What Is a Boil (Furuncle)?

miniseries / Getty Images
Medically reviewed by Casey Gallagher, MD
A boil, or furuncle, is a pus-filled skin bump typically caused by an infected hair follicle. Most of the time, the infection is caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, also known as a staph infection.
Boils are common and sometimes go away on their own. However, they can be painful and lead to complications if left untreated.
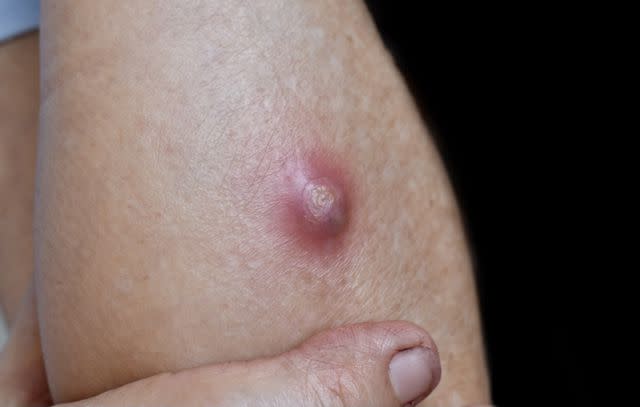
Boil Symptoms
Zay Nyi Nyi / Getty Images
Typically, a boil starts out as a pink or red tender bump on the skin. It might also be itchy. The boil will then develop into a pustule (a pus-filled bump) with a yellow or white center. The skin around it may be red.
Boils grow quickly. As it grows, you will likely experience increased pain. Boils in the ear canal or nose can be especially painful. The pain will improve as the pus drains from the boil. If the boil bursts, the boil will ooze and crust over.
Boils are usually about the size of a pea, but they can be as big as a golf ball. Sometimes they join with other furuncles in a cluster known as a carbuncle.
When you have a boil, you may also feel generally unwell. You may have the following symptoms:
Fever
Fatigue
Muscle aches
Chills
What Causes Boils?
Boils are often caused by folliculitis, an infected hair follicle. This occurs when certain germs get deeper into the skin, often through a break caused by a cut or scrape. It is usually Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) bacteria that cause the infection, but the infection may also be due to other bacteria or fungi on the skin's surface.
Infected hair follicles are especially common in areas like the inner thighs, face, armpits, buttocks, and neck, where shaving, chafing, and clothing can irritate sensitive skin. But a hair follicle anywhere on the body can become infected. When the infection of the hair follicle gets deeper into the follicle and surrounding tissue, a boil can develop.
Risk Factors
Furuncles are common, and anyone can get them. However, the following risk factors may increase your chance of developing recurring boils:
Having diabetes
Being younger than 30 years old
Having obesity
Smoking
Living in a crowded or communal environment, such as a dorm
Not maintaining a nutritionally balanced diet
Having skin conditions like eczema
Having been exposed to S. aureus bacteria
Having iron deficiency anemia
How Are Boils Diagnosed?
If you have a boil, a healthcare provider can typically provide a diagnosis with a physical examination. The provider might be a dermatologist, a doctor who specializes in conditions of the skin, nails, and hair. In some cases, the provider may remove a sample of tissue or pus for testing, but that typically isn’t necessary.
Using visual and physical examinations, they can differentiate between a furuncle and other skin conditions. For example, boils are sometimes confused with warts, acne, or cysts. A healthcare provider can differentiate between the conditions and provide you the proper treatment.
Treatments for Boils
In some cases, boils go away on their own. You can take the following steps at home to encourage the boil to drain and relieve your pain:
Clean the boil regularly.
Apply a warm compress to the boil for 10-15 minutes, three to four times per day.
Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as Advil (ibuprofen), for pain relief.
Keep the affected area covered if it bursts and crusts over.
It can take up to two weeks for a boil to drain on its own. If the boil doesn’t drain on its own, you may need to go to a dermatologist to have it surgically drained. That might be especially true for boils that are large or deep.
Your healthcare provider may also prescribe antibiotics if the infection spreads or doesn’t go away. Multiple antibiotics, including both oral and topical antibiotics, may be required in severe cases.
How to Prevent Boils
Furuncles can’t always be prevented. However, you can try to prevent some boils by regularly washing your hands and taking showers. You should use antibacterial soaps and antiseptic washes.
If you already have a boil, you can prevent other boils from forming by keeping your boil clean. This would include regularly changing the bandage with which you covered the boil. Once you've touched the boil or its bandage, wash your hands. You should also avoid reusing any washcloths or towels that might have touched the boil and instead wash them in hot water.
Complications
You may experience scarring once the boil goes away. But boils don’t usually cause complications. When complications do arise, it may be because the infection has spread or gotten worse.
You may develop a pocket of pus known as an abscess on your skin or other organs, including the brain, spinal cord, and kidneys.
You might also develop an infection in other areas of your body. Infections of the brain, heart, bone, blood, tissue, spinal cord, or skin surface are all possible. Signs of an infection include fever, a severely painful bump that continues to accumulate fluid, and red streaks that come from the boil.
A Quick Review
Boils, also known as furuncles, is a pus-filled bump under the skin usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. At first, the boil is tender to the touch. As the boil grows—which happens quickly—the pain increases. The pain subsides once the pus leaves the boil. Some boils go away on their own. Others will need to be surgically drained by a healthcare provider. If you have a boil that isn’t going away or is particularly big or painful, talk to a healthcare provider like a dermatologist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it OK to pop a furuncle?
It’s best to avoid the temptation to pop a boil yourself. This may push the bacteria deeper into your skin, which could worsen your infection. If your boil doesn’t drain on its own, reach out to a healthcare provider like a dermatologist for help.
Does stress cause boils?
There is some evidence that stress can negatively affect your skin health. Stress and anxiety may affect your immune response in general, making it harder for your body to fight off infection and inflammation. However, boils are usually directly caused by bacterial staph infections. There isn’t enough evidence to suggest that stress itself can cause a boil to develop.
Are boils contagious?
Boils themselves are not contagious. However, the bacteria that typically cause furuncles can spread from person to person through breaks in the skin. To prevent spreading or contracting staph infections, don’t share personal items like razors, towels, or bedding. If you have a staph infection, keep any open wounds covered, and don’t prepare food for others until it clears up.
What's the difference between a boil and a cyst?
A boil is a pus-filled bump on the skin that grows because of an infection in the hair follicle. Meanwhile, a cyst is a pocket of tissue that can be filled with many different substances, including pus, air, water, and dead cells. Cysts can have many causes and can form almost anywhere in the body, including internal organs.
For more Health.com news, make sure to sign up for our newsletter!
Read the original article on Health.com.

