AMD claims Ryzen smashes Intel's Meteor Lake in AI benchmarks — up to 79% faster at half the power consumption

AMD has shared some insight into its "consumer AI performance" with Tom's Hardware, featuring a face-off between the AMD Ryzen 7 7840U (15W) and Intel Core Ultra 7 155H (28W). In the selected large language model (LLM) performance tests using Llama 2 and Mistral Instruct 7B, we see that the red team's solution is far quicker, uses less power, and is available cheaper. Though we expect chipmakers to cherry-pick benchmarks, these results show Intel's AI performance isn't even close to the local AI processing horsepower AMD demonstrates here.

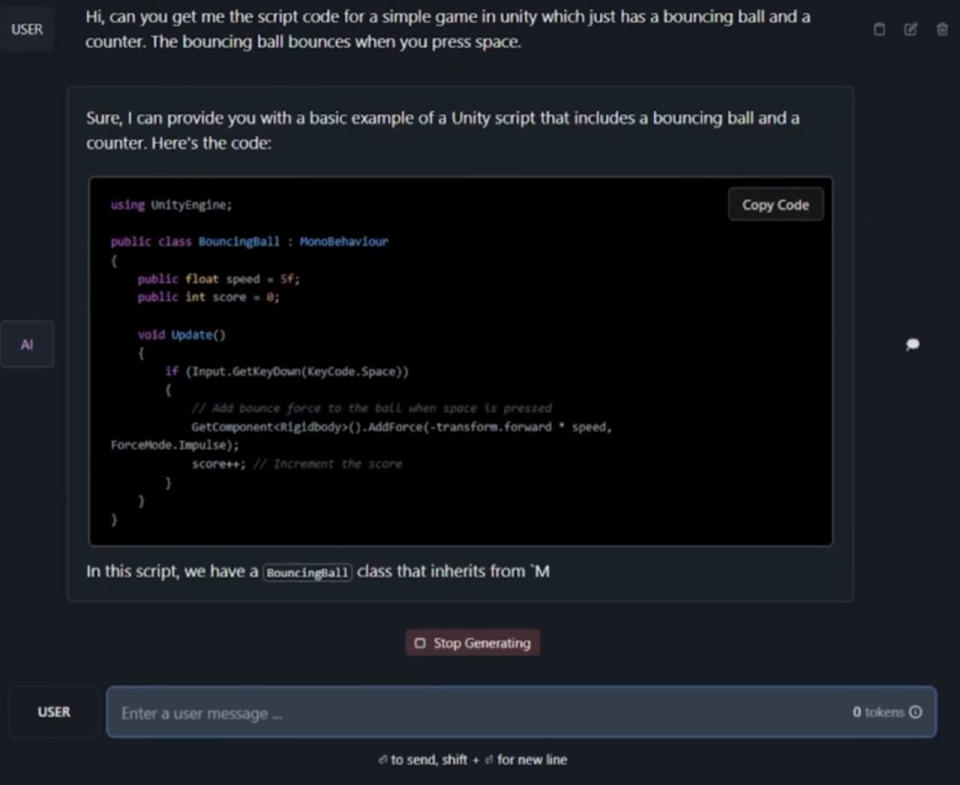
For its test comparisons, AMD installed LM Studio on the competing laptops – a task that it says takes just a few minutes. Once LM Studio is installed, you can run various LLMs locally for utmost privacy, subscription fee-free, and without an internet connection. As we mentioned in the intro, Llama 2 and Mistral Instruct 7B were leveraged for various tasks. Specifically, AMD got the AIs to write a story multiple times, make a demo with a bouncing ball in Unity, and write a poem. For some background information, Llama 2 is a state-of-the-art LLM from Meta, and Mistral Instruct 7B is an LLM with 7.3 billion parameters developed by ex-Meta and DeepMind devs.
