Cthulhu’s evil overlord: why the fantasy world turned on HP Lovecraft

Is it time to cancel Cthulhu? Horror writer HP Lovecraft and his famous tentacled creation are having a moment in the spotlight, with Nicholas Cage’s bug-eyed adaptation of The Colour Out of Space released in cinemas earlier this year, and the Sky Atlantic series Lovecraft Country coming to Sky Atlantic on Monday.
But even as the cult of Lovecraft goes viral, questions are being asked about the author’s racism, homophobia and anti-semitism. (Thus far, his terror of seafood has escaped the inevitable grilling.)
“I wanted to address some of the issues I’ve got with HPL – his atheism, his misanthropy, his racism, his misogyny,” said Richard Stanley, director of Colour Out of Space, recently. “All these things needed to be checked and addressed one way or another.”
Why Stanley would have an issue with Lovecraft’s atheism is unclear. Would he rather he were a Bible-thumper? Still, others have gone further in their criticisms. The horror writer Joe Hill has formally distanced himself from the doyen of existential horror, who passed away in impoverished obscurity in March 1937. Hill’s bestselling graphic novel series Locke and Key is set in a town called “Lovecraft”, obviously named in honour of HPL. But when he adapted the saga for Netflix, he instead named the town for another writer, Richard Matheson.
Matheson, author of I Am Legend, The Shrinking Man and What Dreams May Come, isn’t as iconic as Lovecraft. Nor was he a foaming-at-the-chops xenophobe.
“I suggested changing the town to Matheson, Massachusetts,” explained Hill, who is the son of Stephen King. “I’ve learned too much about Lovecraft in the time since I wrote those first issues to feel the same way about him. And the show seemed like a good opportunity to honour the work of another, different master of dark fantasy.”
Lovecraft is considered the most influential horror writer of the 20th century. He created a new genre of “cosmic horror”. His thesis is that the universe is vast, cold and uncaring. And that humanity is, in this bigger picture, no more significant than algae blooming on a filthy pond.
He also created a pantheon of god-like alien entities, the Great Old Ones. These have, across the decades, caught the imagination. There is tentacled Great Cthulhu hibernating in his underground palace of R’lyeh , scheming Nyarlathotep, bubble-based Yog-Sothoth and more.
It makes little sense to the uninitiated, yet this lore has been drawn on by everyone from Stephen King (The Stand’s big baddie, Randall Flagg, is a reincarnation of Nyarlathotep) to Ridley Scott, whose Alien had unmistakeable Lovecraftian overtones. You can even buy teddy bear “plush” Cthulhus. One stares down at me from a shelf as I write this.
Lovecraft-mania reached a new level in 2014 with HBO’s True Detective. The Matthew McConaughey-Woody Harrelson two-hander explicitly referenced Lovecraftian entity the King in Yellow and his kingdom of Carcosa (created by Lovecraft forerunner Robert M Price, true, but very much part of the so-called “Cthulhu Mythos”).
So Lovecraft was suddenly box-office material. Around the same time, the Shape of Water director Guillermo del Toro moved heaven and earth to make a $120 million adaptation of Lovecraft’s 1931 novella At the Mountains of Madness, with Tom Cruise as a potential star.

The BBC has been getting in on the eldritch action, too, with its acclaimed podcasts based on Lovecraft’s Case of Charles Dexter Ward and The Whisperer in Darkness. And not only is Lovecraft Country almost here, but Stanley has already announced a sequel to Colour Out of Space – an adaptation of Lovecraft’s rip-roaring romp The Dunwich Horror.
All of this new attention, however, has brought fresh scrutiny to Lovecraft’s less savoury qualities. Usually there is room for nuance when discussing a historical author and their unpleasant views. We tell ourselves they were “of their time”; that they were expressing commonly-held opinions, and that to condemn them is to condemn an entire generation.
The trouble with Lovecraft is that his racism has an over-the-top, almost hysterical timbre. If the subject matter wasn’t so serious, his terror of people of ethnicities other than his own white, Anglo-Saxon background would have comedic overtones. This, after all, is the writer, who declared of Hitler: “By God, I like the boy!” His extreme views feel like something from a Little Britain sketch, rather his sleepy home-town of 1920s Providence.
However, his racism wasn’t a background detail. It was often an essential component of his work. Consider arguably his greatest story, The Shadow Over Innsmouth, which concludes with the narrator discovering that he shares the tainted bloodline of a race of foul immigrants from the South Pacific.

