‘Eradicating the bad stuff’: the unwelcome return of book burning
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.

Book burning is creeping back into fashion. It has recently emerged that in 2019 a Canadian school board organised a “flame purification” ceremony, destroying copies of some 30 children’s books that contained “obsolete and inappropriate” representations of indigenous people.
Among the offending books were Tintin in America, which uses the offensive term “redskins”, and Asterix Conquers America, which features an excessively sexy Native American woman – promoting “an image of native women as easy women,” ceremony supervisor Suzy Kies observed.
The fact that both these books are mordantly satirical about the exploitation of Native Americans by white colonisers was not enough to save them. The ashes of the books were used as compost to plant a tree: “We buried the ashes of racism, discrimination and stereotypes in the hope of growing up in an inclusive country where everyone can live in prosperity and security,” according to a video the school board made for students.
One should not assume, however, that only those who would self-identify as woke are currently being seized by the urge to incinerate books. Last month it was reported that, following complaints by parents that their children had access to fiction dealing with LGBTQ+ issues, the Spotsylvania County School Board in Virginia voted to remove “sexually explicit” works from school libraries.
“I think we should throw those books in a fire,” Board member Rabih Abuismail said, while his colleague Kirk Twigg said it was important that residents should “see the books before we burn them so we can identify within our community that we are eradicating this bad stuff”.

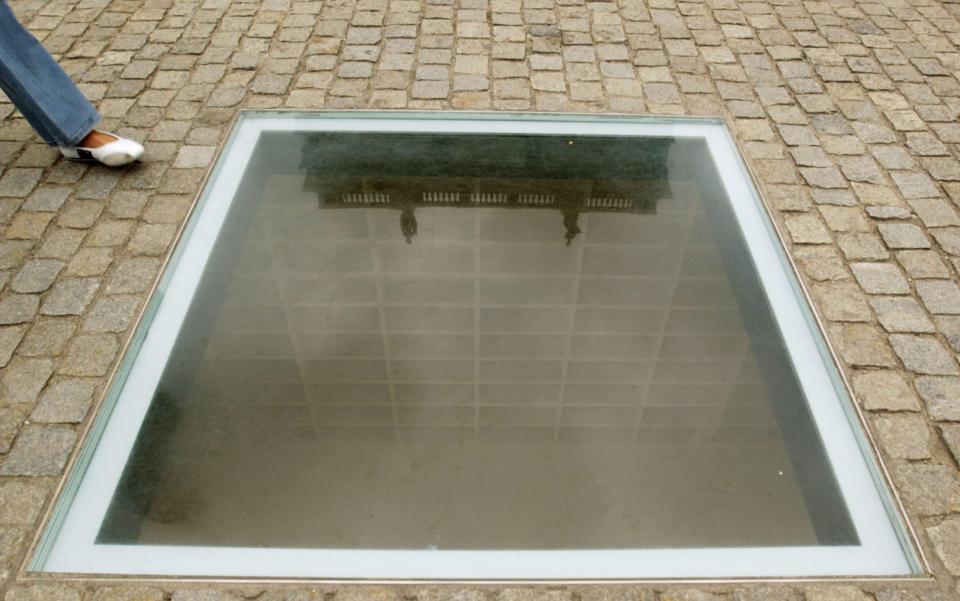
It is an indication of how easily extremism is taking hold in Western society that public officials on both sides of the political divide can advocate the burning of books, a practice indelibly associated with Nazism and other tyrannical regimes. These people have clearly never been to the profoundly moving Empty Library monument in Berlin – or perhaps they have, but decided that the Nazis had the right idea but simply chose the wrong books. If only Hitler had thought to burn Tintin in America!
Any act of book burning is freighted with the weight of history. Earlier this year the novelist Jeanette Winterson posted a photo on social media of a bonfire she had made of some new editions of her own books: “Absolutely hated the cosy little domestic blurbs on my new covers. Turned me into wimmins fiction of the worst kind! … So I set them on fire,” she explained. (What you could call a bonfire of the inanities, I suppose).
Many people were made queasy by this daft publicity stunt: the sight of books curling up as they are licked by flames has too many heinous associations for it to be easily laughed off. Book burning has been so integral a part of repression and despotism throughout history that the sight of anybody setting any book alight evokes for many of us the same visceral disgust as a swastika tattoo.