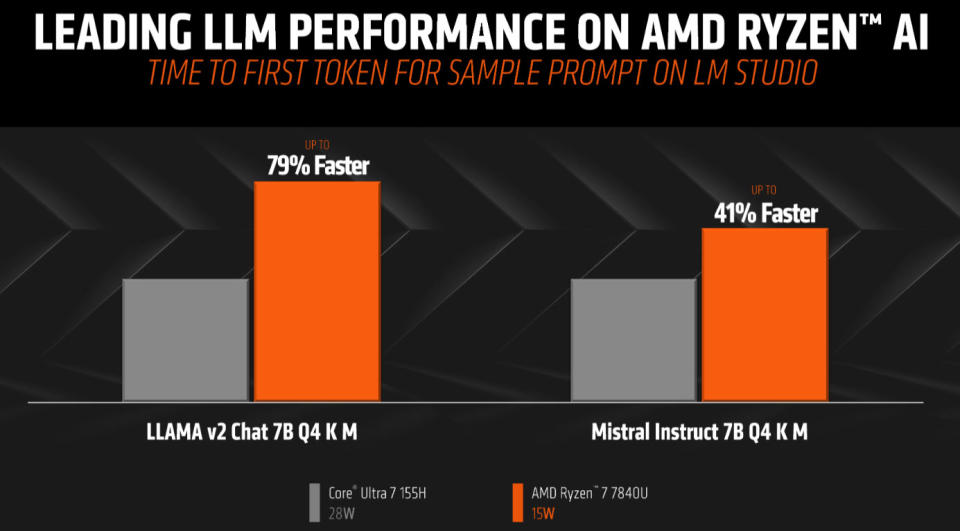
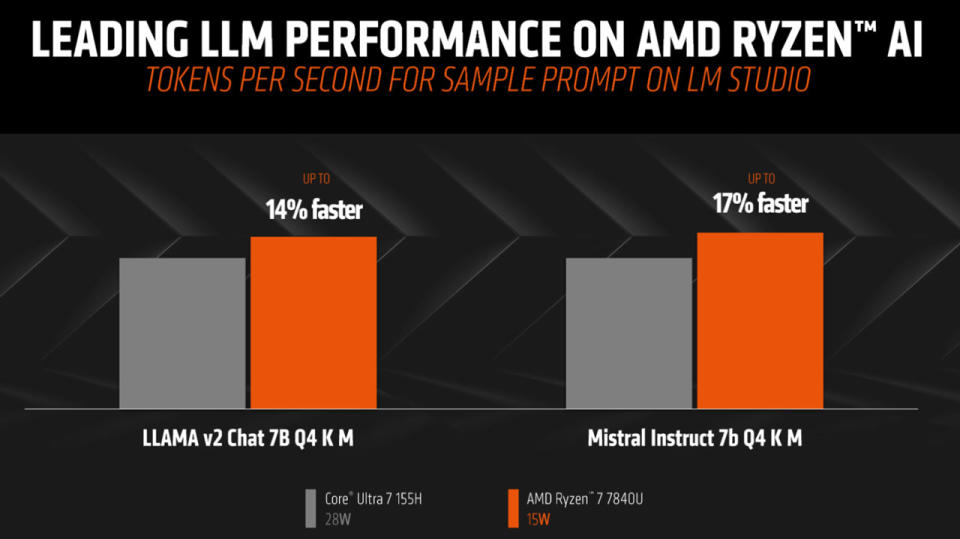
AMD chose performance metrics to showcase its Ryzen's prowess, including measurements of 'time to first token'—which charts the time from inputting a prompt and pressing enter to the first results showing up. Another critical performance measure is 'tokens per second,' where an LLM response is delivered line by line.
As a reminder of the properties of the latest Ryzen chips that align themselves to local AI acceleration, AMD says that three kinds of cores can be used in concert: NPU, RDNA 3 GPU, and Zen 4 CPU. In the demo we watched, an AMD exec said that AVX512 and VNNI acceleration built into the Zen 4 CPU cores were behind the winning results you see in the charts. That's interesting, as we expected to be told about the more powerful NPU in the Phoenix vs Meteor Lake processors.
AMD has published a blog about how to run LM Studio and various LLMs on your local machine. The tutorial guides you through getting started on either an 'AMD Ryzen AI PC' or a PC with a Radeon RX 7000 or newer GPU installed.
Intel is well aware of the relatively paltry AI performance delivered by the Meteor Lake family. The iconic CPU maker has already officially teased that both Arrow Lake and Lunar Lake will have three times more AI performance for GPU and NPU. Intel's next-gen laptop and desktop processors are due later this year.

