Signs and Symptoms of Melanoma
Callista Images / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Casey Gallagher, MD
Melanoma is a serious and deadly form of skin cancer. The condition occurs when cells called melanocytes begin to grow uncontrollably and create a cancerous tumor. The most common symptom of melanoma is a tumor in a changing mole or a new growth on the skin.
This type of skin cancer is more common among older people, but it can occur in people of any age. If caught early, melanoma is highly treatable. But once the cancer metastasizes (spreads), the condition is much more likely to be deadly. That’s why it is extremely important to know the symptoms and stay vigilant for any signs of melanoma.
Common Symptoms
The first sign of melanoma is usually a spot or mole on your skin that is changing in appearance. These changes can sometimes occur to a mole you already have. But in most cases, a cancerous growth appears on a new part of your skin.
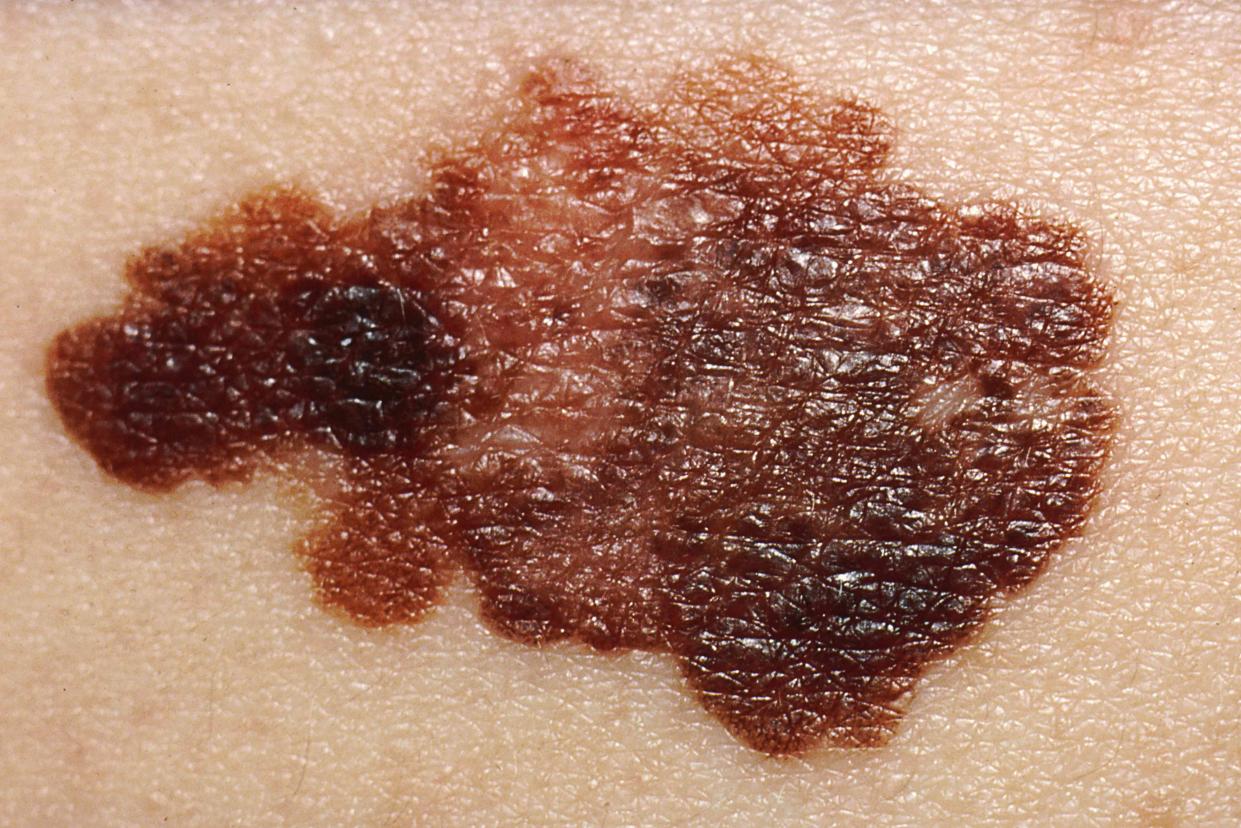
Melanomas don't always look like the average mole. Using the ABCDE rule can help you understand the difference between melanoma growth and a regular mole, and detect the cancer early:
A = asymmetry: One half of the growth looks different from the other half
B = border: The growth has a jagged, blurry, or uneven border
C = color: There are many colors that you can see on this growth, including brown, black, red, white, gray, or blue
D = diameter: It appears that the growth is becoming bigger than 6 millimeter(mm)
E = evolving: Over time, the growth changes in size, shape, color, or texture (such as becoming scaly, lumpy, hard, itchy, or bloody)
Melanoma can develop anywhere on the body, but it often appears on skin that has been exposed to the sun. This is because excessive damage from UV radiation in sunlight is a leading risk factor for this type of cancer. Other risk factors include a family history of melanoma, a weakened immune system, and the presence of many moles on the body.
Superficial Spreading Melanoma Symptoms
While most melanomas share some common symptoms, each type of melanoma can have its own set of signs.
Superficial spreading melanoma is by far the most common type of melanoma. About 75% of all melanomas fall into this type. Superficial spreading melanoma tumors often cause a growth with an irregular or notched border and varying colors and shapes.
These tumors are usually thin and located in the outer layers of the skin (known as the epidermis), and therefore very treatable. But if this type of melanoma progresses without treatment, the tumors may thicken and begin to grow vertically from the skin.
