Amoxicillin Rash: Is It Really An Allergic Reaction?
A pharmacist shares her expertise.
Medically reviewed by Erika Prouty, PharmD
Amoxicillin (brand names Amoxil or Moxatag) is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics in the U.S. Antibiotics are medicines that kill or limit the growth of bacteria.
Amoxicillin is derived from penicillin. It's used to treat ear infections, strep throat, and other bacterial infections in the following sites:
Ear, nose, and throat
Skin
Genitals and urinary system
Lower respiratory tract
About 10% of people who take amoxicillin or Augmentin (amoxicillin with clavulanic acid) develop a rash.
Here's how to determine if an amoxicillin rash is a side effect or a true allergy, how to manage it, and when to call a healthcare provider.
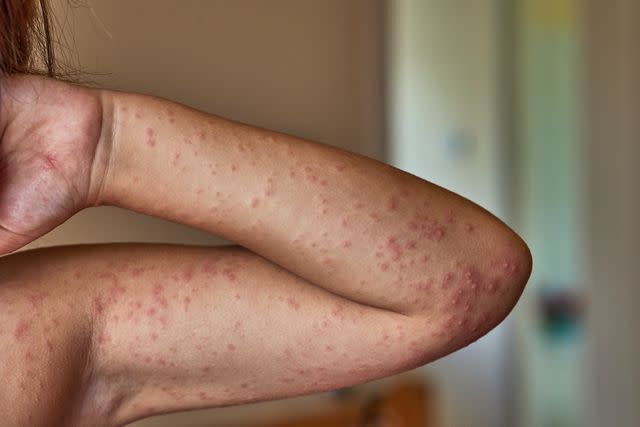
JORGE CORCUERA / Getty Images
Allergic rash on the body of a 5 year oldCan Amoxicillin Cause a Rash?
A skin rash is a common side effect of amoxicillin. It's important to know that although these rashes can be worrisome, they're usually not cause for alarm.
Allergies to amoxicillin and other antibiotics are undoubtedly possible. However, many viruses can cause non-allergic rashes in people who take amoxicillin. Keep in mind that antibiotics only target bacteria, not viruses. If you happen to have a virus at the same time you're taking amoxicillin for a bacterial infection, the virus can affect the way your immune system reacts to the medicine.
This is well-documented in children who take amoxicillin while infected with the Epstein-Barr virus that causes mononucleosis (mono). Up to 30% develop a rash that mimics a drug allergy but is not.
A Word on Probiotics
Probiotics can help protect against allergic reactions and minimize the side effects of amoxicillin. Probiotics restore the body's good bacteria that are depleted by antibiotics.
Try probiotic supplements or add yogurt or kefir to your diet while taking amoxicillin. This might help prevent some side effects like nausea or diarrhea. Taking probiotics after finishing antibiotic treatment also helps rebuild your gut microbiome.
What Does Amoxicillin Rash Look Like?
A non-allergic amoxicillin rash is described as maculopapular. This means that the rash can have either flat or slightly raised bumps. These bumps are usually small and may be red or pink.
An amoxicillin rash can affect most parts of the body. Common sites of a rash while taking amoxicillin include the following:
Abdomen, chest, or back
Face
Arms and hands
Legs and feet
How Long Does Amoxicillin Rash Last?
An amoxicillin rash usually lasts several days and can take up to two weeks to go away. A rash caused by a virus rather than amoxicillin will likely be short-lived, lasting between two and five days.
Remember that some nutrients and herbal supplements can increase amoxicillin levels in the body and increase the risk of side effects. These include:
Black seed (Nigella sativa)
Avoiding these supplements while you're on amoxicillin is safest.
How to Treat Amoxicillin Rash
If you have a non-allergic rash while taking amoxicillin, it will likely resolve independently without treatment. In general, these rashes are not very itchy or painful.
