Climbers have turned Mount Everest into a high-altitude garbage dump, but sustainable solutions are within reach

Spring is go time for climbers who hope to summit Mount Everest, Earth’s highest peak above sea level. Hundreds of mountaineers from around the world travel to Asia in April and May, headed for base camps in Nepal and Tibet.
But jagged peaks won’t be the only thing they see. Especially on Everest’s more heavily traversed Nepal side, they’ll find fields of garbage – including cans, bottles, plastic and human and animal excrement.
Each year, more than 60,000 trekkers and climbers visit the Sagarmatha National Park and Buffer Zone, a high-altitude swath of the Khumbu region in northeast Nepal that includes Everest and seven other peaks. Some 400 to 500 climbers attempt to summit Everest every year.
The trash problem first became evident in the 1980s and 1990s, when climbing on the mountain and trekking in Khumbu began to increase. Climber and trekker numbers have further skyrocketed in the past 20 years.
Most coverage of this issue focuses on negative and sensational aspects, such as the frozen bodies of climbers who remain where they died on the mountain because removal operations are risky and expensive.
We are scholars who study geoscience and mountain geography, and one of us (Alton Byers) has lived in Nepal and worked with communities around Everest. We are encouraged to see increased efforts to address Everest’s massive trash problem. In our view, modern technology and international cooperation are key to ending the pileup of waste in this iconic setting.
Pollution from waste
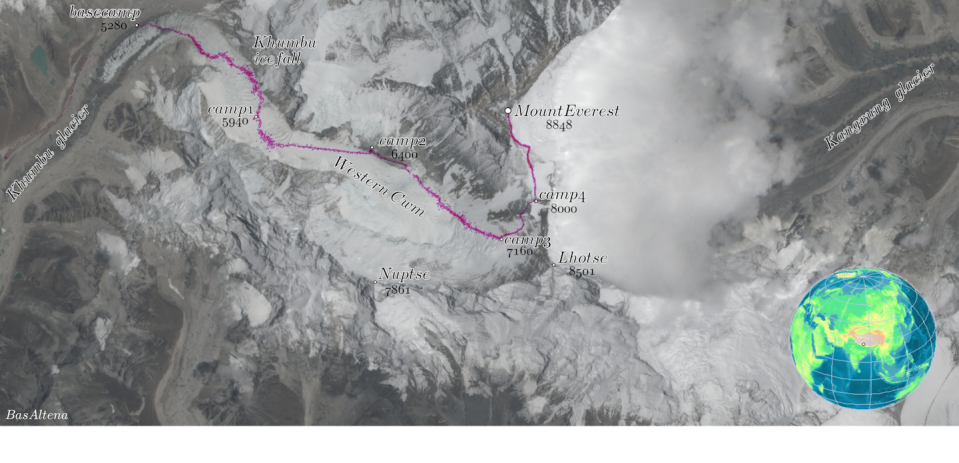
For most visitors to this area of the Himalayas, Everest base camp on the upper reaches of the rapidly receding Khumbu Glacier is the ultimate destination, at an altitude of 17,589 feet (5,364 meters). Formerly a two- to three-week trek from Kathmandu, today the journey is most likely to begin at the Lukla Airport, which sits about 35 miles (60 kilometers) from base camp.
Climbers who aim to summit Everest typically spend up to two months on the mountain, including weeks making short, incremental ascents above base camp and back down again. This enables them to acclimate to the altitude before climbing to higher camps and then to the summit.
Much of the food and equipment headed to Everest also begins its journey at Lukla. Some is shipped to base camp by helicopter, but much of the gear is carried there by yaks, yak/cattle crossbreeds called dzopkio, mules and horses.
Lots of equipment, food and packaging, plus animals and porters, means a lot of garbage. A 2010 study estimated that park tourism generated 4.6 tons of solid waste per day during peak tourist periods in April-May and October-November.
Eventually most of this refuse is dumped into unsightly landfills a short distance from local villages. There it is burned, adding particulates and toxic chemicals to the air. The remaining ash is buried, where it can contaminate groundwater.
