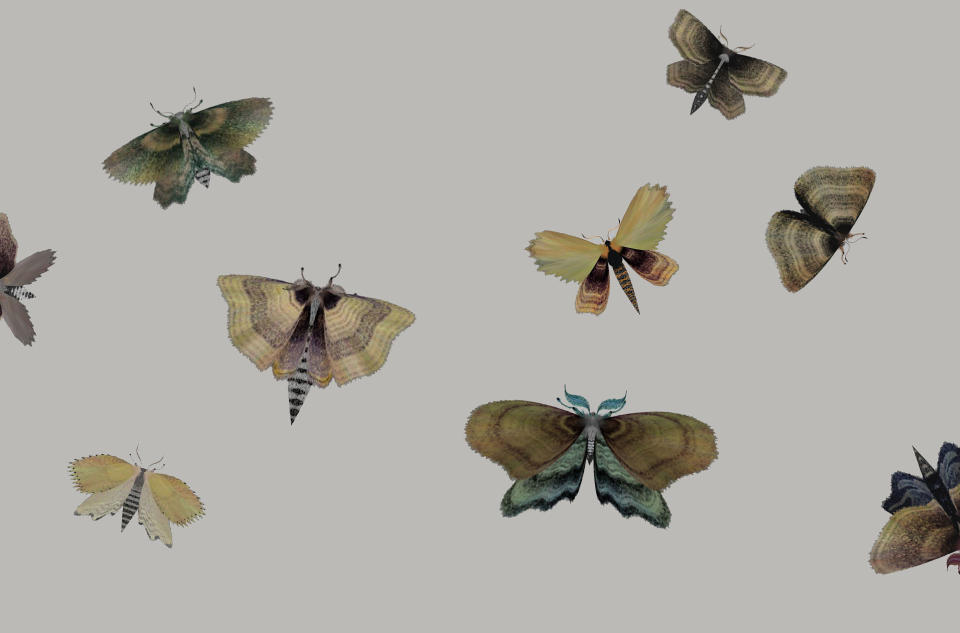
'Til death do us part
Exploring the science, history and consequences of trying to kill every moth in your house.
Great Neck, NY -- As I write this, dozens of moths are being suffocated to death in my kitchen pantry without much ceremony. An exterminator named Danny is spraying an intoxicatingly aromatic layer of cedar oil along the inside corners of my kitchen cabinets and strategically placing pheromone traps in the critters' high-fly zones.
During their yearlong residency in my house, I've become rather intimate with these small, airborne beasts. I know them: We've shared meals and watched each other grow, and they've even accompanied me in the shower, though typically to their own watery demise. I have seen these moths through all phases of their lives, through multiple generations. I know how they are born and what makes them thrive, but most importantly, I know what kills them.
I knew it was over between us when I caught my moths writhing around in my jasmine rice, their squirming, pale-yellow larval bodies cocooned in silk threads, their dark, miniscule eyes and mandibles just large enough to identify with the naked eye. It was disgusting. There had been signs of course. We'd seen the fully formed adult moths fluttering around the kitchen and observed the webbing in the pantries, and we had even found one particularly pioneering larva in the bristles of my partner's toothbrush. But this rice infestation? This was enough.
As a science and environmental reporter, keen to the toxicity and environmental havoc of traditional extermination practices, I hired Danny through one of New York City's many eco-friendly pest-extermination companies -- one that promises to kill the designated pests in your abode without killing the environment (or your wallet). "Pantry moths," explains Danny, stretching a pair of pale-blue surgical gloves over his hands, "are hard to get rid of."
As Danny sprays, I tell him that I'm working on a story about the ethics of extermination and the various species we encounter and kill within our homes. Danny isn't exactly allowed to speak on the record on behalf of his company ("Danny" is not his real name). The word "silica" however, does pique his interest.
As it turns out, that mineral compound is one of nature's most effective natural insect killers. If you've ever had a bedbug problem, you will probably have seen silica in the form of diatomaceous earth -- a white, chalklike powder made up of a fossilized algae. "The bedbugs will crawl all over it, and it dries them up!" explained Jared, an exterminator for Ecology Exterminating, another New York-based, eco-friendly extermination company whose staff preferred not to be fully identified. He continued to describe how as insects traverse DE's chalky plains, the compound sticks to their waxy exoskeletons. The silica, bearing a particular knack for absorbing moisture, then leeches all the lipids from the insect's exoskeleton, causing them to dehydrate and die. As Jared reiterated, "It gets into their skin and it sucks 'em dry."
While diatomaceous earth is not used to address moths, there is still silica present in the cedar oil that Danny has been administering in my kitchen. As he sprays every nook and cranny, he tells me this liquid form of the mineral works to dehydrate the moths while the cedar-oil fumes suffocate them. For my moths and most other insects, the scent of cedar oil forms a noxious, dizzying fog that inhibits their respiratory functions. It also leaves them too disoriented to mate -- something I ruminate over while I watch one affected moth begin to descend into confused swallow loops before it lands clumsily onto the kitchen counter. That moth is in no condition to fly, let alone consent to intercourse.
