Peripheral Neuropathy Treatment
Medication and lifestyle approaches are keys to treatment
AndreyPopov / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Amy Kwan, PT, DPT
Peripheral neuropathy treatment includes symptomatic therapies and medical management to help prevent worsening nerve damage. If you have been diagnosed with chronic peripheral neuropathy, you may need ongoing treatment to control your symptoms.
A few neurological disorders can cause acute episodes of peripheral neuropathy, and treatment can often completely alleviate these conditions. This article describes the medications, procedures, lifestyle interventions, and prevention of peripheral neuropathy.
AndreyPopov / Getty Images
Home Remedies and Lifestyle
If you have been diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy or are at risk of developing the condition, lifestyle factors play a major role in managing symptoms and preventing nerve damage from worsening. They can sometimes even prevent the condition from occurring at all.
Managing Pain
You can try several of these tips to decide which helps reduce your discomfort and then develop a routine that makes you comfortable.
Home remedies for painful symptoms of neuropathy include:
Using a warm (not hot) heating pad on painful areas
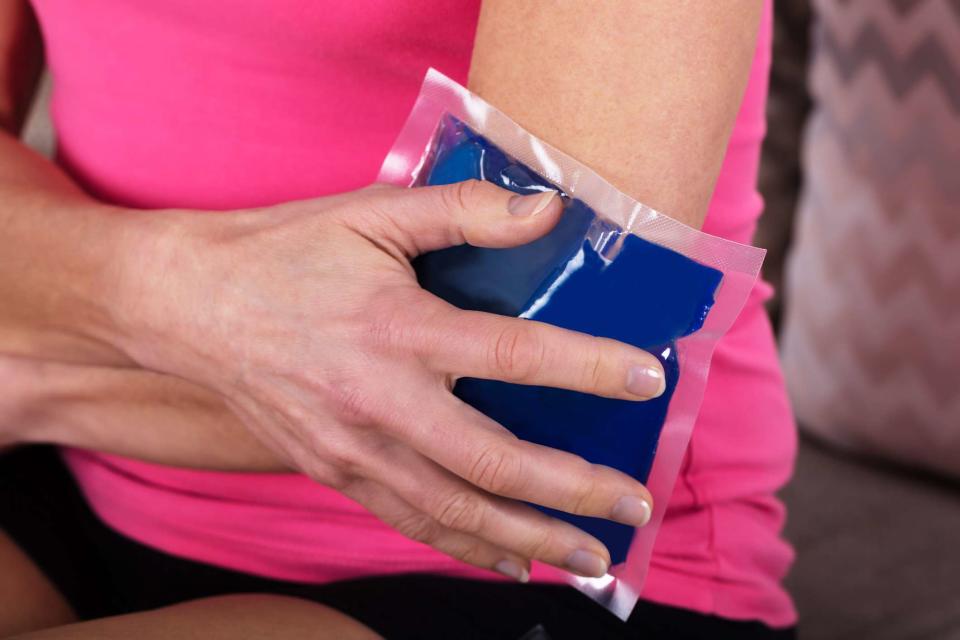
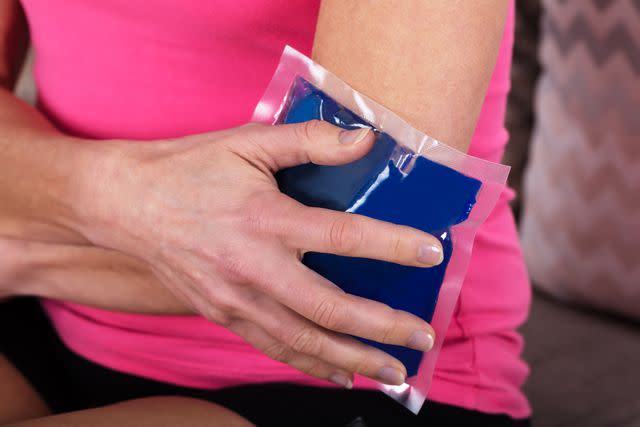
Using a cooling pad (do not use ice) on painful areas
Covering the area or leaving it uncovered, depending on your level of comfort
Wearing loose-fitting clothes, gloves, socks, or shoes that are not made with irritating material on the painful areas
Avoiding irritating lotions or soaps
Using a soothing lotion that’s not irritating
Keeping the painful area clean
It may seem like some of these strategies contradict each other—that's because your symptoms may respond to lifestyle strategies differently from someone else’s symptoms.