At the base camp, microplastics – likely from discarded mountaineering clothing, tents, ropes and boots – have been found in water and snow samples. High levels of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, widely known as “forever chemicals,” have been found on the Khumbu glacier, probably from materials used to waterproof climbing boots, tents and clothing.
These substances could pose health risks for transient climbers, but are a more serious threat for people who live in the nearby settlements of Gorak Shep, Lobuche, Dugla and Pheriche for most of the year. Some of these villagers work at Everest base camp and are exposed there too.
And then there’s sewage. Most septic tanks at the hundreds of lodges located throughout the national park and buffer zone leak, further polluting groundwater. Camp Four, the last site that climbers occupy before they attempt to summit Everest, is covered with garbage and frozen, wind-swept feces.
National parks in developed countries have infrastructure to handle waste management, trash pickup, recycling and wastewater treatment. At Everest base camp, there are just collection barrels under toilets. Each year, some 50,000 pounds (22,000 kilograms) of human waste are brought to landfills several kilometers away.
Solutions for sustainable tourism
Recognizing the scale of this problem, initiatives are in progress to develop solutions.
The Sagarmatha Pollution Control Committee, created by local Sherpa people in 1991, is an Indigenous nonprofit organization that is responsible for monitoring garbage in the permit-required mountains and peaks. The group focuses on litter control and periodic base camp cleanups.
In 2014, the government of Nepal began requiring every mountaineer who climbs above the Everest base camp to bring back 18 pounds (8 kilograms) of solid waste from the mountain or forfeit a US$4,000 deposit. Of course, if you’ve paid $75,000 or more for the trip, losing the deposit may not be much of an incentive. Many people elect to forfeit it.
A nonprofit called Sagarmatha Next, established in 2019, is working to promote sustainable tourism in the Khumbu region, partnering with companies and organizations from around the world. The group has raised awareness by producing art works and souvenirs from trash. It also launched a “Carry Me Back” program that encourages tourists to take two-pound (one-kilogram) bags of solid waste, such as shredded plastic bottles, to the airstrip at Lukla for processing and disposal in Kathmandu.
At the local government’s request, the University of Colorado Boulder developed a sustainable solid waste management plan in 2019 for the national park and buffer zone. The COVID-19 pandemic delayed implementation of the plan, which proposes creating a five-step process: waste segregation, collection, sorting and shredding, transfer to shipment stations and transportation to recycling facilities in Kathmandu.
Another nonprofit initiative, the NeverRest Project, was created during the pandemic to provide environmental solutions for Mount Everest and other fragile ecosystems around the world. NeverRest is working with the Nepal Tourism Board to revolutionize high-altitude waste management using modern technology.
In 2023, the organization presented a concept plan for a sustainable Everest base camp that would install technologies such as portable solar tents to reduce use of fossil fuel; unisex portable urinals with multi-use filters that convert urine into water; incinerator toilets that transform human waste into ash; and modular geodesic dome tents designed for effective heat retention to reduce energy use.
In the 71 years since Sir Edmund Hillary and Sherpa Tenzing Norgay made the first known successful ascent of Mount Everest, this peak has been a setting for daring expeditions, triumphs and tragedies. We hope that the region’s garbage problem soon will fade into history as new approaches and technologies provide solutions for Everest and other remote high-mountain locations around the world.
This article is republished from The Conversation, a nonprofit, independent news organization bringing you facts and trustworthy analysis to help you make sense of our complex world. It was written by: Suzanne OConnell, Wesleyan University and Alton C. Byers, University of Colorado Boulder
Read more:
Alton Byers has lived and worked in Nepal, and has collaborated with communities around Everest to protect and restore ecosystems that have been damaged by trekkers, climbers and the tourism industry. He was lead author of a sustainable solid waste management plan for Sagarmatha National Park and Buffer Zone produced in 2020 by University of Colorado Boulder researchers with support from the National Geographic Society.
Suzanne OConnell does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.