Herbert West: Reanimator, a much-loved tale from 1922, meanwhile, described a black character as “a loathsome, gorilla-like thing, with abnormally long arms which I could not help calling forelegs, and a face that conjured up thoughts of unspeakable Congo secrets and tom-tom poundings under an eerie moon”.
Lovecraft was actually briefly married to a Jewish woman, Sonia Greene, and lived for a year in multicultural Brooklyn. It was not to his liking, as he vented in his 1925 story, The Horror at Red Hook. There, he described the migrant communities as “hordes of prowlers” with “sin-spitted faces . . . [who] mix their venom and perpetrate obscene terrors.” Lovecraft also once wrote a poem called On the Creation of N------. So no, perhaps it isn’t all that funny after all.
The question faced by the modern lover of all things Lovecraftian, then, is how to process their hero’s virulence. The World Fantasy Award has, after a fashion already, “cancelled” HPL. Until 2016, award winners received a trophy bearing the likeness of Lovecraft. His image was removed that year after a campaign by the writer Daniel José Older.
“If fantasy as a genre truly wants to embrace all of its fans, and I believe it does, we can't keep lionising a man who used literature as a weapon against entire races,” Older said. “Writers of colour have always had to struggle with the question of how to love a genre that seems so intent on proving it doesn’t love us back. We raised our voices collectively, en masse, and the World Fantasy folks heard us. Today, fantasy is a better, more inclusive, and stronger genre because of it.”

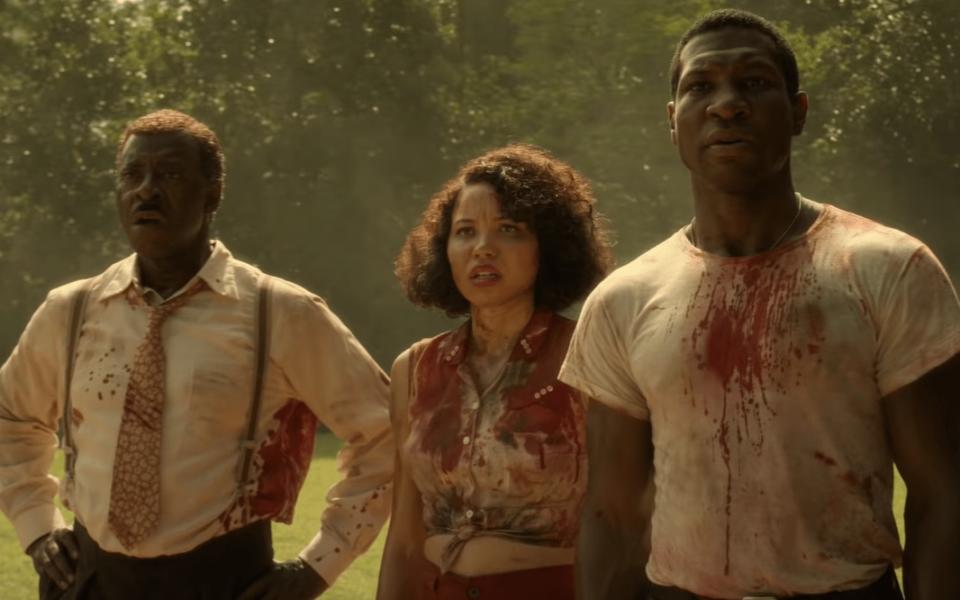
Then there are the authors who have tried to interrogate his views with works of their own. The best known example is Matt Rudd’s Lovecraft Country (2016), on which the Jordan Peele-JJ Abrams adaptation is based, in which a group of African-Americans are plunged into a struggle against nefarious forces inspired loosely – very loosely, some readers have pointed out – by the Cthulhu Mythos.
The twist is that these cosmic monstrosities pale compare to the evils of institutionalised racism, which, in the 1950s milieu, poses a far greater threat to our heroes in their day-to-day lives. “I wanted to take some of my favourite science fiction, fantasy, and horror tropes and see how those stories changed if you put a black character at the centre,” Rudd explained.
“Take some people who might love science fiction themselves, but felt excluded from it like they were excluded from every other part of culture in the 1950s, and make them the stars. That was the core idea. Lovecraft came into it through the back door, because I wanted a thematic bridge between the paranormal horrors and the more mundane horrors of life in the 1950s.
“Lovecraft was kind of perfect for that, because he was both an iconic horror writer and an outspoken white supremacist.”