If your rash is itchy, the following medicines can help:
Antihistamines like Benadryl (diphenhydramine) or Zyrtec (cetirizine)
Corticosteroids like hydrocortisone applied to the skin
Your healthcare provider or pharmacist can help you tailor your treatment to make sure it's appropriate for you and screen for drug interactions with your other medications.
Notably, a non-allergic rash does not mean that you can't take amoxicillin or other drugs in this class. The good news is that 90% of people who get a nonallergic rash with their first course of amoxicillin won't have another one the next time they take the medicine.
Warning Signs of a True Allergic Reaction
Less than 1% of people are allergic to amoxicillin.
Allergic reactions happen when the body's immune system mounts a defense against the medicine itself.
The most dangerous allergic reactions to amoxicillin happen immediately after taking the medicine or within an hour of the first dose. These reactions are caused by an antibody in the body called immunoglobulin E (IgE), and they can be life-threatening.
Be aware of signs of an actual allergic reaction to amoxicillin. These can include:
Hives (red, itchy bumps or welts on the skin)
Angioedema (swelling of the stomach, face, arms, legs, throat, or genitals)
Anaphylaxis (a medical emergency that can include heart rate changes, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, and difficulty breathing)
Stop taking amoxicillin and inform your healthcare provider if you experience any of these symptoms.
Call 911 immediately if you experience any signs of anaphylaxis, which is life-threatening.
When to Stop Taking Amoxicillin
Most of the time, a non-painful rash isn't considered a true allergy, but knowing for sure can be tricky.
If you are concerned that your or your child's rash is due to an allergic reaction to amoxicillin, contact your healthcare provider for guidance on the next steps. If you have a true allergy to amoxicillin, you will need to stop the medicine and may need to avoid penicillin antibiotics altogether.
Definitive diagnosis of a drug allergy is done by skin testing with penicillin or a drug challenge with amoxicillin. During a drug challenge, a small amount of the medicine is taken by mouth, followed by a standard dose, while a healthcare provider closely monitors you.
On the other hand, if you have a nonallergic rash while taking amoxicillin, continuing your entire course of the medicine rather than stopping or switching antibiotics is best.
Stopping your amoxicillin course early can cause your infection to last longer or become more severe.
In addition, switching antibiotics can result in a misdiagnosis of penicillin allergy. A penicillin allergy on your medical record limits the antibiotics for which you can get a prescription. Ruling out penicillin often means you'll get broad-spectrum antibiotics instead. These medicines are active against more types of bacteria but have some significant downsides. Some of these include:
Increased cost of medicine
Antibiotic resistance (bacteria no longer respond to antibiotics)
Other infections, such as Clostridioides difficile, which can cause diarrhea
Summary
One in 10 people will develop a rash while taking amoxicillin. Not all of these rashes are true allergies or reasons to stop taking the medicine.
A rash with small, flat, or raised red bumps on the skin and no other signs of an allergic reaction rarely means a true allergy. These rashes do not require treatment and will go away independently, typically in less than a week. Continuing the entire course of amoxicillin in these cases rather than switching to a different medicine is recommended.
Allergic reactions to amoxicillin generally include hives and may involve other organ systems besides the skin. If you have hives, trouble breathing, swelling under the skin, or any other signs of anaphylaxis, stop taking amoxicillin and immediately seek emergency medical help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can amoxicillin cause a rash?
Yes. Skin rashes are a common side effect of amoxicillin and other antibiotics in the penicillin family. About 10% of people who take amoxicillin will develop a rash.
What does an amoxicillin rash look like?
Amoxicillin rash can consist of flat or raised red or pink bumps. It can affect the trunk, face, arms, and legs. This type of rash by itself is not considered a true allergy but is often caused by viruses.
Signs of a severe reaction to amoxicillin include:
Hives
Fever
Swelling of the mouth or face
Difficulty breathing
If you experience any of these warning signs of an allergic reaction, stop taking the medicine and seek emergency help immediately.
How long does amoxicillin rash last?
Amoxicillin rashes typically last from three to 14 days.
Read the original article on Verywell Health.

