Identifying and Treating Bed Bug Bites
Joel Carillet / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Susan Bard, MD
Bed bugs are tiny insects that usually live near where people sleep, regardless of the cleanliness of the room. The bugs hide in small crevices like bed frames, mattress seams, or cracks in the walls. At night, bed bugs come out to feed on blood. When they do this, itchy bite marks can form.
While a bed bug bite usually causes itching and irritation, bed bugs do not appear to spread diseases. Bed bug bites also rarely need medical attention—exceptions include allergic reaction to the bite or a bed bug bite that leads to a skin infection.
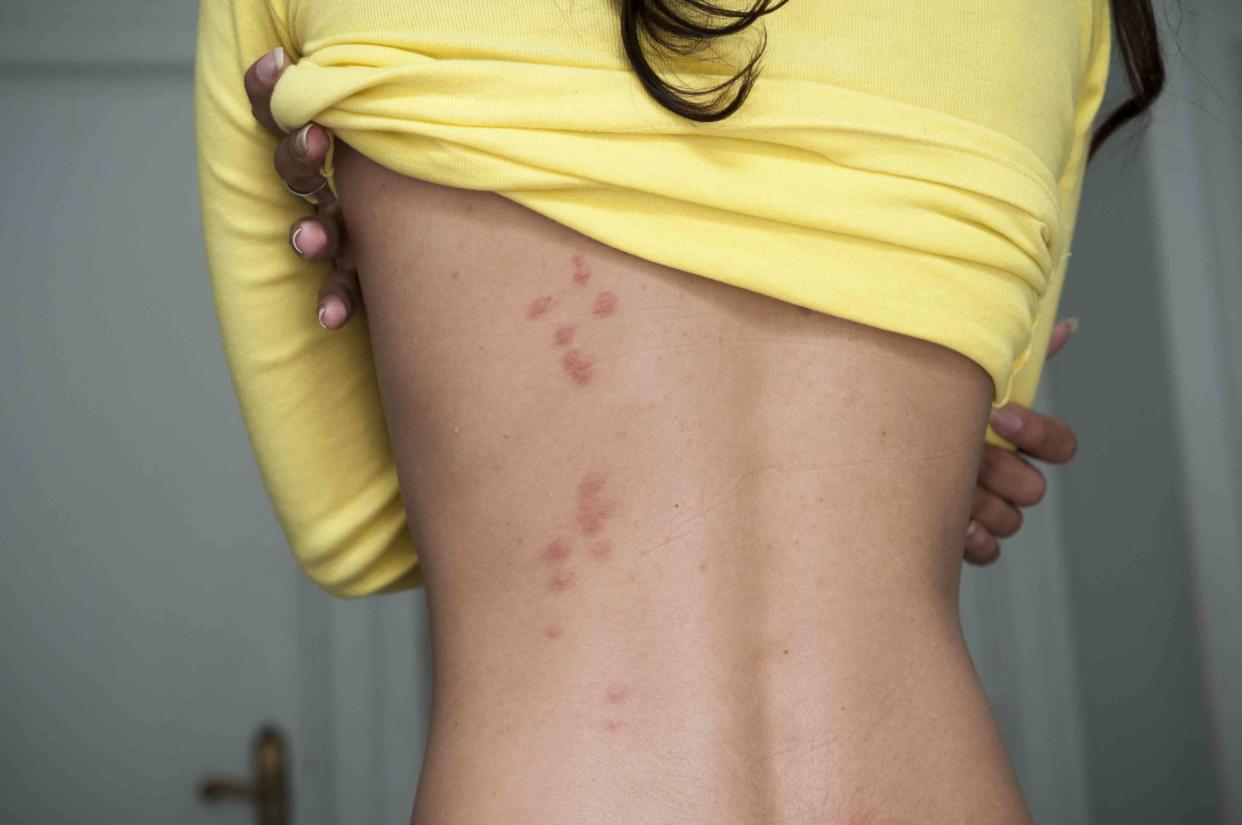
What Does a Bed Bug Bite Look Like?
Some people don't have any reaction to bed bug bites and so will not develop bite marks. Most times, though, bed bug bites appear as welts on the skin. The welts are similar in appearance to a mosquito or flea bite—slightly swollen and red.
The bites may appear at random places on your body. But usually, bed bug bites appear in clusters. Each cluster will have three to five bites in a zig-zag formation.
Bed bug bites form one to several days after the actual bite. It can even take up to two weeks for the bite marks to form.
Some people might be allergic to bed bugs and have an adverse skin reaction. In these cases, the bites can be larger than usual. There might also be painful swelling, skin redness, or the development of hives.
Editor's Note: Bed bugs feed on blood every five to 10 days. Their feeding can take three to 12 minutes. You don't feel it when bed bugs feed on you because the bugs release substances, including an anesthetic that desensitizes you to pain, into you when they bite.
Bed Bug Bite Symptoms
You won't actually feel it when a bed bug bites you. Once the bite mark develops, it will typically cause itchiness and irritation.
