Signs and Symptoms of a Brain Tumor
gorodenkoff / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Benjamin Leach, MD
A tumor is a growth of abnormal cells that forms when the genes that regulate cell growth do not function normally. A brain tumor is a tumor that develops in the tissues of the brain. Brain tumors may be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Primary brain tumors start in the brain, and metastatic brain tumors spread to the brain from another area of the body.
It is estimated that 80,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with brain tumors each year. Unlike other types of tumors, brain tumors have very limited space to grow. The skull bones constrict the tumor, and this causes the tumor to put pressure on the brain. This increased pressure, known as increased intracranial pressure (ICP), then leads to symptoms.
Brain tumor symptoms depend on where the tumor is located and how much injury it has caused to the brain. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, nausea and vomiting, mood changes, personality changes, fatigue, balance problems, and vision changes.
Headaches
The most common symptom of a brain tumor is headaches. Brain tumors lead to headaches when the tumor presses on the brain’s sensitive blood vessels.
A brain tumor headache feels different than other types. People with brain tumors usually describe their headaches as persistent pain that feels different than a migraine. The pain is usually worse when first waking up in the morning. It is common to experience nausea and vomiting with the pain as well.
The headache may feel like throbbing pain and usually worsens with activities that increase intracranial pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or exercising.
Seizures
Another common brain tumor symptom is seizures. A seizure occurs when there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain. A tumor can lead to seizures when it blocks or puts pressure on the brain’s communication pathways.
Seizures are usually classified as generalized or focal. A generalized seizure can affect the entire body. It usually occurs suddenly and causes a loss of consciousness. A generalized seizure causes a loss of control and may lead to pauses in breathing. These types of seizures usually last 2 to 3 minutes.
A focal seizure appears more subtle. It may cause jerking movements and speech problems. A person who is experiencing a focal seizure may see flashing lights.
Nausea and Vomiting
Brain tumors may cause nausea and vomiting, especially with headaches. This happens because of increased intracranial pressure in the skull. People with brain tumors may experience nausea and vomiting throughout the day, or it could come and go.
Related: Reasons You Feel Nauseous
Movement Problems
Some types of brain tumors affect the areas of the brain that affect movement. People with brain tumors may experience movement changes like a lack of coordination and balance problems. It is possible to experience weakness, muscle paralysis, and a loss of physical sensation. A brain tumor can also lead to dizziness and trouble walking.
Memory Loss
People with brain tumors often experience cognitive changes and memory problems. When a brain tumor disrupts normal brain function, it leads to problems with learning and retaining new information.
A brain tumor can lead to problems with short-term memory. Examples of short-term memory include remembering what you ate for lunch or where you left your car keys. It is less common to experience long-term memory loss, such as the names of your loved ones.
Depending on the location, brain tumors can affect the following functions:
Learning and memory
Language and communication
Attention and concentration
Intellectual abilities
Mood Changes
Rapid mood changes and depressive episodes can be common in people with brain tumors. A brain tumor can lead to mood changes when it affects brain function. People with brain tumors may also be at risk of depression because of the psychological burden of being diagnosed with a tumor.
It is estimated that 1 in 4 people with a brain tumor experience a major depressive episode. Depression is defined as persistent feelings of sadness that interfere with your daily life. People with depression often experience a loss of interest in pleasurable activities, persistent fatigue, and sleep problems.
Personality Changes
In addition to mood changes, a brain tumor can lead to personality changes as well. Personality changes, also known as neuropsychiatric changes, can cause a person to act differently than they normally do. For example, a person who is normally calm may become angered and upset quickly.
When a brain tumor causes personality changes, the specific symptoms depend on the tumor’s location. Severe personality changes may include aggression, hallucination, and even impulsive or violent behavior.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom of cancerous tumors and can affect all areas of life. People with brain tumors may experience extreme tiredness or exhaustion. There are different types of fatigue, including:
Physical: Lack of energy, muscle weakness, slow movements
Emotional: Irritability, emotionally reactive, decreased motivation
Cognitive: Trouble concentrating, trouble sleeping, trouble completing simple tasks, short-term memory problems
Hearing and Vision Changes
When a brain tumor grows on or around the cranial nerve, it can cause hearing and vision changes. Vision problems may include blurred vision, double vision, abnormal eye movements, and even vision loss or blindness. Hearing changes may include hearing loss and ringing or buzzing in the ears.
