These Detailed Pictures Show the Exact Tick Bite Symptoms to Look For
This article was medically reviewed by Shonda Hawkins, M.S.N., a nurse practitioner and member of the Prevention Medical Review Board.
You just spent the day outside hiking, grilling, or tending to your yard—but now you have a nasty, red, scratchy, bumpy bite on your arm. Could it be a tick bite?
Unfortunately, figuring out the source of your bug bite can be tricky, especially because mosquitoes, spiders, and fleas also come out to play when warmer weather hits (not to mention, bed bugs and other critters that may wind up in your home).
“Tick and other insect bites can look similar,” says Griffin Dill, Ph.D., coordinator of the Cooperative Extension: Tick Lab at The University of Maine. “Without finding a tick attached and feeding, it’s hard to differentiate one bite site from another,” he says.
But treating and preventing these bites can help keep nasty tick-borne illnesses like Lyme disease out of your future—so knowing how to identify a bite is crucial. Here, the signs and symptoms to watch out for, plus tick bite pictures to refer to when you suspect the blood-sucking critter has made its way onto your skin.
What does a tick bite look like, exactly?
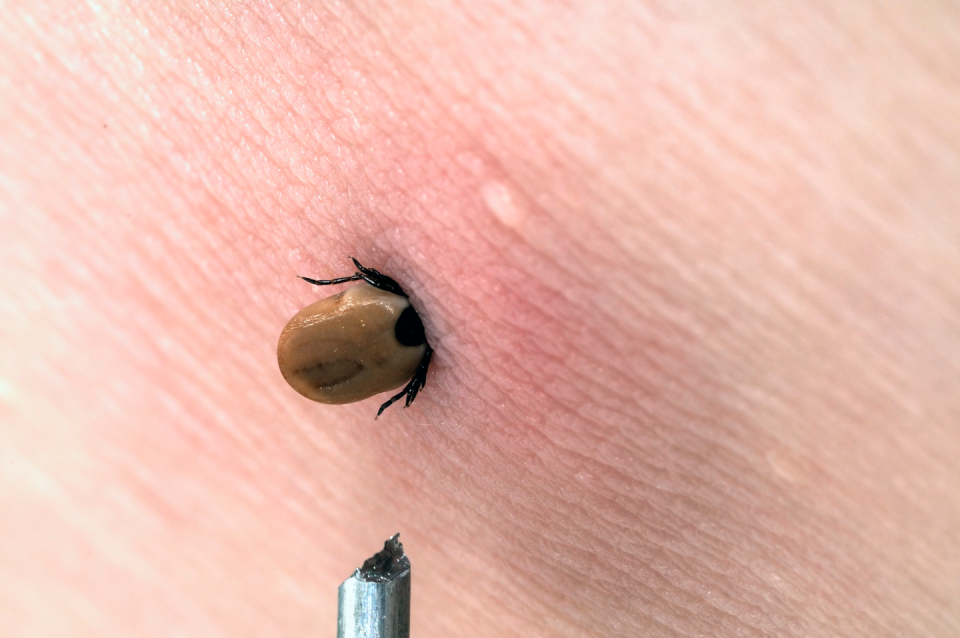
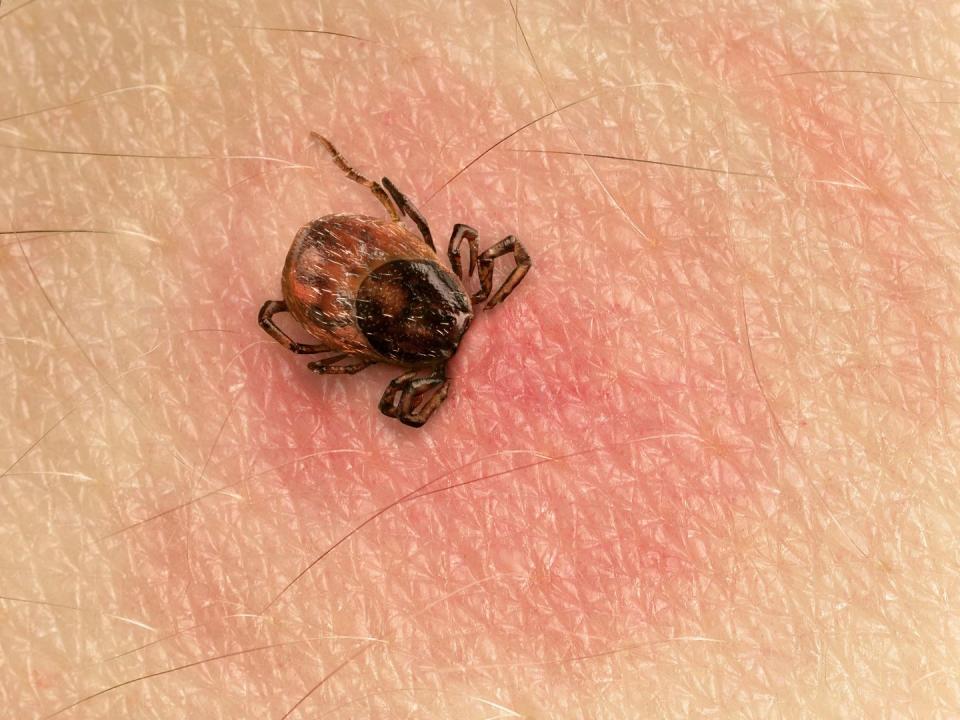

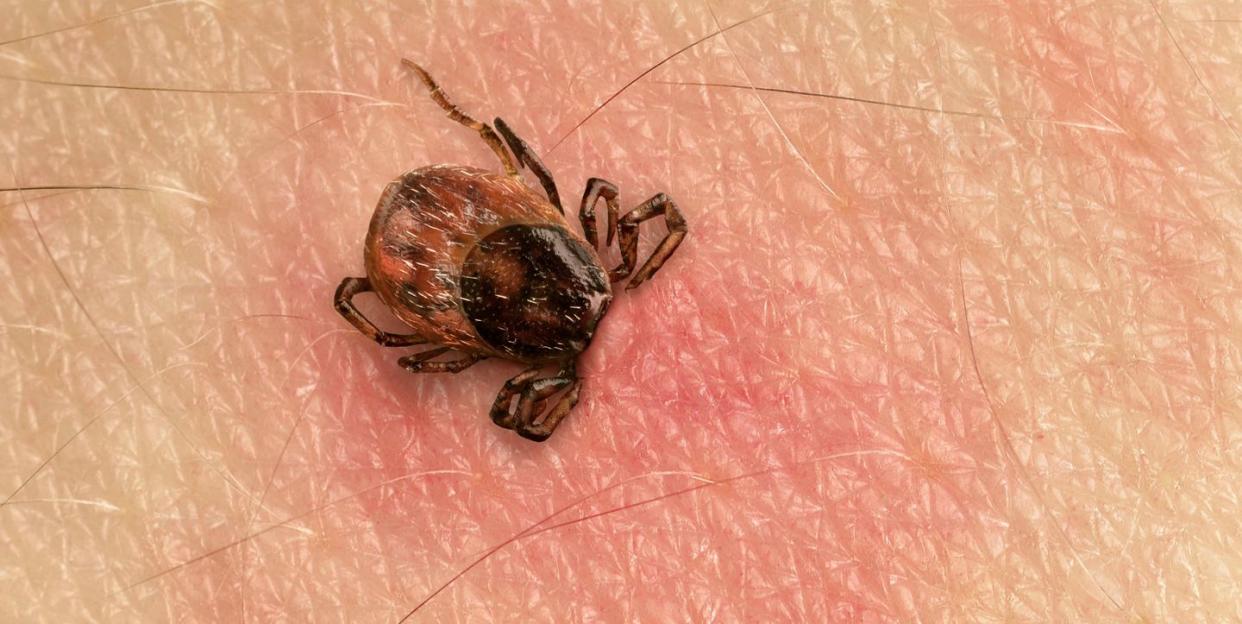
The signs of a tick bite actually vary from person to person, since everyone’s immune system reacts differently to them, explains Thomas Mather, Ph.D., director of the University of Rhode Island’s Center for Vector-Borne Disease and Tick Encounter Resource Center. While someone may have a small, red bump after the tick detaches, others may develop an area of redness and itchiness.
Your best bet is to find the tick while it’s still on your skin. “Ticks are designed to linger when they attach and bite,” says Mather. The mouth of a tick contains a bunch of backward-pointing barbs that they use to stay put, meaning they are “designed to lock and load,” as Mather puts it. The biters also secrete a cement-like substance around their mouths to keep them stuck even if they were to be, say, absentmindedly scratched at.
Depending on where the tick is in its lifecycle—larva (baby, six legs), nymph (eight legs), or adult stage (full-sized critter)—it can stick around anywhere from three to six days, Mather says. The longer they’re feeding, the bigger they get—and the greater the risk of transmitting disease.