Related: Home Remedies for Nerve Pain in Feet
Preventing Injuries
Diminished sensation is one of the most common effects of peripheral neuropathy. This can lead to problems, such as clumsiness, trouble getting around, and injuries. Preventing and regularly checking for injuries can help avoid serious consequences, such as infected wounds.
Lifestyle measures to manage and prevent injuries include:
Wear well-padded shoes and socks.
Look at your feet, toes, fingers, and hands regularly to see if you have any cuts or bruises you didn’t feel.
Clean and cover cuts to avoid infections.
Use extra caution with sharp utensils, such as cooking utensils or tools.
Disease Management
Peripheral neuropathy has a wide range of causes and risk factors. Lifestyle factors that help prevent disease progression are closely correlated with the risks and underlying causes.
Prevent peripheral neuropathy or progression of the condition with these tactics:
Maintain a healthy glucose level if you have diabetes.
Avoid alcohol if you have any type of peripheral neuropathy.
Maintain a well-balanced diet, which may include vitamin supplementation, especially if you are on a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Therapies
A few OTC therapies can help with painful symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. You can take these as needed.
OTC pain therapies include:
Topical lidocaine spray, patch, or cream
Capsaicin cream or patch
Oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Advil (ibuprofen) or Aleve (naproxen)
Oral Tylenol (acetaminophen)
These treatments can help relieve painful symptoms of peripheral neuropathy, but they do not help improve diminished sensation, weakness, or coordination problems.
Talk to a Healthcare Provider
Discuss your treatment plan with your healthcare provider, even when you are taking OTC treatments without a prescription.
Prescriptions
Prescription therapies for treating peripheral neuropathy include pain medications and anti-inflammatories. The prescription treatments for chronic types of peripheral neuropathy (alcoholic neuropathy, diabetic neuropathy, chemotherapy-induced neuropathy) differ from the treatments for acute types of peripheral neuropathy.
Pain Control
Many prescription treatments can help manage the pain and discomfort chronic peripheral neuropathy causes.
Prescription medications for treating peripheral neuropathy pain include:
Lyrica (pregabalin)
Neurontin (gabapentin)
Effexor (venlafaxine)
Cymbalta (duloxetine)
In severe cases, intravenous (IV) lidocaine may prove necessary.
Very few medications have the potential to relieve the underlying disease process of chronic types of peripheral neuropathy or to improve the condition. In some cases, a prescription strength vitamin supplement or injected vitamin B12 can help prevent progression when peripheral neuropathy is associated with a severe vitamin deficiency.
Prescription treatment can help treat the underlying process in some types of acute peripheral neuropathy.
Treatment for acute peripheral neuropathy, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or Miller-Fisher syndrome, may include corticosteroids, immunoglobulins (immune system proteins), or plasmapheresis (a procedure that removes the liquid portion of blood, returning the blood cells), which modify overactivity of the immune system.
Researchers believe there is an association between these acute conditions and inflammatory nerve damage, and that modifying the immune system is beneficial for treating symptoms and the underlying disease process.
Surgeries and Specialist-Driven Procedures
In some cases, surgical procedures can benefit those who have certain types of peripheral neuropathy.
When there is another condition that's exacerbating the symptoms or process of peripheral neuropathy, surgery may help relieve symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and prevent disease progression. This has proved effective when nerve entrapment or vascular insufficiency is a factor in worsening peripheral neuropathy.
Physical therapy can also serve as an important component of living with chronic peripheral neuropathy and recovering from acute peripheral neuropathy. Physical therapy can help a person strengthen weak muscles, improve coordination, and learn how to adapt to sensory and motor changes to get around safely.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Some complementary and alternative approaches can help you cope with the discomfort of peripheral neuropathy. These treatments can serve as an ongoing option for people who have chronic peripheral neuropathy.
Options may include:
Acupuncture or acupressure, both of which involve the placement of needles (acupuncture) or pressure (acupressure) in specific areas of the body, may help reduce painful symptoms.
Massage therapy may help to alleviate muscle tension.
Meditation and relaxation therapies can help relieve symptoms of pain or discomfort for some people who have peripheral neuropathy.
If you decide to consider a complementary or alternative treatment, speak with a healthcare provider to determine whether or not the treatment is safe for your condition.
Summary
For acute types of peripheral neuropathy, medical intervention can treat the underlying process, improving the condition. For chronic types of peripheral neuropathy, medical interventions and lifestyle factors aim to prevent the condition's progression.
The treatment of chronic peripheral neuropathy focuses on controlling the symptoms of pain as well as protecting areas of diminished sensation from damage or infection. Additionally, lifestyle adjustments and physical therapy can help improve a person's ability to move around safely with chronic peripheral neuropathy but will not improve sensation.

