Are Your Flakes From Seborrheic Dermatitis or Dandruff?
Aliaksandr Litviniuk / Getty Images
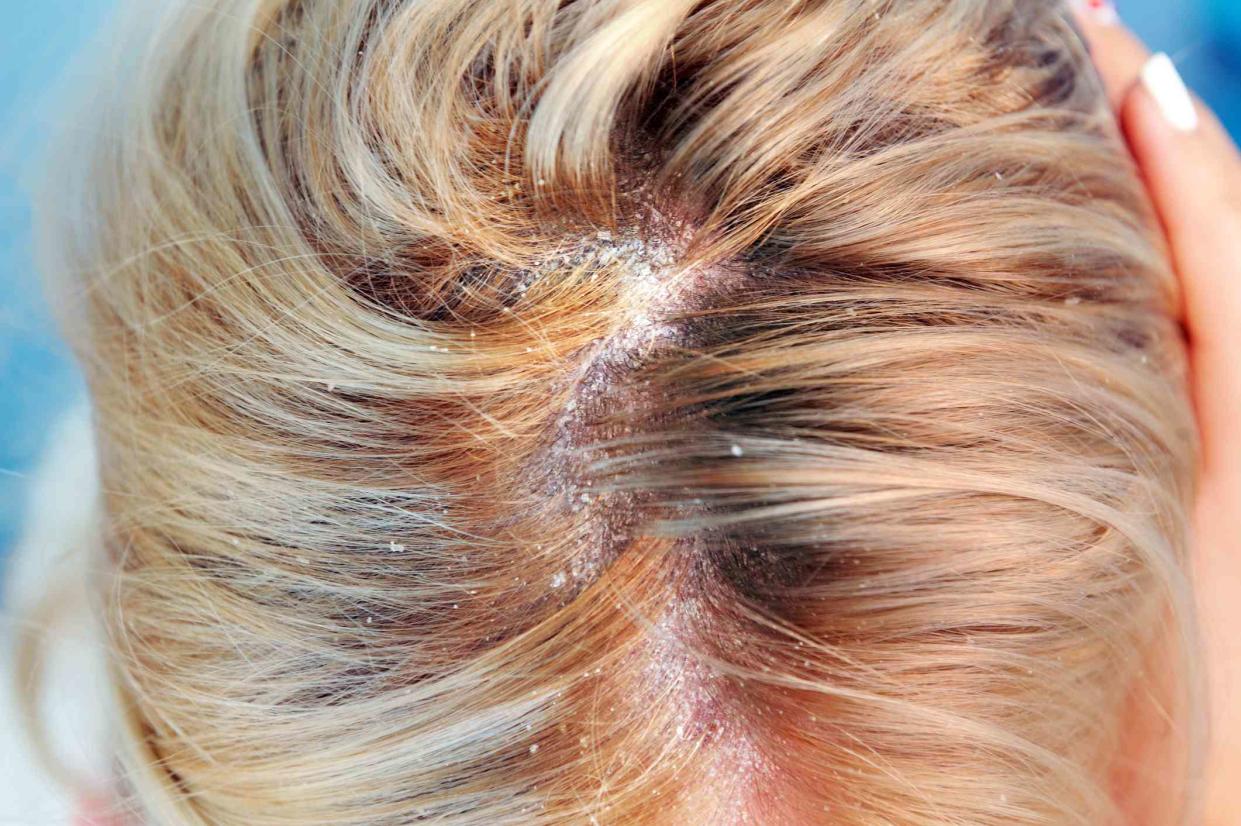
Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff are common skin conditions that affect the seborrheic areas of the body. The seborrheic areas are responsible for producing oil on the skin, also known as sebum.
While both conditions cause a dry, itchy scalp, they have other symptoms that allow us to tell them apart. Dandruff is always found only on the scalp, while seborrheic dermatitis can spread to other seborrheic areas like the face, ears, and upper chest.
Dandruff is basically a mild form of seborrheic dermatitis. Together, these conditions affect about 50% of adults in the United States. Fortunately, both conditions are treatable either at home or by a dermatologist.
This article explains the differences and similarities between seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff and how they are treated.

Aliaksandr Litviniuk / Getty Images
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes a scaly rash on oily areas of the body. The scalp is the most common location, but it can also appear on the ears, eyebrows, beard, skin around the nostrils, or on the chest, especially in men.
Seborrheic dermatitis tends to occur during certain phases of life and peaks during infanthood and adolescence.
Cradle cap, a common skin condition on the scalp of infants, is caused by seborrheic dermatitis. Seborrheic dermatitis affects about 42% of infants, and can be found on an infant’s face and diaper area as well.
In adolescents, seborrheic dermatitis often affects the scalp, face, upper chest, underarms, and inguinal folds, or folds in the groin. It is more common in men than women.
Symptoms can vary depending on age, skin tone, and whether you have other medical conditions, but common signs and symptoms include:
Dry, flaky skin
Rash on affected areas
Burning or itching
Redness, swelling, and inflammation
Dandruff
Dandruff causes white or yellow flakes of dry skin on the scalp and is found only on the scalp, while seborrheic dermatitis can spread to other seborrheic areas.
Dandruff is also more common and occurs more often in men than women. Dandruff usually starts during puberty, peaks around age 20, and is less common after age 50.
Related:What’s Causing Flakes in Your Hair and How to Treat Them
How to Tell the Difference
Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff can both cause itchy, flaky skin on the scalp.
