What Severe Weather Looks Like from Space
Ever wondered what thunderstorms look like from space? Wonder no longer.
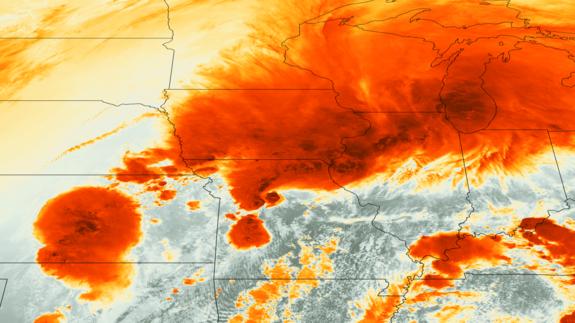
A false-color image, taken by the GOES-13 satellite yesterday afternoon (April 17), shows a series of strong thunderstorms in the Midwest. The dark orange of the cloud tops indicate that they are very cold, a marked contrast to the warm, humid air surrounding it. (The warm air can't be seen since it is transparent in this image.)
This contrast between cold, upper-level air and warm, humid air beneath powers instability in the atmosphere, which gives rise to thunderstorms and occasionally tornadoes, said Bob Henson, a meteorologist and science writer for the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) in Boulder, Colo.
Today (April 18) a new cold front has moved across the center of the country, as can be seen in a second image from NCAR. This has created a "squall line" of cold, high level air that stretches from north to south across the country. This system also produces instability and wind shear, which involves wind speed and direction changing with altitude. This situation creates optimal conditions for tornado formation — in fact, there are tornado watches stretching from Michigan to Texas, Henson said.
This cold front is particularly frigid for this time of year, and it has led to an impressive accumulation of snow throughout the Great Plains. Right now, there are more than 4 inches (10 centimeters) of snow stretching from Denver to Minneapolis, Henson said. On Sunday (April 14), a total of 17.3 inches (44 cm) of snow fell in Bismarck, S.D., the most snow ever to fall on the town in a 24-hour period, Henson added.
The front has also brought record cold. Lubbock, Texas, is expecting freezing temperatures tonight, Henson said. That would be the latest freeze ever recorded for the city, by more than a week. Oklahoma is also expected to see freezing temperatures, which would be the first time this has happened since the 1950s, Henson said.
Email Douglas Main or follow him @Douglas_Main. Follow us @OAPlanet, Facebook or Google+. Original article on LiveScience's OurAmazingPlanet.
Copyright 2013 LiveScience, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.