The Citroën 2CV – celebrating 70 years of a French design icon

It is apt that a car so evocative of freshly-baked baguettes was the product of a Pierre-Jules Boulanger. Having been appointed as vice-president at the then-struggling Citroën in 1935, Boulanger – supposedly inspired by the sight of struggling horse-drawn cart near Paris – realised that France needed simple, cheap transport.
Existing cars, like the Peugeot 201 and newly-launched Simca 5, were small and basic, but even these were out of reach to the average French paysan, both in terms of retail price and ongoing cost of maintenance. Boulanger saw a gap in the market for minimalist motoring, and decided that Citroën should fill it.
The following year he instigated what would become one of the greatest design projects in European history. The brief was simple – the car must be tough enough to cope with the potholed country roads, strong enough to carry four people and 50kg of produce (an instinctive salesman, Boulanger specified a sack of potatoes or a keg of beer depending on his audience), economical enough to consume a maximum of three litres of petrol per 100km and refined enough to transport a box of eggs across a ploughed field without any breakages.
Boulanger installed André Lefebvre as chief engineer and Flaminio Bertoni as stylist. They named the project très petite voiture, or 'TPV' for short.
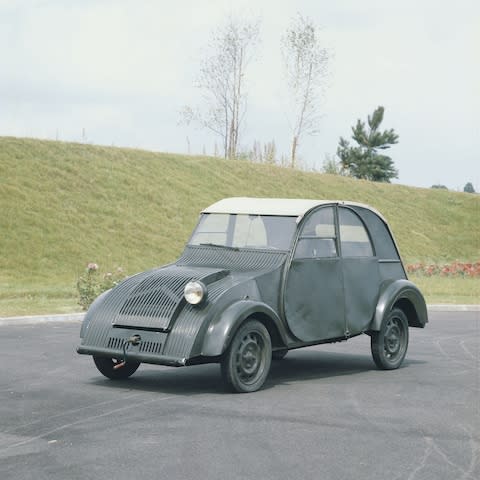
They began designing the TPV in secret at the Michelin facilities in Clermont-Ferrand, with Boulanger keeping a hawk-like watch over proceedings. He even created a department to weigh and tweak each component to ensure minimum waste. But the vigour with which Boulanger embraced minimalism was evident in his first prototype; its bodywork rubbed, the chassis creaked and the hammock-style seats suspended from the roof of the car were dangerously unstable. The TPV was being consumed by its own cheapness.
To ensure that TPVs did not fall in to Nazi hands, Citroën had prototypes buried on farms for safekeeping
Changes were made, austerity was pared back, and by 1939, the TPV was deemed suitable for the French public. An initial run of 250 cars was produced, and on 2 September 1939, the first model was cleaned, polished and ready to be shown to the waiting public.
The following day, France and Britain declared war on Germany. The Paris Motor Show, where the model would have been revealed, was called off, and the Citroen assembly line converted to produce military equipment. The project to build an affordable car for the French masses was officially cancelled.
Unofficially, however, Boulanger persevered. Development continued in secret and to ensure that TPVs did not fall in to Nazi hands, Citroën had prototypes disguised as pickup trucks, hidden in barns and buried on farms for safekeeping. The French Resistance re-labelled the train carriages transporting further examples to fool the Germans into thinking that they only contained agricultural equipment. Boulanger refused point blank to collaborate with German authorities, and was listed as an enemy of the Reich by gestapo who tried to arrest him several times.

By 1941, some key changes had been made. The water-cooled two-cylinder 375cc engine was replaced with an air-cooled unit of the same size, which had been designed by Walter Becchia. He also fitted a four-speed gearbox, an improvement on other small French cars of the time such as the Peugeot 202 and Citroën’s own Traction Avant, while the awful hammock seats were replaced with something more closely resembling a chair. The 2CV had not only survived the war, but had been significantly improved by it.
Boulanger’s battle wasn’t over, though. The French government introduced Plan Pons, a strategy to restructure the automotive industry named after naval officer turned civil servant Paul-Marie Pons. This plan not only limited car production to ensure that scarce materials were being used for essential rebuilding projects, but also crudely divvied-up the car market among existing manufacturers.
The 2CV had not only survived the war, but had been significantly improved by it
Simca and Panhard would continue building entry-level cars, Peugeot and Renault would produce larger cars, while Citroën was allocated the ‘premium’ end of the market. It was decreed that Citroën were allowed to create just one model, the elegant and upmarket Traction Avant, thwarting Boulanger’s plan to create an affordable car for the people.
But the roads in les années grises were in even greater need of the 2CV than they were before the war. Horse-drawn vehicles had re-emerged out of necessity; only around five per cent of the cars in France were still serviceable after the war, mostly running on town gas, and the road network had fallen into disrepair. France needed its ‘people’s car’.