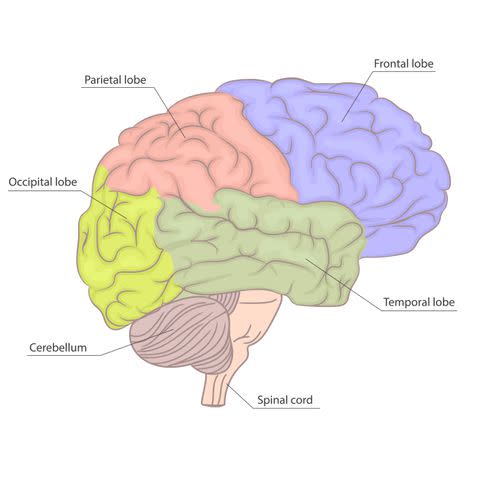
Brain Tumor Symptoms by Location
Different areas of the brain are responsible for different functions in the body. A brain tumor’s symptoms greatly depend on its location in the brain, as well as its size and type.
Tumor symptoms to expect by brain location include:
Frontal lobe: Personality changes, seizures, speech problems, memory problems
Parietal lobe: Changes in sensory and processing, spatial awareness problems
Temporal lobe: Seizures, behavioral changes
Occipital lobe: Vision loss
Thalamus: Behavior changes, speech and language problems
Cerebellum: Loss of coordination, movement problems, uncontrolled eye movements
Brain stem (spinal cord): Vision loss, uncontrolled eye movements, loss of coordination
ambassador806 / Getty Images
Symptoms in Children
Brain tumors are the second most common type of childhood cancer in the United States. Each year, more than 4,000 children and adolescents in the United States are diagnosed with brain tumors.
Brain tumor symptoms in children are similar to those in adults. Brain tumor symptoms in children include:
Frequent, severe headaches
Seizures
Nausea and vomiting
Loss of balance or coordination
Behavior changes
Infants with brain tumors often develop swelling that leads to an increased head size. Infants with a widening head or bulging crown should see their healthcare providers right away.
When to Contact a Healthcare Provider
It is important to see your healthcare provider any time you develop brain tumor symptoms such as severe headaches or seizures. Call your healthcare provider if you develop new-onset headaches with any of the following characteristics:
Most painful when waking in the morning
Occur with nausea and vomiting
Become worse with activity, coughing, or sneezing
Vision changes or loss
It is also important to see your healthcare provider any time you develop changes in your mood, personality, or ability to function.
A Quick Review
A brain tumor is a growth of abnormal cells in the tissues of the brain. Brain tumors may be benign or malignant, and both types can cause symptoms.
Brain tumors compress or put pressure on the brain. This increased pressure then leads to symptoms such as headaches, seizures, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, mood or personality changes, balance problems, and vision changes.
Brain tumor symptoms can vary widely and depend on the tumor’s location and how much injury it has caused. A person’s age and overall health also affect their symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do you have symptoms during the first stage of a brain tumor?
The symptoms of a brain tumor depend on the tumor’s location. Some brain tumors cause no symptoms at all. A brain tumor that is compressing blood vessels in the brain will cause symptoms such as severe headaches right away.
How is a brain tumor headache different than a regular headache?
A brain tumor headache causes persistent, severe pain. It usually feels worse when first waking in the morning. People with brain tumors often experience nausea and vomiting with their headaches. This type of headache does not respond to over-the-counter medications like Tylenol (acetaminophen) or Advil (ibuprofen).
How long can symptoms of a brain tumor go undiagnosed?
Brain tumor symptoms and their severity greatly vary and depend on where in the brain the tumor has developed. A benign tumor usually grows slowly and may not cause symptoms. A malignant tumor usually grows quickly and may start causing symptoms right away.
For more Health.com news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.com.