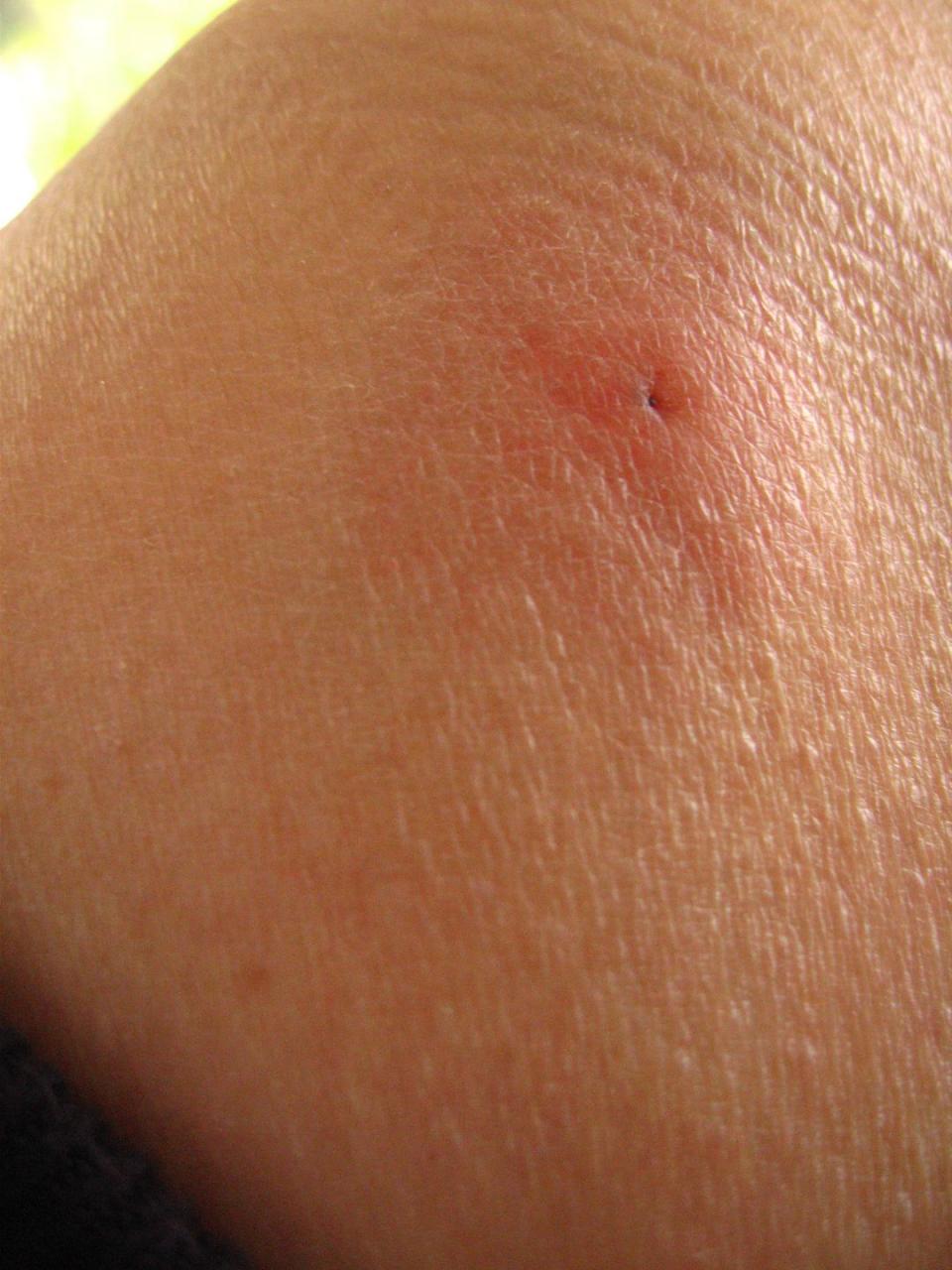
If you’ve been previously bitten, there’s a greater chance you will have an allergic reaction to the tick saliva within 20 to 40 hours of the bite, says Mather. After a bite, the area may appear as a small red spot that doesn’t expand to be larger than a dime. However, more severe reactions can occur, and rashes can develop. Because tick bite signs vary wildly and can mimic the appearance of other insects, even tick experts can’t always tell one red mark from another.