Heeding the common adage, I've made it a point to keep these enemy moths very close. In my dogged quest to gain a deeper understanding of my cohabitant species, I also consulted entomologist Lou Sorkin of the New York Entomological Society about my pantry-moth problem. "Oh!" he exclaimed. "Is it plodia? Indian meal moths? That's a common one."
The "plodia" he is referring to is plodia interpunctella, the taxonomic term for pantry moth. These insects also go by the colloquial "Indian meal moth," a colonial relic born of a time when European settlers in the Americas referred to Native Americans as "Indians" and cornmeal (a favored food source of the plodia) as "Indian meal."
Just as their name is the product of colonial expansion, so too is their origin as an American pest. "Pantry moths are not native to [this area]," Sorkin informed me. "They're an invasive species originally from Asia. They wound up here through international trade routes, when we started importing and exporting food around the world." Even today, pantry moths are typically introduced into households by hitching a ride in a grain source, from cereals to flours, or in my case, a bag of Kokuho brand jasmine rice. Today, plodia interpunctella can be found in a kitchen pantry on every continent on earth, with the sole exception of Antarctica.
Uh oh! It looks like CRITTERS from Moth Generator, a rogue twitter bot that spawns procedurally generated Lepidoptera have invaded! If they're bothering you, just tap or click them to shoo them away.
On the northeastern coast of the continental United States, under the dark gray roof of my house in the suburbs, these moths have found a particularly happy home. "They like to mate at around 4 to 5 PM," said Sorkin. "Female moths will release pheromones to attract males." The results of these late-afternoon copulations are microscopic eggs. An individual female moth can lay up to 400 of these in her short lifetime as a winged, adult moth. I quickly estimated that there were at least thirty moths floating around my house at any given time. Assuming half of them were females laying their 400-egg capacity, I deduced that within three days, up to about 6,000 infantile moths could have been planted inside my house. That's way too many eggs and way too many moths.
When I asked Jared, my second extermination expert, what inspired his 11-year career in pest extermination, he replied with a simple truth: "Things change, technology changes, but one thing that's not gonna change is that there's always gonna be mice and rats and roaches. They'll be around forever." My moths, I thought, had better not be around forever. Still, Jared is absolutely right. Since the dawn of agriculture, humanity has been trying to eradicate species we deem pests from our areas of dominion in all manner of ways.
According to a timeline of major developments in the history of pest management from Penn State, ancient Sumerians used sulfur compounds to exterminate insects as far back as 2500 BC. In 1101 AD, soap was first used as an effective pesticide in China. The 1930s introduced DDT and the use of chlorinated hydrocarbons and organophosphates, which would be rolled back 30 years later after scientists discovered their detrimental ecological and human-health effects. As a result, the field of integrated pest management was established in the 1970s, dedicated to more-holistic methods of pest control.
"Things change, technology changes, but one thing that's not gonna change is that there's always gonna be mice and rats and roaches. They'll be around forever."
Personally, independent of any sprays, traps or professional help, I have maintained an approximate kill rate of about five moths per day, obliterating them between my two palms or against a flat surface. Their coppery, brown wings leave small, unsightly smudges of corporeal evidence on the kitchen wallpaper, the bathroom tiles, the shower curtain. I can't keep up with cleaning, and there's proof of their expiration everywhere between the kitchen and its nearby bathroom.
When I asked amateur Dutch entomologist Bart Coppens about what he thought of my moths, he succinctly replied, "They are an invasive species and should be exterminated." During my own brief stint as an amateur entomologist, I came across Coppens' videos on YouTube. In them, he showcases the moths he has raised as pets. His, unlike mine, are fantastic.
There are mystifying luna moths and acorn-sized hawk moths with hidden underwings that bear a bright, eye-shaped pattern that reveals itself when the insects are threatened. There are giant yellow comet moths the size of Coppens' hand fluttering around his living room. My personal favorite, however, has to be the rosy maple moth featured in a video appropriately titled "CUTEST Moth in the WORLD." Its stout frame is about one square inch all around, with little striped pastel-pink-and-yellow wings and a small body covered in yellow fur. It scuttles across Coppens' hand and arm before going for a little flight. In most of Coppens' videos, his moths rest gently on his hand. One can't help but feel as though these moths really trust him, and Coppens them. The mutual respect for each other is something that I, beleaguered by my moths, find enviable.
"If I had to pick one word [to describe my relationship with my moths], it would be 'obsessive,'" said Coppens. Mine is "unhealthy." I wish I could love my moths the way Coppens loves his, or the way I've loved other species who I've shared my life with before.
Interview: Bart Coppens
Shannon Lee:
The "About Me" section on your website mentions that you've been interested in moths and butterflies since you were young. What is it about them that spoke to you?
Bart Coppens:
This is a difficult question, because I do not remember it being a conscious choice. Even as a small child, I was very fascinated by insects -- it seems a trait deeply ingrained in my mind. Partially, it is because I have the tendency to strongly notice details and small things, and also because I typically have very strong preoccupations with "specific" subjects that I can be obsessive about.
