'I thought my skin cancer was a bite'

“Our lives came crashing around us, myself, my wife and my kids. Everything just fell apart at that stage.”
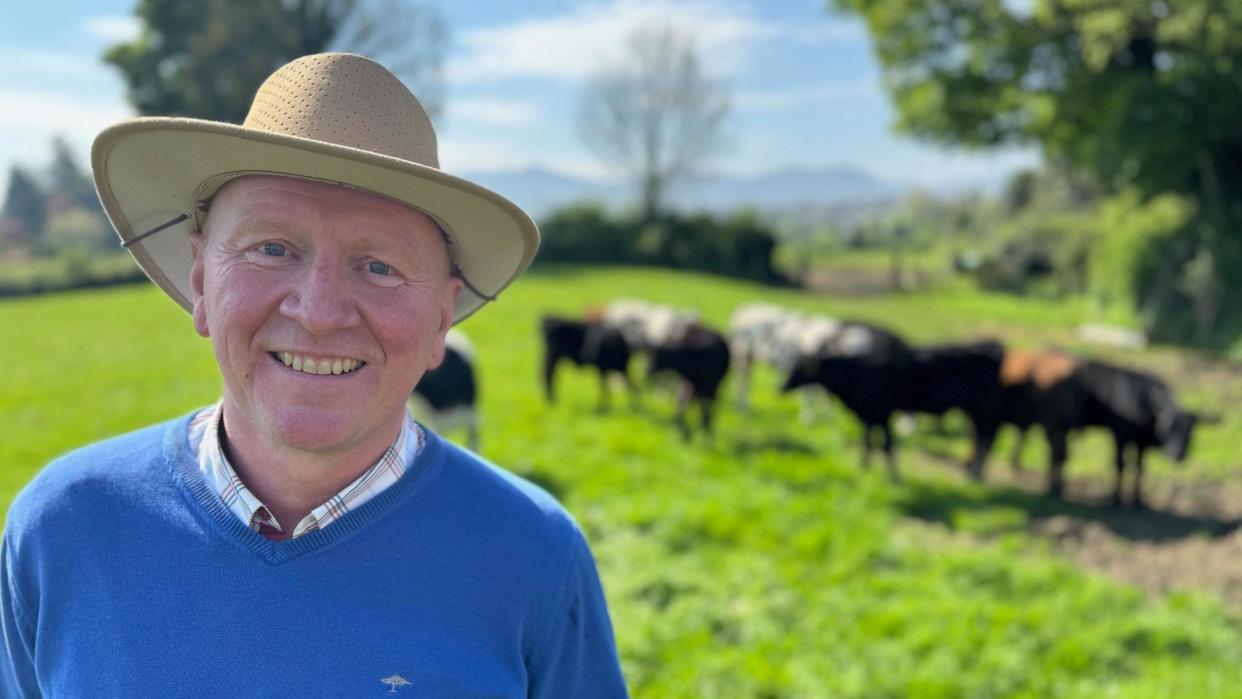
Aidan McKay is a stage four melanoma patient.
First diagnosed in 2019, he had successful treatment, but in 2022 he found out it had returned and was in his brain and lungs.
He blames his skin cancer diagnosis on his childhood growing up on a farm.
New research from Melanoma Focus shows that one bad episode of sunburn in childhood or adolescence more than doubles your chances of developing melanoma skin cancer later in life.
