China, India would pick up America's clean energy slack under Trump

China and India stand to benefit if America's progress on clean energy slips under President-elect Donald Trump, energy experts say.
Trump has vowed to gut U.S. climate policies that favor wind, solar and other lower-emissions technologies and instead revive the struggling coal sector.
But the world's energy market is moving in the opposite direction, the International Energy Agency (IEA) said Wednesday in its annual World Energy Outlook.
SEE ALSO: In energy milestone, renewables overtake coal for first time
Clean energy is projected to grow exponentially in the next two decades as countries work to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and fight climate change while expanding access to electricity. The shift will create millions more jobs and spur trillions of dollars in annual investment, the Paris-based IEA said.

Image: Ma fengcheng - Imaginechina
The U.S. could forfeit some of those economic gains if Trump lives up to his campaign promises to reinvigorate the fossil fuel sector and tackle "real environmental challenges" instead of "phony" ones like climate change.
China and India — two rapidly growing economies with rising energy needs — would gladly pick up that slack, said Tim Buckley, director of energy finance studies for the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis.
"China and India are very happy to have the global leadership of industries of the future that employ millions of people and are seeing close to $2 trillion of investment a year," Buckley said, citing figures from the new report.
"If America wants to forfeit that leadership, or erode it, then China or India will very happily grasp it," he said.

Image: Chinatopix via AP
China and India, each of which are home to over a billion people and counting, represent a significant share of the renewable energy projections outlined in the report. The IEA said renewables could represent the largest source of power generation in both countries within two decades.
China has already warned Trump not to back away from U.S. commitments under the Paris Climate Agreement, and signaled that it would lead future climate negotiations if the U.S. were to step back.
The energy future
The energy agency will present the report on Thursday at the United Nations' climate conference in Marrakech, Morocco, where leaders are meeting to create an action plan to implement the Paris accord.
Countries have agreed to keep global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, or 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit, above preindustrial levels through 2100 to avoid catastrophic impacts from climate change.
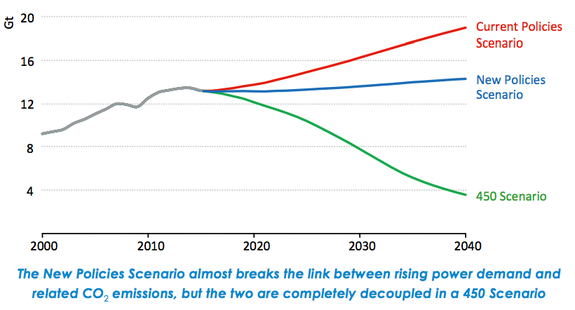
Image: iea 2016 world energy outlook
In its report, the IEA describes how energy markets should look by 2040 to keep the world on track for a 2-degree climate outcome:
A third of global power generation will come from wind and solar, up from 4 percent today.
Renewables overall will account for 58 percent of power generation, up from 23 percent today.
Coal's contribution will shrink to only 7 percent of the mix, down from about 40 percent.
Annual investment in power plants will rise to $700 billion a year. Three-quarters of that is for renewable technologies, and less than 15 percent for fossil fuels.
Almost half of all passenger cars will be electric vehicles, up from a tiny fraction today.
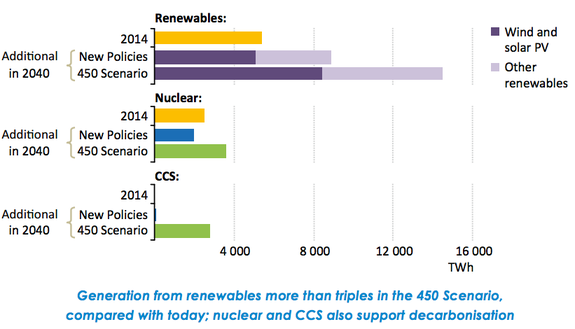
Image: iea 2016 world energy outlook
Yet even these projections are considered too modest by many climate and energy experts. The IEA's most aggressive scenario still only gives the world a 50-50 chance of limiting global warming to below 2 degrees.
Greg Muttitt, a senior adviser at the environmental group Oil Change International, urged the IEA to update its forecasting methods to show how the world should actually look to meet the goals of the Paris agreement.
"The world needs better odds of avoiding dangerous climate change than a toss of a coin," he said in a statement.