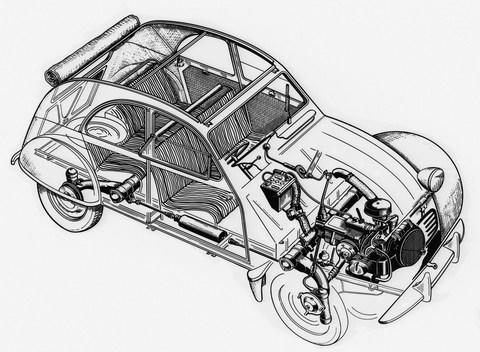
In 1948, almost a decade late, it was unveiled at the Paris Salon. Plan Pons came to an end in 1949 and the first car – the 2CV Type A – was delivered. It remained a basic machine despite ten years of progress; a 375cc two-cylinder engine produced around 9bhp, its design focussed on reducing moving parts to a minimum in order to reduce the need for costly repairs. Often misconstrued as a reference to the car’s physical horsepower, the “deux chevaux” refers to a taxation bracket based on fiscal horsepower rather than anything you could measure at the crank.
The cooling fan and dynamo were integrated in to the one-piece crankshaft, making drive belts surplus to requirement. The only hydraulic part in the entire car was the brakes, and the instruments were limited to just the speedometer and the ammeter. If you came to a stop and wanted your wipers to keep going, you had to do it by hand. The only creature comfort was an electric starter motor, added just before the launch; it was a far cry from the Delahayes, Bugattis and Delages of pre-war France.
The motoring press were heavily critical, with one British Autocar correspondent remarking that “it is the work of a designer who has kissed the lash of austerity with almost masochistic fervour”. Yet Citroën were flooded with customer orders (proving that we motoring writers are often wide of the mark) and early adopters were delighted with the 2CV’s simplicity.
Within months of its release, the waiting list stretched to five years. Second-hand examples became more valuable than new versions as buyers could halve their waiting time. Production soared from 876 units in 1949 to more than 6,000 in 1950.
In the true spirit of égalité, Boulanger’s policy stated that priority was to be given to those who have to travel by car for work such as vets, country doctors and farmers, and to those for whom ‘ordinary’ cars are too expensive to buy. Boulanger died in November 1950 but his idea was coming alive; by the end of 1951, 100 cars were leaving the factory a week. Millions would go on to be sold all over the world.
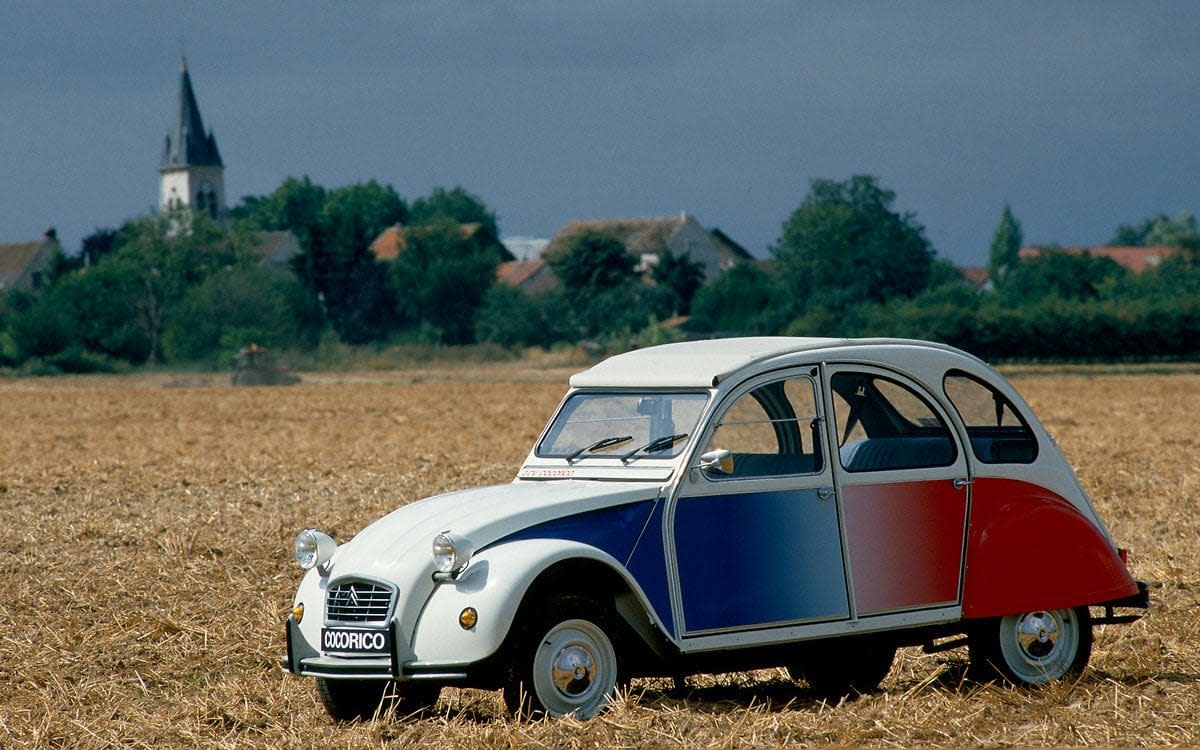
One thriving market was the African continent. The 2CV Sahara was a four-wheel-drive version designed for more treacherous terrain than that of France; it boasted two engines, two transmissions, two petrol tanks and twice the asking price of a standard 2CV. There followed an unstoppable stream of improvements and special editions, such as the AZ, the Dolly, the 6 Club and the snazzy two-tone Charleston. My favourite is the Cocorico – translating broadly as ‘cock-a-doodle-do’ in French, the car sported a tricolore paint job and was optimistically designed to support the French football team at the World Cup in 1987.

(Even after France was knocked out of the competition by West Germany, Citroen ploughed ahead with the model. They removed the football decals and launched as planned, selling all 1,000 examples almost immediately. It remains one of the most sought-after 2CV special editions.)
For 42 years the 2CV trundled off its production line. Eventually it began to feel antiquated and by 1990, as the French automotive industry turned its efforts to models like the Clio and the 605, Citroen stopped building its tinny little 2CV. Developed on the eve of war in Europe, this model survived virtually unchanged until the days of the World Wide Web.
The Nineties were to become a wonderfully optimistic period in car design, especially for the French manufacturers, and the 2CV had played no small part in taking them there. Totemic of a certain gallic pragmatism, the beauty and longevity of the 2CV lies in the sincerity of its design. We may never see such a profoundly honest car again.
As the French would say, ‘Moins, c’est plus.’