Every Lovecraft fan must deal with the issue in their own way. Surprisingly, the most vociferous calls for Lovecraft to be shunned have come from the video game industry The sector has witnessed a proliferation of Lovecraft games across the past decade. Because HPL’s stories were written so long ago, many have passed out of copyright, so that you can use Cthulhu without needing to seek permission or pay licensing.
“HP Lovecraft was a racist,” wrote Sam Greer in Eurogamer in 2018. “And before you go making an argument for separating the art from the artist, let’s be clear on another point: so are his stories. They encompass other problematic elements too, of course – misogyny, homophobia.
“Right down to their core, right down to the very themes that recur throughout his works, you’ll find the hateful perspective he had of the world: the ignorance of someone who viewed anything unlike himself with revulsion. While he drew inspiration from works predating him, what Lovecraft gave to the genre of cosmic horror was his hate.”
“There are good reasons to dump Lovecraft beyond over-saturation of the source material. Lovecraft was a racist who terrified of women,” agreed Matthew Gault, reviewing the Call of Cthulhu video game in Vice two years ago. “Call of Cthulhu is not an overtly racist or misogynist game, but the problem with Lovecraft is that the latent themes of xenophobia are inescapable in his work. Many of his stories, including Call of Cthulhu, include thinly veiled references to cultures and people Lovecraft found alien and objectionable.”
Others take a different perspective. ST Joshi, the greatest living Lovecraft scholar, argues that the author has been unfairly vilified. He names Roald Dahl, TS Eliot, Jack London and Raymond Chandler as other influential writers of the 20th century whose work contains examples of racial prejudice. Why is nobody clamouring to “cancel” them? Agatha Christie’s And Then They Were None was originally published under what would today rate as a deeply offensive title. It didn’t put the BBC off adapting the novel in 2015.
“I don’t believe that anybody can make a blanket assertion about whether one should consume a piece of art or literature,” says Chad Pfeifer, co-host of the HP Lovecraft Literary Podcast. “With Lovecraft, we highlight the personal attitudes of his and talk about how it reflects on his stories. For some readers, it’s enough to turn them off – and that’s fine. We don’t make any excuses for this person. But he created a lot of neat stuff that many other writers have then developed, and those are the things we’re interested in.
“But we analyse all of the writers we cover by looking at bits of author biography, the social structures at the time the story was written, and casual attitudes that may be offensive in the modern day, so we’re talking about this stuff day in and day out with all sorts of artists and a diverse audience. Looking at how perceptions of a story may change depending on the audience is a great way into discussion.”
“In some circles there is a backlash against Lovecraft. It’s absolutely true that he was a racist,” says Sean Branney of the Los Angeles-based HP Lovecraft Historical Society, which, among other projects, has produced excellent movie adaptations of Lovecraft’s The Call of Cthulhu and The Whisperer in Darkness.

“It was a prevailing attitude of his time, but nevertheless he embraced it in a manner which can rightly be appalling to modern sensibilities. Some people may choose not to read him because he held those views. I would suggest, though, that Lovecraft’s contributions to the field of weird literature are ultimately of far greater significance than the fact that he held some odious personal opinions. Ultimately, we as readers make such judgements all the time.”
He cites Shakespeare and Thomas Jefferson as examples of historical figures who importance is accepted, notwithstanding their questionable views (for instance, the anti-semitic caricature Shylock in Merchant of Venice).
“We’ve collectively arrived at the notion that in spite of some of Shakespeare’s disturbing world views, his literary contributions outweigh those,” says Branney. “Thomas Jefferson may have not only been a racist but he actually owned slaves. Ultimately the impact of his political writings are so significant that they too outweigh his social beliefs and actions.
“Lovecraft’s fear of the ‘other’ proved to be a creative fuel for his fiction,” he continues. “And ultimately, his fiction proved to be his legacy to the modern world. Lovecraft’s influence on 20th-century horror fiction and even on popular culture can’t be denied.
“At the HPLHS… we think most folks are able to make a distinction between an author and his or her works and their enduring value.”
And some writers question the dominant view altogether. “For me, Lovecraft’s achievements far outweigh his faults as a man,” says Ramsey Campbell, one of Britain’s most esteemed horror writers and a significant contributor to the Cthulhu Mythos.
“Just now we’re seeing an emphasis on the latter, often at the expense of appreciating the former. I believe balance will eventually be regained, as it has been with Wagner, for instance. I do regret that the concerted outcry about Lovecraft’s racism began after everyone who knew him had died – it would have been useful to have their views on it.
He adds: “I’m struck by Robert Bloch’s comment in his 1993 autobiography – that Lovecraft was ‘a kind, considerate, thoughtful man, generous to a fault with his time and talent… one of the last true gentlemen.’”
Lovecraft Country will be available weekly on Sky Atlantic and Now TV from Monday

