What Does Folliculitis Decalvans Look Like?
Medically reviewed by Leah Ansell, MD
Folliculitis delcavans is a rare chronic ailment that often affects the scalp. It is an inflammatory problem that destroys hair follicles, leaving scars that result in alopecia (hair loss).
This problem usually appears as red, swollen, and scaly patches on your scalp. Symptoms can range from mild to extreme pain.
There is no cure, but symptoms can be reduced. Treatment varies by person and often includes oral antibiotics and topical treatments that control symptoms and prevent further hair loss. It is not possible to restore lost patches of hair.
This article describes folliculitis delcavans symptoms, causes, treatments, and outlook.
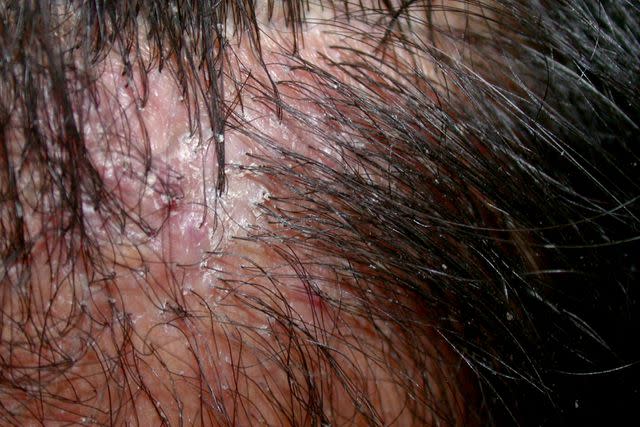
Reproduced with permission from © DermNet dermnetnz.org 2023.
Symptoms of Folliculitis Decalvans
Symptoms of folliculitis decalvans can differ by individual. Some people have this problem without pain.
Symptoms are usually confined to the scalp. Rarely, the problem can affect other areas of hair such as the beard area, pubic area, armpits, and legs.
Common symptoms of folliculitis decalvans include the following:
Inflammation (swelling) and redness
Pustules around hair follicles
Scaly areas, scabs, or crusts
Pus-filled spots
Itchiness
Pain
Scalp inflammation
Bleeding
Yellow pustular discharge
Growth of several hairs from the same hair follicle, creating tufts that resemble the bristles of a toothbrush
Bald patches at later stages
Scarring
Hair loss
What Causes Folliculitis Decalvans?
The cause of folliculitis decalvans is unknown. Research indicates that the problem may occur due to a reaction to a bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is often found when affected areas are swabbed.
For most people, this doesn't cause a problem. The bacterium occurs naturally on your skin.
Folliculitis decalvans may occur due to a hypersensitivity reaction to "superantigens." Superantigens are a class of toxins produced by bacteria and viruses that trigger an intense response in people who have a compromised or defective immune system. This response may be hereditary because folliculitis decalvans is known to occur more frequently among members of the same family.
Despite its appearance, folliculitis decalvans is not skin cancer. Though it is linked with a specific bacterium and often improves with antibiotics, the problem is not considered contagious.
Common Triggers for Folliculitis Decalvans
Folliculitis may be triggered when the hair follicle becomes damaged or blocked. This can occur when the follicle rubs against clothing or shaving, leaving the damaged hair follicle susceptible to infection.
The cause of folliculitis decalvans is not understood. The following circumstances have been identified as possible triggers, though they have not been proved as causes:
Abnormal immune response to Staphylococcus aureus
Males, usually in their 40s and 50s
Family history of the condition
Treatment for Folliculitis Decalvans
Treatment for folliculitis decalvans varies by individual in its effectiveness. The goal of treatment is to encourage disease remission (no symptoms). Most therapies can be administered at home, though some may require outpatient visits to a healthcare provider.
For most people, treatment involves a combination of topical solutions and/or oral antibiotics. It is a lengthy process because this condition can return after a course of successful therapy and trigger a recurrence of symptoms.
There is no specific treatment approved for folliculitis decalvans, so there is a wide range of approaches. The following therapies are the most common:
Antibiotics
Systemic antibiotics are regarded as the first-line treatment for folliculitis decalvans because they can eradicate Staphylococcus aureus. Though these treatments can be effective, symptoms often relapse after the interruption of therapy. Antibiotic resistance is also a concern with long-term use.
