Earth just had its second-warmest February on record

As the saying goes: Another month, another disconcerting report from top U.S. climate agencies.
Last month was Earth's second-hottest February on record since at least 1880, NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) recently reported.
At the same time, the extent of sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctica hit record monthly lows.
SEE ALSO: Here’s why it's so frickin’ hot right now
In February 2017, the average global temperature was 1.76 degrees Fahrenheit above the 20th-century average of 53.9 degrees, NOAA's National Centers for Environmental Information said late last week.
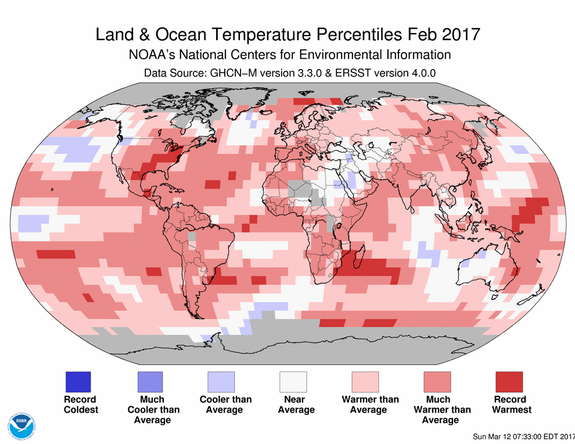
Image: NOAA/NCEI
Only February 2016 was warmer, at a staggering 2.43 degrees Fahrenheit above average, NOAA said. The entire year of 2016 was also the hottest on record, with last year's temperatures exceeding all previous years since record-keeping began 137 years ago.
NOAA and NASA scientists said human-caused global warming was responsible for a majority of the annual temperature gains — a fact the Trump administration seems determined to ignore.
For U.S. residents, it's probably not surprising to learn that last month was exceptionally warm. February 2017 saw widespread record warmth across the country and a series of record highs.
Other parts of the world similarly experienced an atypically warm winter.

Image: NOAA
From December 2016 to February 2017, the global average temperature was 1.60 degrees Fahrenheit above the 20th-century average of 53.8 degrees, NOAA said. This was the second warmest for this season, second only to December 2015 to February 2016.
The first two months of 2017 also landed in second place. The year-to-date average temperature for January through February 2017 was 1.69 degrees Fahrenheit above average, just below the first two months of 2016.
Those balmier temperatures meant troubling news for the planet's sea ice.
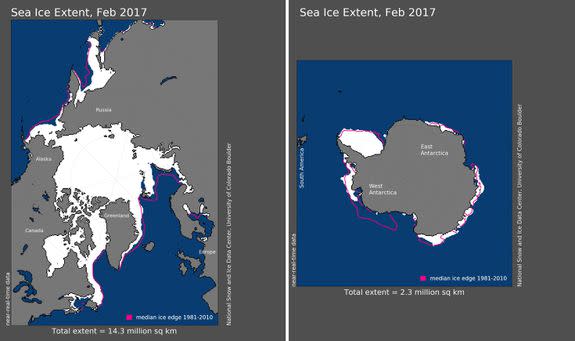
Image: National snow ice and data center/university of colorado, boulder
Both the Arctic and Antarctic seas logged the smallest February sea ice extent since satellite records began in 1979, according to NOAA data analyzed by the Rutgers Global Snow Lab.
The average Antarctic sea ice extent was 24.4 percent below the 1981-2010 average for February, the U.S. climate agency reported. In the Arctic region, the average sea ice extent was 7.6 percent below average.
But warmer air temperatures aren't the only culprit in shrinking sea ice. Ocean temperatures are similarly heating up, in part because of human-driven climate change.
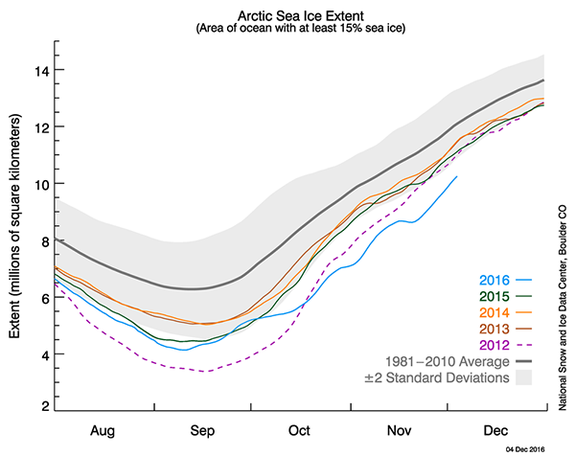
Image: national snow and ice data center
A new study found oceans may be warming about 13 percent faster than scientists previously thought. The warming rate from 1992 is nearly two times the warming rate from 1960, according to a paper published March 10 in the journal Science Advances.
In its monthly report, NOAA said the globally averaged sea surface temperature also ranked as second-highest on record for February, the December-February season and the two-month year-to-date.
Anyone want to guess how March's report will look?
