The mysteries of faith: why Mary, Queen of Scots still haunts our imagination
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.
- Oops!Something went wrong.Please try again later.
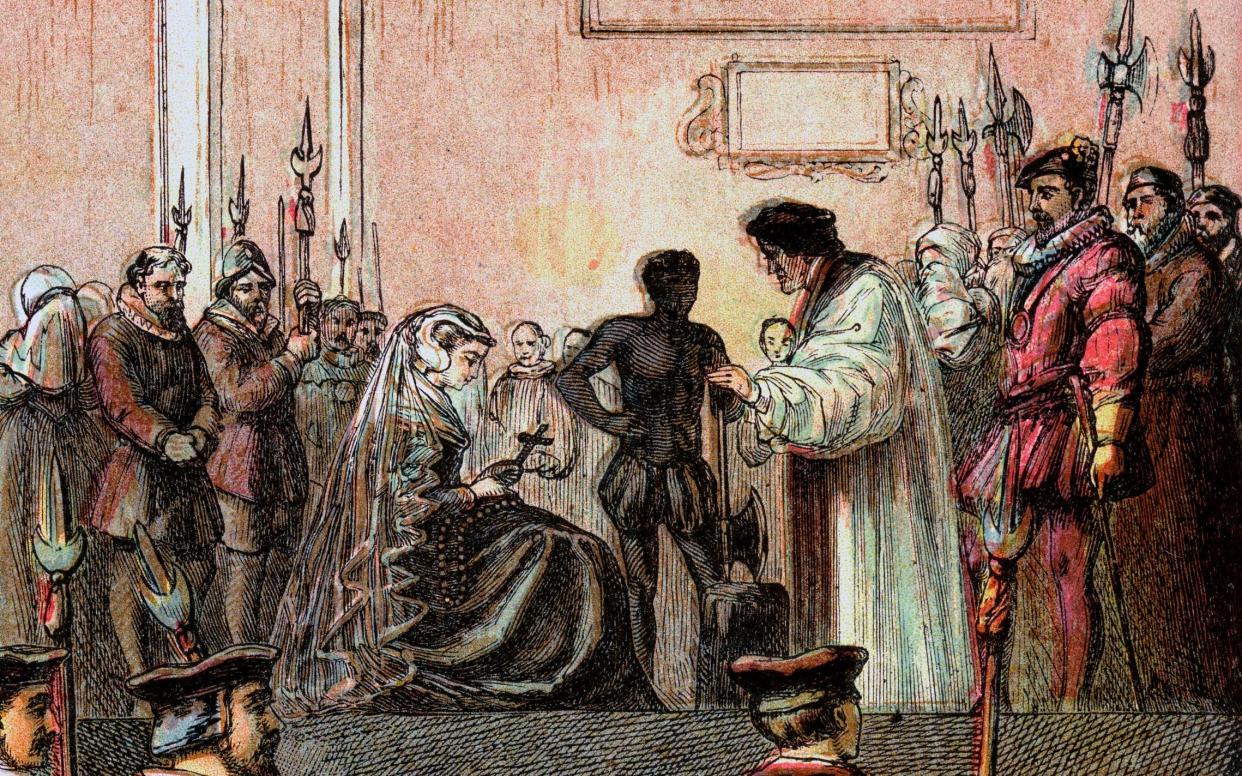
The execution of Mary, Queen of Scots, which took place in the hall of Fotheringhay Castle on February 8 1587, was a nasty business. The queen, who had been found guilty of plotting from jail to have her cousin Elizabeth I murdered, was beheaded, rather inexpertly, with an axe. It took the executioner two swings and a bit of sawing to get her head off; when he had finished his butchery, and tried to raise his prize up by the hair, Mary’s wig came off and her head fell on the floor.
The queen’s servants, who had been allowed to watch her die, were sobbing. Her pet dog was going berserk. Her death enraged her son, James VI of Scotland, and Elizabeth, who had ordered it and tried to lay the blame on those who had delivered the warrant. All in all, this was a tragic farce. But it made a secular martyr of Mary, whose unfortunate life and grotesque death have combined to ensure she is still the object of public fascination today.
Last weekend, one of the two rosaries Mary carried at her execution was stolen from Arundel Castle. It was not the only piece to be taken in the raid. Arundel is the ancestral home of the Howards, Dukes of Norfolk, and it heaves with fine art, plate, jewellery and historical artefacts, plenty of which is on public display. The estimated value of the pieces that were stolen from a single display case is around £1 million.
But of all the missing haul, Mary’s rosary is charged with a special resonance. She left the string of gold beads to the Howards, who were then England’s leading Catholic family, and her most important aristocratic allies. It has remained in the family collection ever since. Its loss is keenly felt, for as a spokesman for the castle’s trustees put it, the rosary has “little intrinsic value as metal, but as a piece of the Howard family history and the nation’s heritage it is irreplaceable”.
It is strange, is it not, how attached we are to artefacts once owned by the rich and famous? Mary, Queen of Scots, a Catholic, died amid the 16th-century Reformation, which was supposed to sweep out of England the rites and superstitions of the old, medieval faith. Among the old ways to be abandoned was the popular attachment to relics.
Throughout the Middle Ages, small trinkets said to have been connected with saints were collected, traded and treasured. Some of these had magnificent lineage: Henry III substantially rebuilt Westminster Abbey in the 13th century to house a vial of Christ’s blood; Chaucer’s pilgrims in The Canterbury Tales were on the road because they were off to visit the shrine containing St Thomas Becket’s remains at Canterbury Cathedral. Others were mean and lowly: Chaucer’s Pardoner jokes about selling pig bones to gullible punters who want to believe that they’re bits of long-dead saints.
Thanks to the Reformation, most people in Britain today would put no more store by a wizened saint’s finger than they would a KitKat. Yet when it comes to the relics of monarchs and celebrities, we are still prone to go cuckoo. Witness, for example, the excitement generated last week by another (supposed) scaffold artefact: Anne Boleyn’s prayer-book, currently displayed at Hever Castle. A bright young scholar named Kate McCaffrey identified the names of Boleyn associates which had been written in the book’s margins over the years, suggesting that it had been passed around the queen’s circle after she was beheaded in 1536. That alone does not prove the book was in Anne’s hands when she died. But the whiff that it might is enough to set the pulse racing.
This is not history as rational enterprise, but as an emotional pursuit in which there is as much value on empathy as deduction. And this is not a criticism. Because I think we’re better off admitting that our hearts, not only our heads, draw us to study the past. All the evidence suggests that this is so. Take, for example, sports memorabilia. Twenty years ago one of Pele’s 1970s football shirts was auctioned in London for £150,000. Last year a pair of Nike Air Jordan 1s, trainers worn and signed by the great basketball player during his pomp in 1985, sold at auction for $560,000.
History is no different. There is something deeply compelling about knowing (or merely believing) that an item has a chain of provenance back to an important person or event. I remember some years ago when a rather odd collector of Nazi memorabilia handed me a little statuette and told me with a smirk that it was Heinrich Himmler’s paperweight. I was as physically revolted by this dumb lump of metal as I might have been thrilled if he had passed me poor Mary, Queen of Scots’ now-missing rosary. Is that logical? No. But human beings are not logical creatures. I do hope the Howards recover their beads, and soon.
Dan Jones’ next book is Powers & Thrones: A New History of the Middle Ages