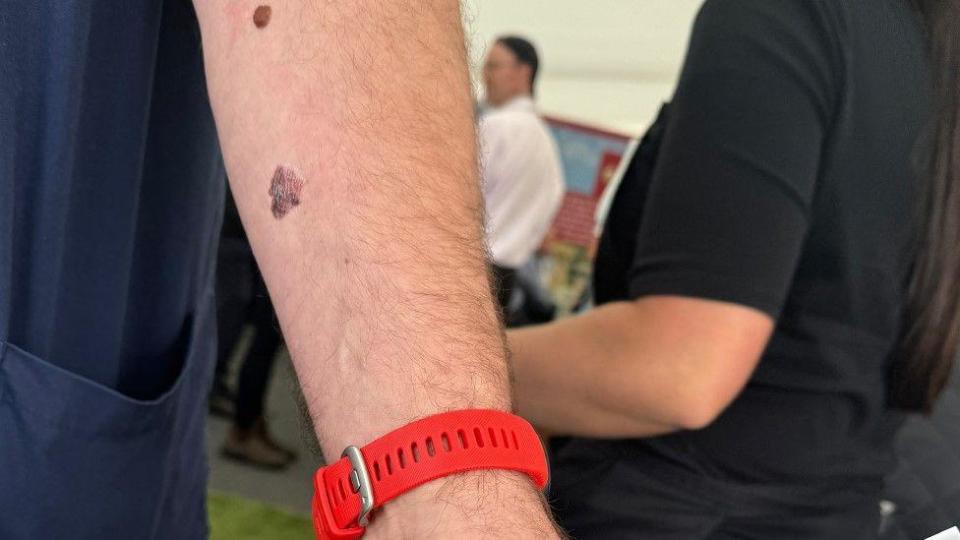
Some farmers attending the Balmoral Show agricultural event are sporting some worrying moles. But not all of them are real.
It is part of a campaign from Action Cancer and The Agri Rural Health Forum to raise awareness of the risk of skin cancer for farmers by offering them temporary melanoma tattoos.
Aidan McKay said when he was a child sun cream was not used.
“We were brought up, baling hay, stooking corn, doing all the things during the summer. There was no sunscreen then and getting a good roast during your summer holidays was just part of the process.
"The only thing we had was calamine lotion as the cure for it afterwards," he told BBC News NI.
'Dangerous place to be'
Mr McKay said he wished he had known more about how to avoid skin cancer when he was younger.
“Wear sunscreen and wear a hat," he explained.
"The other thing is when you find a lesion go straight and get attention to it.
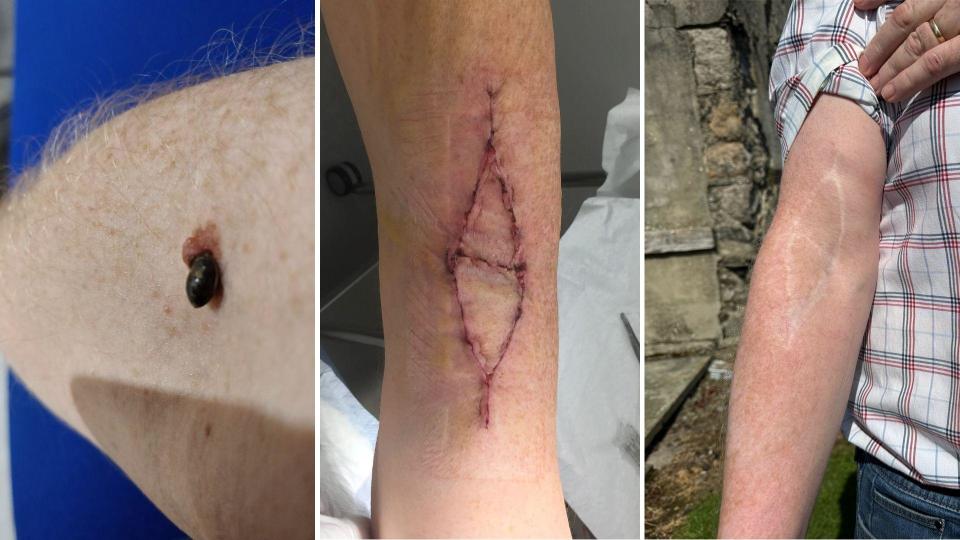
"My lesions come up a bit like a blood blister and I thought it was a bit of a blood blister, maybe a bite.
"I ignored it probably for no more than eight weeks. And those eight weeks were enough to make the difference between what would have been maybe a stage one, possibly stage two, to a stage four cancer."
Mr McKay said he is not terminally ill but added: "It's a dangerous place to be".
Stage four is a term used to mean that a cancer has spread to another body organ from where it was first found.
As an adult Mr McKay farmed as a hobby but has had to give up his farm because of his cancer treatment.
He said: "The cancer has completely curtailed any of those activities. The treatment is fairly severe. Climbing stairs is a struggle so trying to work on a farm is almost impossible."
Farmers are a particularly ‘at risk’ group because their outdoor work means they are more exposed to the elements.