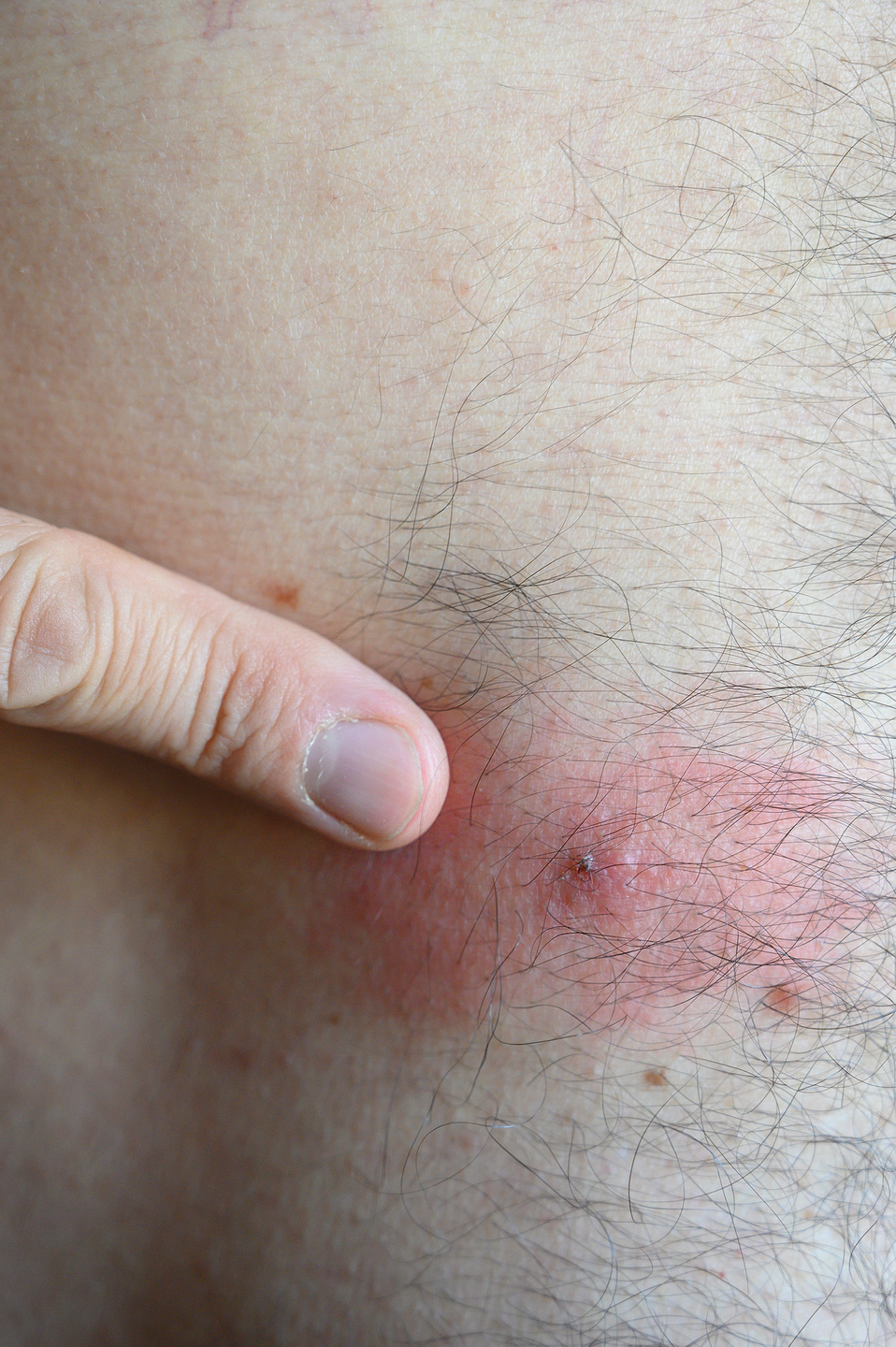
Where do ticks bite?
You can find a tick bite anywhere. However, “although they can and do attach to any part of the body, there are certain body parts they more commonly move toward, like the hairline, or in tucked-away places, like the armpits, groin, and behind knees,” says Dill. That’s because ticks have heat sensors that allow them to seek out warmer, moist places. Recently, doctors even discovered a tick attached to a 9-year-old boy’s eardrum.
Are tick bites itchy? Do they hurt?