The earliest recorded example of book burning is that of King Jehoiakim, who was displeased by the predictions made in a scroll written by the prophet Jeremiah and “cast it into the fire” before ordering the author’s arrest (as recounted in the Old Testament). But the first ruler to have tried to consolidate his position through extensive book burning is said to have been Emperor Qin Shi Huang (259-210 BC) of China.
The ruler of the state of Qin, he conquered the other six Chinese states and in 213 BC ruled that all works of history from outside Qin should be burnt – thus erasing from recorded history the period when he was not supreme ruler of all China. Books on medicine, agriculture and astrology could be preserved, but philosophical books that did not conform to his ideas were also incinerated, especially the works of Confucius. Many of these were later reconstructed by scholars who had learned them by heart, although the emperor allegedly did his best to prevent this by having 460 Confucian scholars buried alive in 212.
Although the extent of Emperor Qin’s tyranny may have been exaggerated by grudge-bearing historians, there are many examples of book burning by a colonising power as a means of extirpating a nation’s history. When the Romans sacked Carthage at the conclusion of the Punic Wars they burned its records and histories, and what we now know of Carthage is drawn largely from the work of Roman historians such as Livy, written with an eye to pleasing mercurial Roman emperors.
The same thing happened when the Spaniards conquered the Aztec Empire, with a huge conflagration of Aztec books at Texcoco in 1530; it is possible that the colonisers thought the pictograms and hieroglyphs used in Aztec script were dangerous pagan magical symbols, but equally likely that they wanted to erase the indigenous culture the more easily to impose their own.
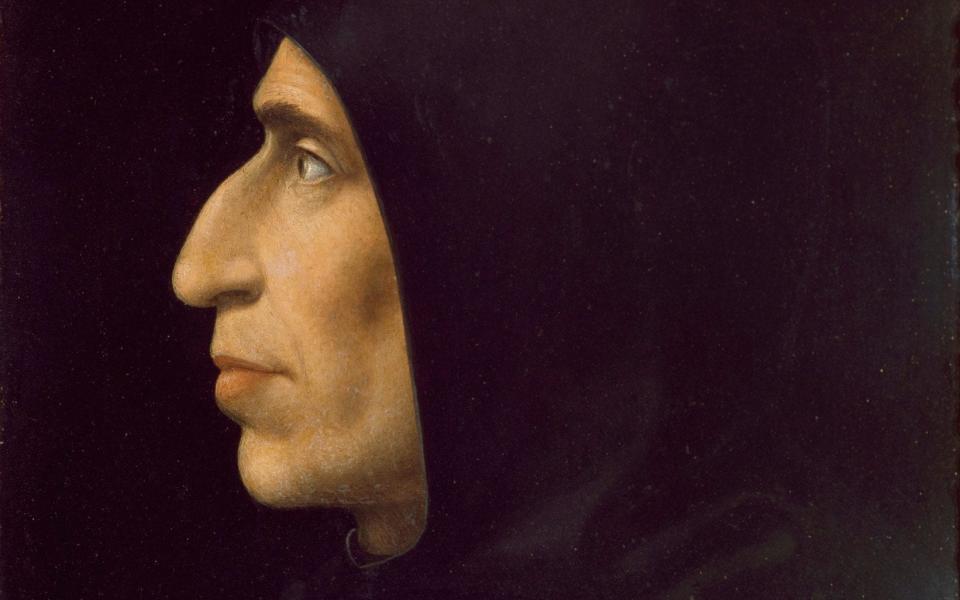

Book burning is not just a method by which a regime consolidates power, however; it has also been carried out by individuals on moral grounds. One of the most famous of all book-burners was the Italian priest Savonarola, who organised the famous “Bonfire of the Vanities” of February 7 1497.
His supporters – who proudly adopted the insulting nickname of Piagnoni or “Weepers” hurled at them by the people of Florence – pillaged hundreds of items denoting luxury, including supposedly lewd books by Ovid, Dante, Petrarch and Boccaccio: one feels that Savonarola would have been very much at home on the Spotsylvania County School Board. His fanatical moralising was not in tune with the times, however, and in 1498 he was burned to death on the site where his Bonfire had been held.