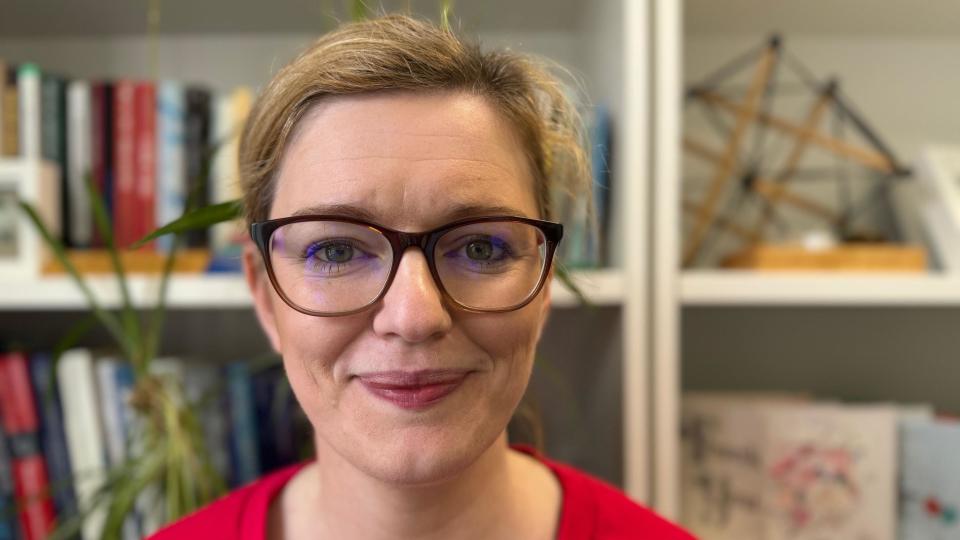
Dr Rebecca Orr, a GP and a part time beef and suckler farmer in Ballymoney, understands why some are reluctant to get medical treatment.
She said: “We work long hours and we're often isolated and may not be thinking about ourselves, we're more often thinking about crops and animals.
"Who's going to do the work whilst you're away?"
Dr Orr said the message was to "please check" and "please protect" skin.

But with more than 110,000 people expected at the Balmoral Show over its four day run getting people to pay attention to a message can be a challenge.
That's why Action Cancer and The Agri Rural Health forum reached out to the medical school at Queens University Belfast (QUB).
Professor Gerry Gormley, a GP and Professor of Medicine at QUB said the temporary melanoma tattoos were more interactive than a leaflet.
He said: "The tattoo on their skin engages people and they start to understand that they need to be more aware of their skin and be more aware of particular skin conditions that we need to be alerted to early. What to do, how to look for it in each other.
"It's more meaningful to them than a leaflet."

What is melanoma?
Melanoma is the fifth most common type of cancer in the UK, according to the NHS.
It is a type of skin cancer that can spread to other parts of the body.
Anyone can develop melanoma regardless of age, race or gender.
What are the symptoms of melanoma?
The most common symptom is the appearance of a new mole, or a change in an existing one.
This could be a change in colour, shape or size, or if the mole has become painful or itchy.
The NHS also advises people to see their GP if they find a new or unusual mark on your skin that has not gone away after a few weeks.
The ABC of checking a mole
Asymmetry: two halves differ in shape
Border: edges irregular or jagged
Colour: uneven/patchy; shades of black, white, grey, brown or pink; two or more colours = suspicious
Diameter: for most melanomas, at least 6mm
Evolving: changing in size, shape or colour
‘Funny’: if it looks odd, or you aren’t happy about it for any reason get it checked
Can melanoma be prevented?
More people now die from melanoma in the UK than in Australia, according to Melanoma Focus.
Its CEO Susanna Daniels said the disease was “largely preventable”.
“Protecting children from burning is the best way we can reduce their chances of developing melanoma in the future.
"About 9 in 10 melanoma skin cancer cases are preventable and it is vital that people take the warnings about the dangers of excessive sun exposure seriously."
'Nasty cancer'
For now Aidan McKay is in remission but he knows the cancer could come back at any time.
"So every three months, everything's put on hold," he said.
"You get to find out whether you get to go on [and] enjoy another three months or you're back in the middle again and you constantly have this thing hanging over you.
"Melanoma is a nasty, nasty cancer."

