Breakthrough breast cancer drug Herceptin cures disease 'twice as quick' as previously thought
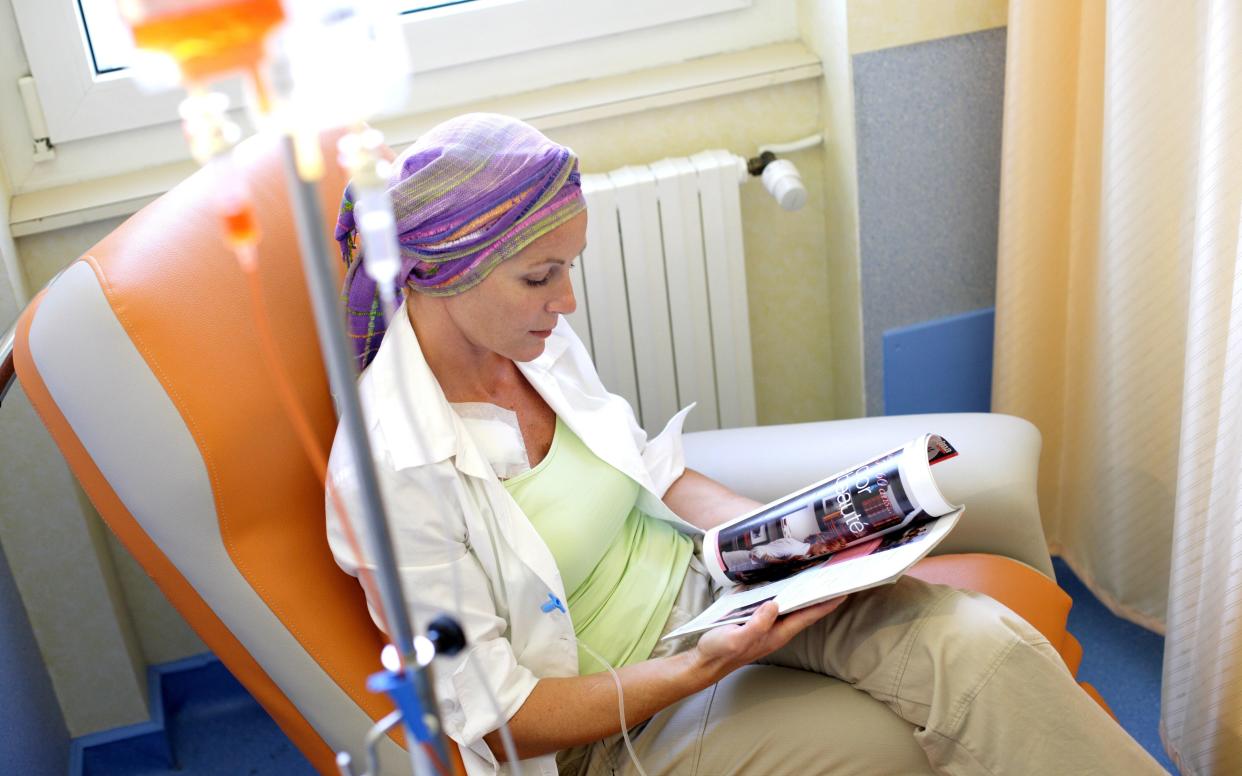
Women with aggressive breast cancer can be effectively cured in half the time compared to current treatment, minimising harmful side effects, researchers have said.
A new trial of patients suffering from HER2-positive breast cancer found survival rates were almost identical among those given six months of therapy compared with a year.
Around one in five cases of breast cancer is characterised by an excess of the HER2 protein, which has traditionally made affected women harder to treat.
But Trastuzumab, commonly known by its brand name Herceptin, has significantly improved survival for HER2-positive patients since 2005.
However, the medication can prompt a range of side effects ranging from high temperatures to heart problems, which often become more severe the longer treatment goes on.
In the new study, to be presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology in Chicago, researchers at Cambridge University examined the outcomes of 4,088 women with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer who were being treated with Herceptin.
About | Breast cancer
The disease-free survival rate at four years was 89.4 per cent in those given six months’ treatment, compared to 89.8 per cent in those who underwent the standard 12 months.
Additionally, only 4 per cent of the women in the six-month cohort were forced to stop using herceptin due to cardiac problems, half the proportion of those in the 12-month cohort.
Professor Helena Earl, who led the Cambridge researchers, said: “We are confident that this will mark the first steps towards a reduction in treatment duration for many women with HER2-positive breast cancer.
“Everyone involved in this study is very excited by these results.”
The new analysis, taken from data gathered as part of the Persephone trial, is the largest to date to examine the impact of shortening the duration of Herceptin treatment, according to the authors.
Other scientists cautioned, however, that the study’s follow-up period has been relatively short and that further research will need to analyse longer-term survival rates.
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research, a body overseen by the UK Government.