The burning of books on political and religious grounds was a constant occurrence for centuries after the invention of the printing press. Those who worked for the Inquisition spent much of their time incinerating books, especially after Pope Paul IV compiled his Index of Forbidden Books in 1559.
In Britain the Bishop of London, Cuthbert Tunstall, outraged at the idea of ordinary people being able to read the Bible rather than need it explained to them by clerics, bought up every copy he could find of the first English translation of the Bible, by William Tyndale. In 1526 he burnt 6,000 copies on the steps of St Paul’s Cathedral. There wasn’t much of the Inquisition’s ruthless efficiency in Tunstall’s make-up: it didn’t seem to occur to him that the more copies he bought, the more money Tyndale made and the more he could print.

Bishops have often led the way with British book burning: in 1599 the Archbishop of Canterbury and the Bishop of London prohibited the publication of various satirical works, and had several of them burned at Stationers’ Hall in the so-called “Bishops’ Bonfire”. Later on, in a more civilised era, the Bishop of Wakefield, Walsham How, had to content himself with publicly announcing that he had thrown his copy of Thomas Hardy’s Jude The Obscure (1895) into his own fireplace, because of its “insolence and indecency”.
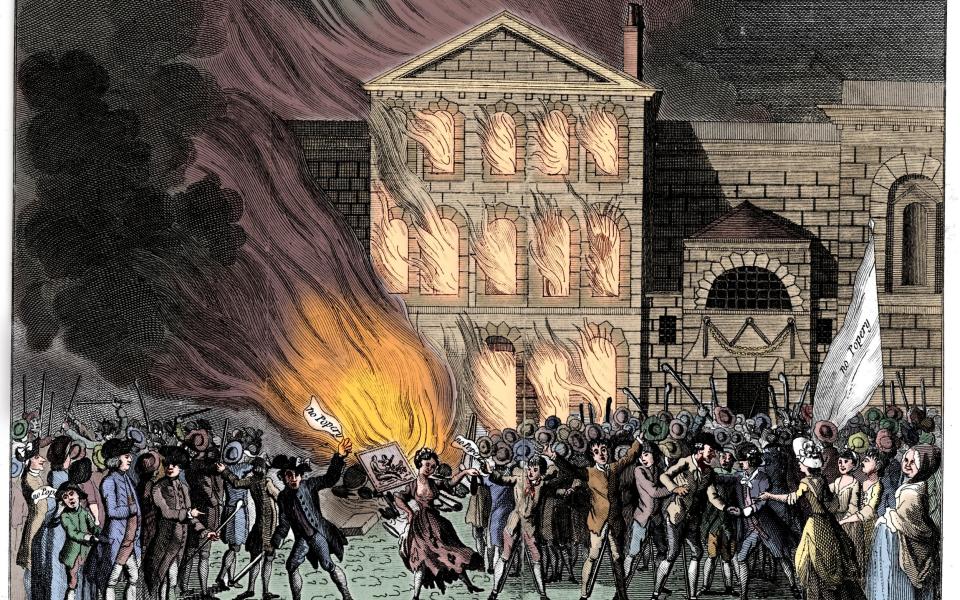
Book burning has not just been the preserve of governments and clerics, however: rampaging mobs have often gone in for it too. During the Peasants’ Revolt of 1381, the townspeople shouted “Away with the learning of clerks [ie. scholars], away with it!” as they ransacked Cambridge University and burned books and papers. The anti-Catholic Gordon Riots of 1780 saw a mob burn down the house of Lord Mansfield, the Lord Chief Justice, including his library – it is said that they were particularly incensed when they saw his extensive collection of books by Alexander Pope, and mistook them for works by the Pontiff.
On the other hand, mobs could collectively turn against book burning. In the 18th Century it was common for seditious works to be burned by the public hangman; but when this was attempted with a pamphlet by the reformer John Wilkes in 1763, a mob of 500 attacked the hangman and rescued the work, before rioting.
The sad truth is that book burning seems to have been instigated, or at least relished, by intelligent people and even scholars more often than by illiterate mobs. In 1683 the convocation of Oxford University voted to burn the works of John Milton, and one eyewitness reported that the academics watching the spectacle of the combusting books were positively jaunty: “scholars of all degrees and qualities surrounding the fire, gave several hums whilst they were burning.”