The following antibiotics are the most common:
Oral tetracyclines:
Minocin, Solodyn, others (minocycline)
Vibramycin-D, Efracea (doxycycline)
Adoxa, Declomycin, others (tetracycline)
Tetralysal (lymecycline)
Rifadin, Rimactane (rifampicin) with or without Cleocin (clindamycin) (oral)
First-generation cephalosporins:
Keflex (cephalexin oral)
Velosef (cephradine oral)
Duricef (cefadroxil oral)
Ancef (cefazolin) (intravenous and intramuscular)
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can help manage symptoms of itching, pain, and inflammation. They are also effective in treating the scar tissue common with folliculitis decalvans.
These treatments work by suppressing your immune system's reaction to toxins. Corticosteroids are typically taken for short periods of time to avoid thinning and bruising of the treated area. They can be administered in the following ways:
Topical products (creams, gels, and ointments applied over the surface of the affected area)
Intralesional injection (injection into a lesion)
Systemic treatments (administered orally or intravenously for treatment throughout your body)
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are applied directly to your skin to ensure that the medication is administered where it is needed. These products may be appropriate when you want to avoid the side effects of systemic medications or boost the results of oral therapy.
Topical treatments come in a wide range of over-the-counter and prescription medications. They are available in formulas that include gels, ointments, lotions, creams, foams, and sprays. Some of the most common topical treatments for folliculitis decalvans include:
Topical antibiotics:
Bactroban, Centany (mupirocin)
Fucidin (fusidic acid) with or without zinc sulfate
Topical corticosteroids:
Topical antiseptics:
Hypochlorite
Betamethasone dipropionate
Topical retinoids:
Retin-A (tretinoin)
Tazorac (tazarotene)
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) directs natural or artificial light to the site of the folliculitis decalvans. Studies show this treatment can succeed in stabilizing the condition and decreasing symptoms in some people. Tolerance of this treatment may be an issue for some.
Shampoos for Folliculitis Decalvans
There is a wide range of over-the-counter and prescription shampoos available. Consult your healthcare provider to determine the product that might work best for you.
Antiseptic shampoos or those containing tar can help eradicate the bacterium linked with the condition. These products typically supplement systemic or topical therapy.
Outlook for Folliculitis Decalvans
The outlook for folliculitis decalvans is generally favorable. This condition often responds well to treatment. Results can usually deliver a noticeable cosmetic improvement.
However, folliculitis may return or spread to other body areas even if it is resolved at one site. In some people, the disease may progress slowly over time and continue to flare for months or years.
Though treatments may improve symptoms, dealing with a chronic condition that affects your appearance can be challenging. It can have a negative impact on your quality of life for the following reasons:
Severe scarring may result in permanent hair loss in the affected sites.
Regrowth of the hair lost to folliculitis decalvans is rarely possible.
The side effects of long-term treatments can affect the way you feel.
For many people, folliculitis decalvans can affect their quality of life.
Hair transplantation to correct bald patches can't be attempted until the condition has been inactive for several years without treatment. This ensures that the problem does not recur and damage the newly transplanted hair.
If you're feeling overwhelmed by folliculitis decalvans, consider speaking to your healthcare provider or seeking mental health counseling to help you cope with your feelings.
Summary
Folliculitis delcavans is a rare ailment that causes red, swollen patches on your scalp. The patches destroy your hair follicles, causing scars and permanent hair loss at the affected sites.
While there is no known cause, the problem is linked to a bad response to Staphylococcus A. bacteria. It is believed that the bacteria trigger an extreme immune response that causes symptoms.
Treatments can reduce symptoms and slow the damage to hair follicles. The nature and chronic course of this problem can also have a negative impact on those who have it. Enduring long-term treatment only to have the problem recur can be difficult. This can also have an impact on your self-image and affect your quality of life.
Working with your healthcare provider and a counselor can help you manage the mind and body aspects of this problem. Despite its long course, the outlook is good for most cases.