Nodular Melanoma Symptoms
As the second most common type, nodular melanomas make up somewhere between 15% and 30% of all melanoma cases. This type of cancerous tumor protrudes (sticks out) from the skin and causes dark spots. These spots are less likely to meet the ABCDE test, so they tend to be difficult to diagnose. Nodular melanoma spots generally grow quickly as well.
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma Symptoms
Accounting for between 5% to 15% of all melanomas, symptoms of lentigo maligna melanomas usually occur on the face or other areas of skin that are repeatedly exposed to or damaged by the sun. These tumors are most likely to grow gradually over time on older people. They may initially take the form of a flat spot with a brown or tan color. But over time, these growths become darker, more irregular, and more raised.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma Symptoms
This type of melanoma usually appears on the palms of the hands, on the bottom of the feet, or beneath the nails. On the hands and feet, the spot may be dark brown or black and become raised, form a sore, or bleed as it spreads. Under a nail, it may appear as a line running from the nail bed to the tip of the nail or a spot that damages the nail.
Rare Types of Melanoma
In rare cases, other types of melanoma can develop, including the following:
Amelanotic melanomas: Growths with no color at all or sometimes appearing slightly pink in color. These spots can be any type of melanoma, but because they lack pigment, they look like benign (non-cancerous) tumors. For this reason, they are often misdiagnosed as harmless.
Desmoplastic melanomas: Growths that look like scar tissue and grow very slowly. They can look colorless or appear as very light brown or pink in color. These growths are also often mistaken for other benign tumors.
Nevoid melanomas: Growths that look like regular, dome-shaped moles and are therefore very hard to diagnose. This type of cancer often occurs on the upper arms and upper legs of young adults.
Mucosal melanomas: Growths that appear on mucus membranes like the walls of the vagina, mouth, or gastrointestinal tract.
Uveal melanoma: Growths that develop in the eyes.
Symptoms in Children
Only 1% of all cases of melanoma occur in people under the age of 20. And because diagnosis in young people is so rare, it can be hard to diagnose. Experts also suggest that melanomas in children may present differently than melanomas in adults, and they may not meet the ABCDE criteria at all. Children and teenagers often have late or incorrect diagnoses, which can lead to delayed treatment.
Children born with many moles or especially large moles are more likely to develop melanoma. Their healthcare provider may recommend removing larger moles or monitoring the growth of their moles as the child ages.
How Melanoma Affects People Differently
Among people under the age of 50 in the United States, those assigned female at birth have higher rates of melanoma. But among people over age 50, those assigned male at birth have higher rates, and they die from melanoma more often. In people assigned male at birth, melanoma often develops on the head, neck, or back. In those assigned female at birth, the cancer more often appears on the back or legs.
It's also worth noting that melanoma occurs more commonly in white people than in all other races. For example, the cancer is more than 20 times more common in white people than in Black people. Experts believe that this is the case because darker skin tones are less likely to be damaged by UV light from the sun.
But it's important to note that people of color are much more likely to die from melanoma than white people. This is because the cancer is usually detected much later at a more advanced stage, often because melanoma growths look different on darker skin tones. Later stages of melanoma are more difficult to treat and have worse outcomes for survival.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
Noticing and reporting any changes to your skin is key to catching melanoma early and treating it successfully. A missed or incorrect diagnosis can increase your risk of delayed treatment and poor health outcomes.
One way to keep a close eye on your skin is by taking photos of yourself or using a body mole map to track your skin over time. If you have a new or existing mole or other spot on your skin that meets any of the ABCDE criteria, or a sore that will not heal, make an appointment with your healthcare provider. Some forms of melanoma spread quickly, so it's best to not delay seeing a specialist.
Questions to Ask Your Provider
If you've made an appointment with your provider, it's important to ask them the right questions about any changes you've noticed on your skin. Consider some of the following examples:
How can I tell the difference between a regular new mole vs. a possible melanoma growth?
What kinds of tests will you do to diagnose this spot on my skin?
Do I need a biopsy of the spot on my skin?
Will I need to work with any other healthcare providers or specialists if I test positive for melanoma?
A Quick Review
Melanoma is a serious form of cancer that usually appears on the outer layers of the skin. If the cancer is caught and treated early, the large majority of people with melanoma will survive. Advances in cancer treatment have made survival much more common in recent decades.
However, if melanoma spreads to other parts of the body without early detection, the likelihood of survival decreases greatly. That’s why it is crucial to monitor your skin over time and contact your healthcare provider if you notice any new or changing spots, such as changes in color, shape, size, or texture.
Frequently Asked Questions
How fast do melanoma symptoms spread?
Melanoma symptoms can spread at different rates depending on the type of melanoma. Some types of melanoma, such as lentigo maligna melanoma, tend to be slow growing. Other types, such as nodular melanoma, tend to grow more rapidly. Make an appointment with your healthcare provider as soon as you notice any change to a spot on your skin.
Do you need chemotherapy to get rid of melanoma symptoms?
Most cases of melanoma use surgical excision, in which a surgeon cuts out the cancerous growth along with some healthy tissue around it. If the melanoma has spread to other parts of the body, you may need treatments like immunotherapy, molecular targeted therapy, or radiation therapy.
Does melanoma make you feel sick?
Most cases of melanoma cause no symptoms aside from a new or changing spot on the skin. If a melanoma goes untreated and spreads to other parts of the body, however, it may cause other symptoms.
For more Health.com news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.com.