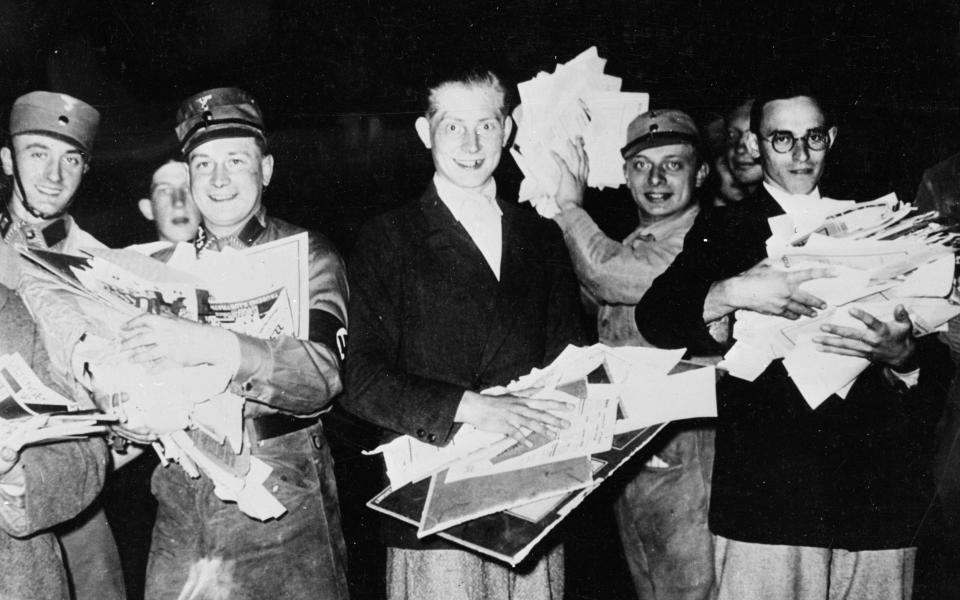

In the preface to his fascinating anthology On The Burning Of Books (2016), the former Education Secretary Kenneth Baker observes that for the most part “those who inspired or organised the destruction of books were not louts, looters or thugs, but well-educated people – often scholars who would have described themselves as civilised, just like the German professors who instructed their students to follow Goebbels’s order to burn certain ‘un-German’ books.”
Thus, intellectual respectability was conferred on the great book burning that took place on the Opernplatz in Berlin on May 10 1933, only weeks after Hitler came to power. This was only the start of a systematic programme of destruction for books written by Jews, Communists and so on: by 1941 George Orwell was able to declare that “the most characteristic activity of the Nazis is burning books”. One estimate puts the number of “degenerate” books burned by the Nazis at 18,000.
Of course, book burning was no less prevalent in the totalitarian Communist regimes of China and the USSR. Because Stalin took literature so seriously as a means of propaganda and kept Russian writers under close surveillance, many of them took to burning their books while they were still in manuscript form, in case they were seized and used in evidence against them. Anna Akhmatova would burn her poems almost as soon as she had finished composing them; Mikhail Bulgakov observed that “the stove [is] my favourite editor”.