The itchiness may make sleeping difficult. And so, insomnia—which is trouble falling or staying asleep or getting good-quality sleep—may be a symptom of bed bug bites.
Excessive scratching may lead to a skin infection. Symptoms of a skin infection include a bed bug bite that feels tender or that oozes pus.
Having bed bug bites might also lead to anxiety as you worry about getting bitten or the infestation.
How to Know If It's a Bed Bug Bite or Something Else
Bed bug bites can look and feel similar to rashes, hives, chickenpox, and other bug bites. So knowing what you have is a bed bug bite means confirming that you have bed bugs in the first place.
Signs that you have or are staying in a place with bed bugs include finding the following on your mattress or sheets:
Small reddish spots: This indicates that a bed bug has been crushed.
Small dark spots: This is bed bug excrement. The spot may seem to have bled into the mattress or sheet as a marker might.
Pale yellow skins: These are eggs and eggshells that lymphs shed as they grow. The skin flecks are tiny, measuring in at 1 millimeter.
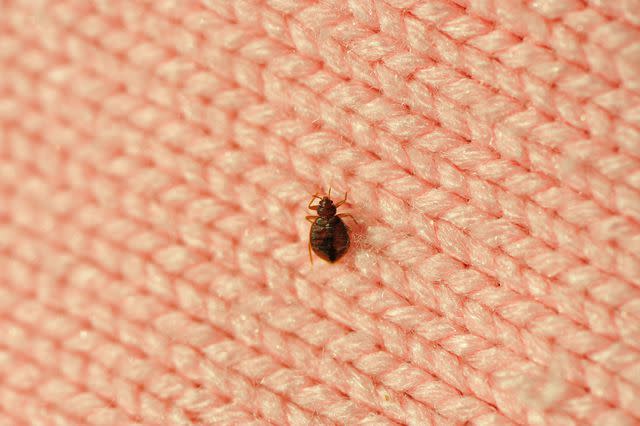
You may also be able to see live bed bugs. The bugs might be near mattress and box spring piping, seams, and tags, as well as in cracks on the bed frame and headboard.
Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed. If they recently had some of your blood, they are reddish-brown and elongated. If they have not recently had some of your blood, they are long, brown, flat, and oval-shaped. Younger bed bugs are smaller and can be translucent or whitish-yellow.

Getty Images
How To Treat Bed Bug Bites
Bed bug bites will usually heal on their own in a week or two.
In the meantime, there are several things you can do at home to reduce the itch and prevent infections, including:
Keep the area clean by washing the bites with soap and water.
Apply antiseptic ointments to prevent infections.
Take over-the-counter antihistamines to reduce itching.
Apply over-the-counter corticosteroid ointments to relieve itching.
Avoid scratching the site.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
You should visit a healthcare provider about your bed bug bites if it seems you have developed an infection or allergic reaction. Signs you should go to a healthcare provider include:
Blisters
Bites that are tender or that have a substance oozing from them
Red or swollen skin
Hives
Your healthcare provider may recommend a prescription antihistamine for the itching or antibiotics for infections. If you're having a severe allergic reaction, they might inject an antihistamine, corticosteroid, or epinephrine (adrenaline).
You should also visit a healthcare provider if you have many bites.
Preventing Bed Bug Bites
The way to prevent bed bug bites is to prevent bed bugs in the first place. This means you should protect your yourself at home or anywhere you might share spaces with others, such as at work. Steps you can take to protect yourself against bed bugs include:
If you purchase already-used furniture, check the furniture for signs of bed bug infestation before you bring it into the home, office, or school.
Vacuum frequently.
Use a protective cover on your mattress and box spring.
Get rid of clutter.
Keep your belongings separated from others in shared public spaces.
If you already have bed bugs, then prevention of future bed bug bites means getting rid of the infestation you have.
Bed bugs can be a challenge to get rid of, and you may need to treat the infested area multiple times to ensure the bugs are completely exterminated. If one treatment does not completely eradicate the bed bugs, you may need to try a different method.
There are both chemical and non-chemical options for getting rid of bed bugs. The most effective treatment is usually a combination of the both.
You can go the do-it-yourself route or hire a professional to get rid of the bugs. Research into which methods is most effective and safest is key.
Once you decide on how you want to eradicate the bugs, you'll also want to take measures like putting infested bedding and clothing in the dryer on high heat and continuing to check for bed bugs a week after treatment.
A Quick Review
Bed bugs are tiny bugs that live near areas where people sleep. They are usually not dangerous and do not spread diseases, but their bites can be itchy and uncomfortable. Bed bug bites may not show up for up to two weeks, but the bites usually heal by themselves within a week or two. If your bites become infected or you react severely to them, contact a healthcare provider. They can provide any necessary treatment. The only way to prevent bed bug bites is to prevent bed bugs in the first place. If you already have bed bugs and need to get rid of them to prevent future bites, you'll need to treat the infected area. Exterminating bed bugs and removing an infestation can be challenging and often takes a while. Research the different extermination methods and choose the best one for you and your situation.
For more Health news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.

