upper respiratory infections and be viral (caused by a virus), or bacterial (caused by bacteria). Viruses and bacteria that cause upper respiratory infections spread through respiratory droplets when someone who has the infection coughs or sneezes. Symptoms typically develop within one to three days after exposure to the infection-causing germs, such as rhinoviruses (common cold) or influenza viruses (flu).
Symptoms of URIs can vary, depending on which part of your upper respiratory tract is affected. Most types of URIs share common symptoms, including:
Runny or stuffy nose
Sneezing
Coughing
Congestion
Sore throat
Body aches
Headache
General malaise (feeling unwell)
Common Cold Symptoms
Common cold symptoms typically start mildly, and you may initially develop a scratchy or sore throat. Symptoms develop gradually, peaking within two to three days, and may include:
Sneezing
Runny or stuffy nose
Sore throat
Coughing
Watery eyes
Post-nasal drip (mucus running down your throat)
Low-grade fever
With the common cold, your nose may be runny for a few days before the mucus thickens and your nose feels stuffy or congested. Most people feel better within a week, but some symptoms, such as a cough, can linger for up to two weeks.
Influenza (Flu) Symptoms
Influenza (flu) symptoms tend to develop suddenly, reaching peak intensity within two to three days before gradually improving within several days to two weeks.
Flu symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
Fever
Chills
Sweating
Fatigue (tiredness) and weakness
Muscle and body aches
Headache
Scratchy and/or sore throat
Dry cough
Runny or stuffy nose
Some people with the flu will develop nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which is more common in children than adults.
Sinusitis Symptoms
Sinusitis, also known as a sinus infection, is an infection that develops when fluid (mucus) builds up in the air-filled pockets in your face (sinuses), often after a common cold or due to allergies (allergic rhinitis). There are several types of sinusitis:
Acute: Lasts four weeks or less
Subacute: Lasts 4 to 12 weeks
Chronic: Lasts 12 weeks or longer, sometimes persisting for months or years
Recurrent: Repeated sinus infections
Symptoms of sinusitis can include:
Runny nose with thick, yellow, or green mucus discharge
Nasal congestion and stuffiness
Facial pain and pressure
Headache
Post-nasal drip (mucus dripping down the back of your throat)
Sore throat
Productive (wet) cough that may worsen at night
Bad breath
Decreased sense of smell
Fever
Laryngitis Symptoms
Laryngitis is inflammation of the larynx (voice box), which can develop during or after a viral or bacterial upper respiratory infection, such as the common cold. Acute laryngitis usually lasts for three to seven days and causes mild symptoms, including:
Hoarseness, making your voice sound raspy or weak
Loss of voice
Dry cough
Sore throat that may feel raw or tickly
Persistent urge to clear the throat
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes (glands) in the neck
In more severe cases, people with laryngitis may experience shortness of breath or hear high-pitched, whistling sounds when breathing (stridor).
Pharyngitis Symptoms
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the pharynx—the middle of the throat between the tonsils and voice box (larynx). Most people develop pharyngitis as part of a viral or bacterial upper respiratory infection. It usually goes away within five to seven days.
Along with a sore throat, other pharyngitis symptoms may include:
Headache
Fever
Muscle or joint pain
Skin rash
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
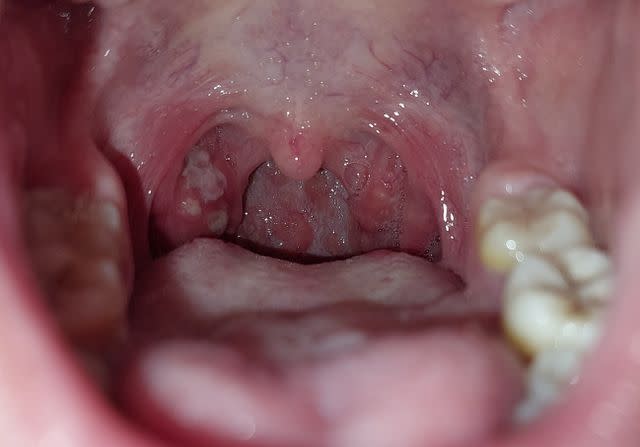
Tonsillitis Symptoms
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils—the two lumps of tissue on each side at the back of the throat. Tonsils are part of your body’s lymphatic system, helping clear away infection and keeping body fluids balanced. Tonsillitis is more common in children than adults and usually develops due to a viral or bacterial infection.
Inflamed tonsils may appear red and swollen and have a white or yellowish coating or spots. Tonsillitis symptoms usually clear up within four days, but some may last up to two weeks. Common symptoms include:
Sore throat
Difficulty swallowing
Bad breath
Fever
Swollen lymph nodes (glands) in the neck
Headache
Fatigue
In some cases, children with tonsillitis may develop a bright red rash (scarlet fever). The rash may develop on the neck, chest, or face and then spread to other body areas, such as the arms, legs, and trunk. This occurs when a bacterial infection causes tonsillitis and requires medical attention and treatment.
Suphanni Chongmithom / Getty Images
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
While most upper respiratory infections are viral and resolve with rest and at-home care, certain symptoms warrant a trip to your healthcare provider.
Make an appointment to see a healthcare provider if you experience:
Symptoms that worsen or last longer than ten days
Prolonged fever of 102°F or higher
Feeling faint
Severe vomiting, especially if you are experiencing symptoms of dehydration
Severe sinus pain
Swollen lymph nodes in your neck
Earache or fluid draining from your ear(s)
Worsening symptoms of chronic conditions (e.g., heart disease, lung disease)
Seek immediate emergency care if you experience:
Difficulty breathing or severe shortness of breath
Chest pain lasting two minutes or longer
Confusion
Coughing up blood (hemoptysis)
Vision changes
Difficulty speaking
Fainting or sudden dizziness or weakness
Questions to Ask Your Provider
Here are a few questions to consider asking your healthcare provider when you visit them with an upper respiratory infection:
How long can I expect my symptoms to last?
Are there any medicines you can prescribe to help manage my cough?
Is there anything I can do at home to relieve my symptoms and support my recovery?
Should I be concerned if my mucus is green or yellow?
Can I take over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or supplements to help me get better faster?
A Quick Review
Upper respiratory infections (URIs), such as the common cold and flu, cause unpleasant symptoms like sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, mild fever, body aches, and cough. Fortunately, most URIs are viral and resolve within a week or two. Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated can help support your recovery. See a healthcare provider if your symptoms don’t improve or worsen over time or if you get better and your symptoms suddenly return.
For more Health.com news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.com.