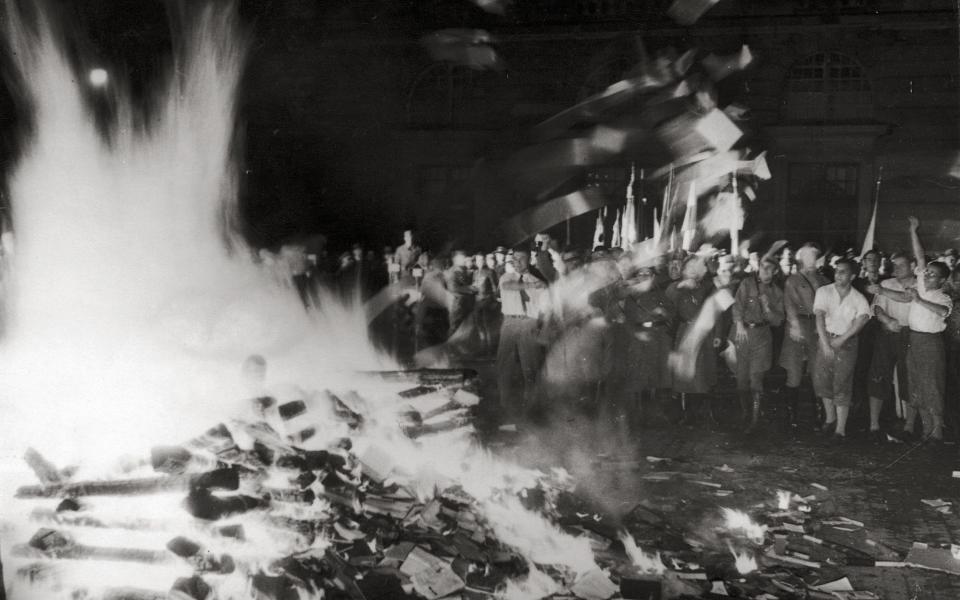
The burning of books on grounds of heresy continued into the 20th Century, meanwhile, with a Muslim organisation arranging a public burning of HG Wells’s A Short History Of The World in 1938, because of its criticisms of the Prophet Muhammad. The same thing happened on a much larger scale with the publication of Salman Rushdie’s novel The Satanic Verses in 1988, with book burnings organised in Bolton and Bradford.
Rushdie had a brief insight into the book-burner mentality some years later when he was approached at a book reading by a young man, who “confessed that in 1989 he was the leader of the Islamic Society in Coventry and had been the ‘West Midlands convener’ of demonstrations against The Satanic Verses. ‘But it’s all right,’ he burst out in embarrassment, ‘I’m an atheist now … And then recently I read your book and I couldn’t see what all the fuss was about!’”
One has to wonder how thoroughly people read the books they are happy to burn. Has Terry Jones – the American Baptist preacher who publicly burned a copy of the Qur’an in 2011 - read every word of it? In 2013 he was arrested before he could carry out a plan to burn 3,000 copies of the Qur’an - thankfully so, as the 2011 incident sparked a riot in Afghanistan that left seven UN workers dead, among others.
If you happen to see a book on fire these days, however, the probability is that it was written by J K Rowling - a huge number of people have immolated Harry Potter novels, for a wide variety of reasons. The practice kicked off in New Mexico in 2001, when preacher Jack Brock organised a bonfire of the Potters – “Behind that innocent face is the power of satanic darkness. Harry Potter is the devil and he is destroying people” – and as recently as 2019 there were reports of Catholic priests burning the Potter canon in Poland.
@elmcdo #fyp #harrypotter #books #lgbt #lesbian #gay #bi #trans #translivesmatter ♬ A Moment Apart - ODESZA - Hannah Stater
Burning Potter books because they encourage witchcraft and Satanism seems almost rational, however, compared with the recent craze for burning them because of the author’s political and moral stances. In 2017 ex-fans posted pictures of their Potter libraries aflame after Rowling tweeted criticisms of Donald Trump. And last year the Irish popsters Jedward told their fans that Rowling’s books would make a good firewood substitute, on account of her supposed transphobia; several videos of smouldering Potter novels were uploaded to TikTok.
It’s a depressing development. We all know the truth of Heinrich Heine’s observation that “those who burn books will in the end burn people”, but book burning is disgusting not just because it is a gateway to greater acts of inhumanity. It is an expression of philistinism and intolerance – a negation of the idea that the way to deal with a book you don’t like is to challenge its arguments using reason and logic. Book burning is a substitute for the effort of thinking.
It is no wonder that some of the most vivid dystopias in fiction feature the burning of books – see the “memory hole” in Orwell’s Nineteen Eighty-Four, or the futuristic world in which professional “firemen” destroy books on sight that is depicted in Ray Bradbury’s Fahrenheit 451 (named after the temperature at which paper catches fire).
You have to be very sure of your moral ground if you choose to burn a book; and in our current cultural climate, that’s exactly what many people are – often without much justification. To destroy your ideological enemy’s book is seen as more righteous than sullying yourself by reading it. But before this becomes standard practice among North American school boards, might more of their members be persuaded to have a think about how many book-burners have actually been on the right side of history?