Generally, tick bites do not hurt. You might feel a bite—but you may have no idea when it happens either. Both are possible. “Early in the process of biting, ticks inject a pain mediator via their saliva,” says Mather. Because it’s more likely that subsequent bites will elicit a reaction, the first bite can often go unnoticed, he says. However, many people do find them itchy. If you continue to itch at a certain spot on your body, Mather encourages you to take a look to see what you’re scratching at, since it’s one common way people find ticks.
Does a tick bite always cause a rash?
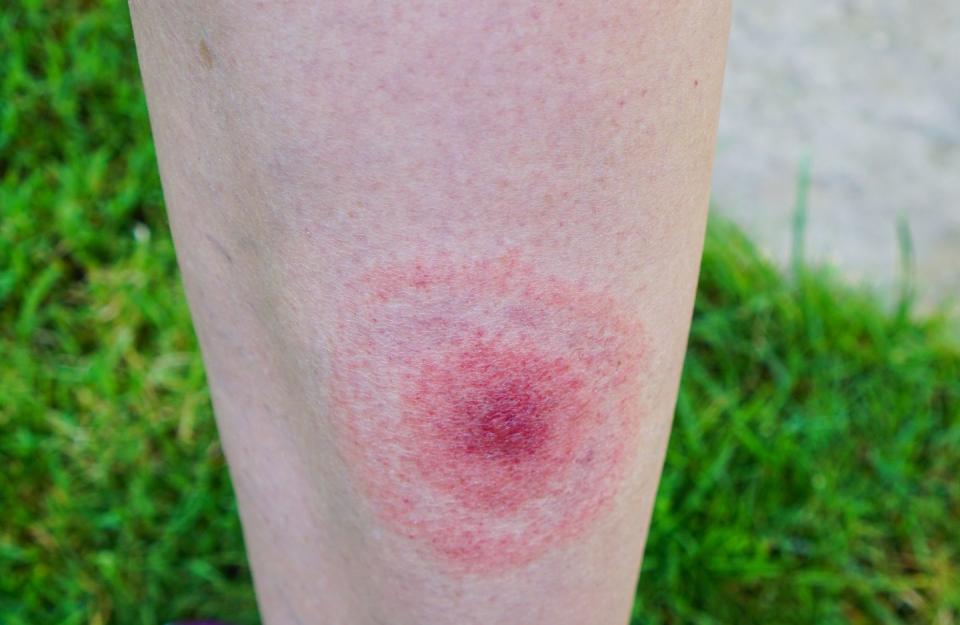
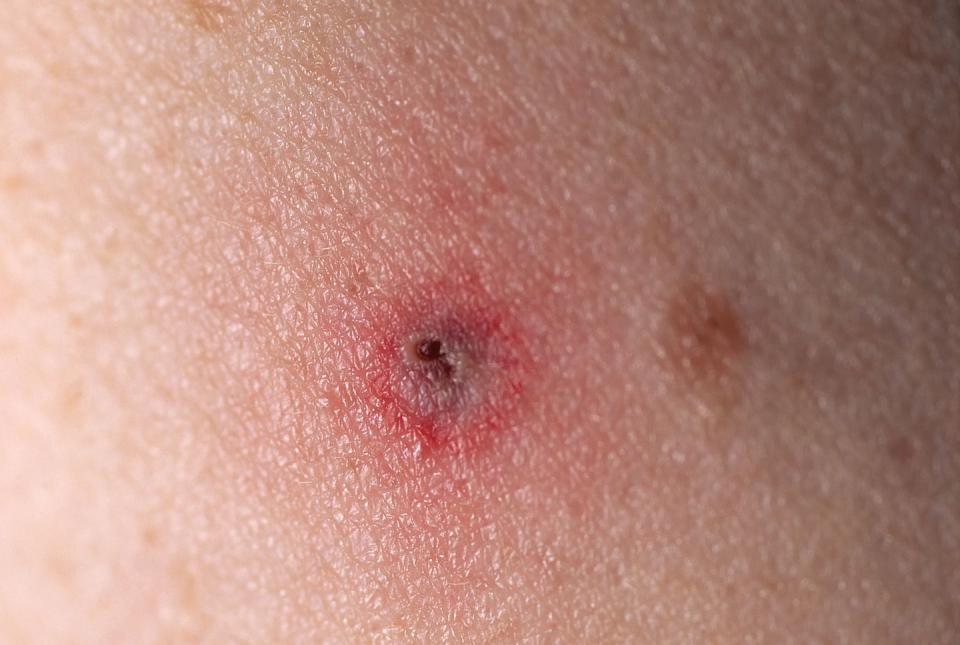
You’ve probably heard of the classic “bullseye” rash, which is one of the most distinct symptoms of Lyme disease. This circular rash is dark in the center and expands outward, like a bullseye, appearing about a week after the bite on any part of the body. It doesn’t always look like that, though.
