Quadrantid Meteor Shower Peaks Tonight: How to See It
The annual Quadrantid meteor shower each January provides one of the most intense annual meteor displays, with a brief, sharp maximum lasting only a few hours. And while the 2015 Quadrantids peak tonight (Jan. 3), the bright moonlight may outshine these dazzling "shooting stars."
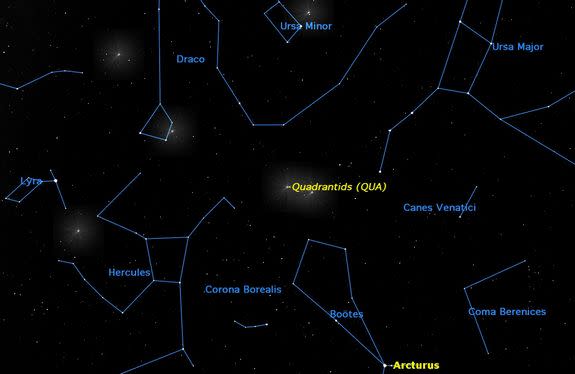
The Quadrantid meteor shower of 2015 appears to radiate from the northeast corner of the constellation of Boötes, the Herdsman, so you might expect them to be called the "Boötids." But back in the late 18th century, there was a constellation in the same area called Quadrans Muralis, the "Mural or Wall Quadrant" (an astronomical instrument). It is a long-obsolete star pattern, invented in 1795 by astronomer J.J. Lalande to commemorate the instrument used to observe the stars in his catalogue. But the name survives in the Quadrantid meteors.
Adolphe Quetelet of Brussels Observatory discovered the shower in the 1830s, and several astronomers in Europe and America noted these meteors shortly afterward. They were christened Quadrantids, and even though the constellation from which these meteors appear to radiate is no longer officially recognized in astronomy, the shower's original moniker continues to this day. [Amazing Photos of the Quadrantid Meteor Shower]
2015: A poor Quad year
Unfortunately, this will not be a good year to look for the "Quads." Chalk it up to poor timing. First, the peak of this year's shower is predicted for 10 p.m. EST on Jan. 3. But on Jan. 5, the moon will turn full. That means that all through the overnight hours of Saturday, Jan. 3 into Sunday, Jan 4, the sky will be lit up with brilliant moonlight.
That moonlight will squelch all but the brightest of meteors. This particular meteor shower display is at its best just before the break of dawn, about 6 a.m. local time, when the radiant of this shower — the point from which the meteors appear to emanate — is ascending the dark northeastern sky.
If you do head out to look for meteors, remember to bundle up! It is, after all, wintertime. As one astronomer said prior to a midwinter meteor watch, "Take the advice of a man whose teeth have chattered on many a winter's night: Wrap up much more warmly than you think is necessary!"
Crumbs of a dead comet?
At greatest activity, 60 to 120 shower members per hour should be seen. However, the Quadrantid meteor shower influx is sharply peaked: Six hours before and after maximum, these blue meteors appear at only half of their highest rates. This means that the stream of particles is a narrow one, possibly derived relatively recently from a small comet.
In fact, in 2003, astronomer Peter Jenniskens of NASA, found a near-Earth asteroid (2003 EH1) that seemed like it was on the right orbit to have made the Quadrantids. Some astronomers say that this asteroid is really a piece of an old, "extinct" comet, perhaps a comet that was recorded by Chinese, Korean and Japanese observers during the years 1490-91. Maybe that comet broke apart, and some of the pieces became the meteoroids that make up the Quadrantid stream, some scientists say.
Next year could be a winner!
As bad as it is for the Quadrantids in this New Year, it will be a much different story in 2016.
The peak of the shower next year is set for 3 a.m. EST on Jan. 4, which favors eastern North America. And the moon will be at a much more favorable phase: a waning crescent just 29-percent illuminated and much less of a hindrance to meteor viewing. Given clear skies, it could turn out to be one of the best meteor displays of 2016. Mark your calendars!
Editor's note: If you capture a stunning photo of the Quadrantid meteor shower, or any other amazing night sky view, and would like to share it with Space.com for a story or gallery, send images and comments in to managing editor Tariq Malik at spacephotos@space.com.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York's Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, the Farmer's Almanac and other publications, and he is also an on-camera meteorologist for News 12 Westchester, N.Y. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Copyright 2015 SPACE.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.