However, dandruff usually presents as small, white flakes in the hair and on the scalp. In contrast, seborrheic dermatitis usually presents as defined plaques of greasy, yellow scales on the scalp, behind the ears, and on the nose, upper lip, eyelids, eyebrows, and upper chest.
The following chart shows the differences and similarities between dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis.
Characteristics | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Dandruff |
White flakes | No | Yes |
Greasy, yellow scales | Yes | No |
Itchiness | Yes | Yes |
Can appear on the scalp | Yes | Yes |
Can appear on face, eyes, ears, chest | Yes | No |
Swelling, redness, irritation | Yes | No |
Risk Factors of Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff
Seborrheic dermatitis has several known risk factors, including:
Presence of yeast on the skin: Studies have shown that higher levels of Malassezia yeast on the skin are associated with an increased incidence of seborrheic dermatitis. This may be due to the skin’s inflammatory response to yeast overgrowth.
Increased oil production: Both seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff are associated with increased sebaceous activity in the skin. The sebaceous glands are most active shortly after birth and again at puberty. Males tend to produce more sebum than females, putting them at higher risk of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff.
Immunosuppression: You are more at risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis if your immune system is compromised. Individuals diagnosed with HIV/AIDS are at increased risk of developing the condition.
High cholesterol: There may be a connection between high levels of cholesterol and your risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis. This may be due to the fact that the Malassezia yeast can cause a breakdown of triglycerides in the blood, leading to high cholesterol and free fatty acids.
Parkinson’s disease: There is a high correlation between Parkinson’s disease and seborrheic dermatitis. This may be due to the sebum changes that occur during the disease.
Family history: Recent research suggests that there may be a genetic component to seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff. If these conditions run in your family, you may be at higher risk of developing them.
Emotional stress: Seborrheic dermatitis tends to be more common in people who are experiencing depression or emotional stress.
Risk factors for dandruff include:
Age. Dandruff usually begins in young adulthood and lessens around middle age, but some people have it lifelong.
Being male. Dandruff is more prevalent in males than in females.
Certain medical conditions. Parkinson's disease, other diseases that affect the nervous system, and human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) seem to increase the risk of dandruff.
Learn More:HIV and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Treatment
Both dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis are treatable. Dandruff is often treated at home, and seborrheic dermatitis may require a visit to your dermatologist.
The best treatment for seborrheic dermatitis will depend on where the lesions appear on your body and how severe they are. Treatment often requires a topical antifungal ointment or shampoo. If the lesions don't respond to this treatment, a dermatologist may recommend:
Anti-inflammatory medications
Coal tar shampoo
Immune modulators
Dandruff can usually be treated effectively using a dandruff shampoo regularly. Dermatologists recommend using a treatment shampoo once weekly if you are Black. If you are Asian or White, aim to wash your hair every day and incorporate a dandruff shampoo about twice weekly.
Home Remedies
To relieve itching at home, the following remedies may be helpful:
Moisturize: Apply a gentle moisturizer to your skin after showering or bathing to help prevent dry skin and flaking.
Opt for lukewarm water: Hot showers may feel amazing, but they can be rough on your skin. Try keeping baths and showers to five minutes and using lukewarm water that won’t dry out irritated skin.
Go for unscented: When choosing household items that touch your skin like soaps or laundry detergents, look for gentle, unscented types since these are less likely to cause skin irritation.
Try coconut oil: Using coconut oil on the scalp has been shown to hydrate the skin and may reduce inflammation as well.
Look for tea tree oil: Tea tree oil has been used for other skin conditions like athlete’s foot, and a 2002 study found that shampoos infused with tea tree oil may be effective at treating dandruff.
Manage stress: Because stress can increase the risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis, find healthy ways to reduce stress like getting enough sleep, practicing mindfulness, and meeting with a therapist.
Other Causes of Dry, Itchy Scalp
Besides seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, there are other skin conditions that could lead to a dry, itchy scalp in children and adults. Examples include dry skin, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, tinea capitis, rosacea, and lupus.
Dry Skin
Dry skin occurs when the skin loses moisture, leaving it dry and flaky. This common skin condition can be caused by a number of factors, including aging, medication side effects, ethnicity, cold weather, smoking, nutritional deficiencies, and chronic health conditions.
While dandruff and dry skin can both cause flaky skin, dry skin can appear anywhere on the body. Dandruff only appears and causes flakes on the scalp.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes the skin cells to reproduce too quickly. This leads to a buildup of dead skin cells that cause plaques on the skin. Psoriasis tends to run in families and is not contagious.
While seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis both cause plaques of skin to form, the plaques appear differently. Seborrheic dermatitis plaques are yellow and greasy, while psoriasis plaques are usually much thicker and have a silvery-white color. Psoriasis plaques are also covered in scales.
If you are experiencing psoriasis, work with a dermatologist to find the right combination of medications and light therapy to address the skin plaques.
Related:Is Psoriasis Hereditary?
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when something that has touched your skin causes irritation. This skin allergic reaction can come from soaps, laundry detergents, clothing, the sun, or any other irritant that causes a reaction on your skin.
Contact dermatitis presents as a dry, itchy rash and sometimes blisters. While both dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis can cause itching, the sensation is usually not as intense as contact dermatitis.
Treatment for contact dermatitis will depend on identifying which irritant is causing the reaction. Once you know why you are experiencing an allergic reaction, you will be able to avoid the irritant and prevent contact dermatitis.
Summary
Seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff are common skin conditions that have some similar characteristics, but also have different symptoms that allow us to tell them apart. If you're unsure whether you have dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, or another skin condition, talk with a healthcare provider who can help you find the right treatment and refer you to a dermatologist if needed.