You may have a crusty spot with a splotch of redness around it that gets bigger, bluish rashes, or a red, oval plaque, per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Catch is, this rash only appears 70 to 80% of the time, says the CDC. Remember that not all ticks carry the bacteria that causes Lyme disease; there are other types of rashes associated with other tick-borne illnesses. For instance, Rocky Mountain spotted fever can cause a red, speckled rash that appears first on wrists and ankles.
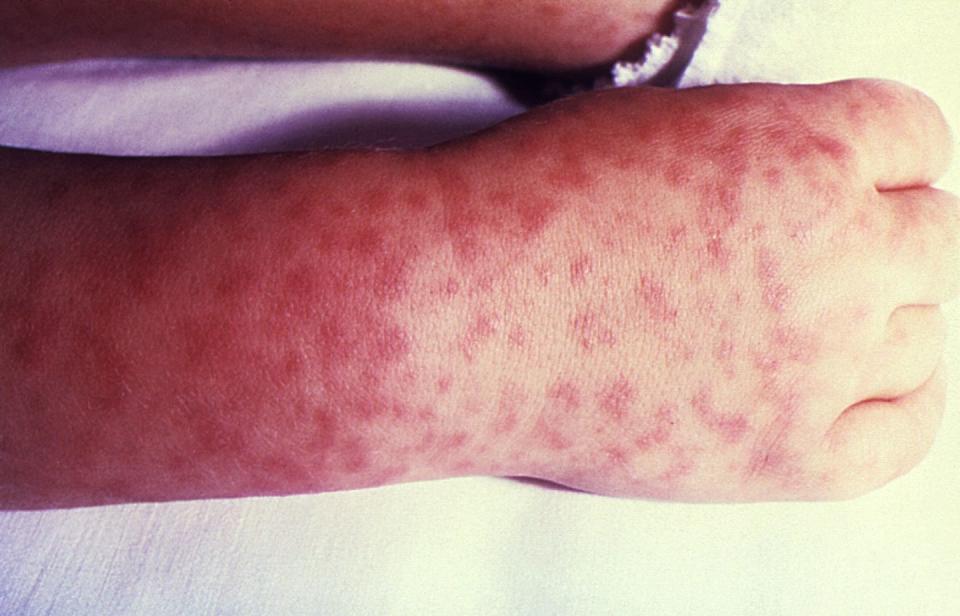
It’s also important to keep in mind that rashes can be tough to distinguish from one another. The CDC has a whole page on rashes that resemble the bullseye associated with Lyme, but aren’t. These include large, itchy rashes, the ringworm fungus, and hives. If you’re concerned about any rash or are worried you may have been bitten by a tick (or know you have), call your doctor. In certain circumstances, they can prescribe a course of preventative antibiotics if Lyme disease is suspected or you live in a state with a high risk of Lyme.
How to remove a tick and treat a tick bite
First, don’t panic. If you find one attached to your skin, remove the tick as quickly as possible using a set of fine-tipped tweezers. Grab the tick as closely to the surface of your skin as possible, and pull upward with steady, even pressure. If mouth-parts are left in the skin, try your best to remove them, but if not just let your skin heal normally, says the CDC. Then, make sure to clean the bite area with soap and water or alcohol.
Dispose of the tick in a sealed bag or container, wrapped up tightly in tape, or by flushing it down the toilet, says the CDC. Never crush it with your fingers, and of course, in the weeks to follow you should keep an eye out for any lingering symptoms, like a rash. See your doctor if you experience flu-like symptoms, such as achy muscles, fever, swollen lymph nodes, or other unusual reactions that don’t feel normal
Ticks can be tiny (sometimes no bigger than a poppy seed!) and they can be easily missed, so it’s important to do thorough body check after you’ve spent time outdoors. Be sure to look carefully under your arms, around your ears, inside your belly button, behind your knees, between your legs, and in your hair. “Checking yourself, kids, and pets can go a long way in minimizing contact with these critters,” says Dill.
And as always, stock up on the best tick repellents before your next outdoor adventure.
Go here to join Prevention Premium (our best value, all-access plan), subscribe to the magazine, or get digital-only access.
You Might Also Like