However, life in general is very fascinating to me. Not just insects, but weird animals and plants in general. When I see them, I feel the urge to find out how they work. I think that by studying the many organisms we share our planet with, we can also find out a lot about ourselves and our own origins. Insects fascinate me because they are representative for `life on Earth: They are extremely diverse (estimations that have been made say there are about 1 to 5 million species of insects) and can be found in many shapes, sizes and colors and occupy many ecological niches. I think that all the "principles" of life including reproduction, population ecology, biodiversity and evolution are something that can be easily seen and studied in insects.
The reason I chose moths is because insects in general are too broad a topic to study: If one wants to become knowledgeable, generally, the best choice is to specialize yourself in one family of insects. Moths have the biggest appeal for me because of their incredible biodiversity, and because I think their life cycles and metamorphosis are fascinating. There is also not a lot of information available about most moth species, especially those in (sub)tropical areas.
Shannon Lee:
What have been your most exciting discoveries about moths?
Bart Coppens:
As a young aspiring entomologist, the things that I have discovered are still limited (I'm only 24). However when I breed moths from eggs and cocoons that have been imported from all over the globe, sometimes I do discover a few new things. Most of my research focuses on the life cycle of moths from egg to adult in captivity; there is a fair share of species of which these life cycles are completely unknown. In many cases, I have been able to photograph caterpillars or adults of which there were no previously known photographs. This sort of research is not very complicated if you are able to figure out how to breed a moth, but there is no information available that tells you what they will eat or how they live in the wild. Sometimes I can extrapolate that information by looking at closely related species and combining it with my breeding experiences. There are a few scientific manuscripts that I am working on that describe the life cycle of a few obscure or poorly studied species.
Shannon Lee:
My relationship with my moths is terrible. How would you describe yours?
Bart Coppens:
Hmm, if I had to pick one word: obsessive.
Shannon Lee:
Is there anything we can we learn from moths?
Bart Coppens:
Many people fail to see the significance in understanding life in general. From the smallest bacteria to worm to plant, the biodiversity on our planet has a lot of secrets. Anything from evolution to understanding our environment and origins on a macro scale or finding useful appliances on a micro scale (much of medicine and technology are directly derived or inspired by natural resources). Think of developing bulletproof fibers based on silk or spider webs to the toxins in plants and animals we have used to synthesize medicines. Penicillin, one of our most important antibiotic medicines, is derived from a fungus.
Shannon Lee:
You also mention rearing rare moth species. Are there any moth species that only exist in captivity?
Bart Coppens:
Yes there are, but not because they're rare. Breeding moths is not a modern phenomenon: For the purpose of silk production, people have been breeding moths for over 5,000 years. Especially in ancient China and India, silk always had a great cultural significance. This has resulted in some moth species to become domesticated in captivity after thousands of years of selective breeding.
Shannon Lee:
What do you think about my pantry moths?
Bart Coppens:
An invasive species. Thus they should be exterminated. Although this is practically impossible at this point.
This past February, as my pantry moths began a particularly dramatic crescendo in population, we put the family dog to sleep. An incredibly kind veterinarian provided the premium service of coming to our house to administer the euthanizing cocktail (a combination of a sedative called Telazol to render a deep, comatic sleep followed by pentobarbital, which stops the heart) that she promised would deliver Sunny, the steadfastly loyal, 14-year-old golden retriever, to her final place of rest.
I bore the necessary responsibilities of scheduling the appointment and sobbing. Wilson, my partner, cried too, in our own tiny procession of mourners. "Remember the time your pet rabbit died?" my mom later asked me over the phone. Thumper. He died in 2001, not 24 hours before 9/11. "You were inconsolable," she reminded me. Meanwhile, a nearby moth loitered on my bedroom mirror, observing Sunny's final breaths through its tiny compound eyes. I wondered if I could learn to appreciate the dusty, copper stripes of its small, delicate wings the way I adored the waving tendrils of fur behind Sunny's ears.
"I mean, you could probably catch just one and try to domesticate it," amateur entomologist and Silica contributor Joe Sutton recently suggested to me. He has started raising his own insects, beetles, as pets.
I figured if I could talk to anyone about a personal shift in perspective when it came to the insect life cycle, it would be him. "I will say, raising bugs is really bittersweet," he lamented. "You can't really interact with them for most of their lives. For example, I've been raising my Hercules beetle for over a year now. It's still pupating, but once it's an adult, I'll still only get to spend a few months with it before it dies. Despite the fact that I've been watching over this little guy for its entire life, I don't think my beetle knows who I am at all."
Interview: Joe Sutton
Shannon Lee:
How are your beetles doing?
Joe Sutton:
They're good! There's not really much to report though. I feel bad when people ask about them and I'm just like, "Yeah, they're chillin' under some dirt." I should actually probably add water to the soil. I've been meaning to do that for the past couple of days.
Shannon Lee:
Nice! How big are they?
Joe Sutton:
I'm not actually sure! The last time I dug them up was when I got the last one that I ordered a few months ago. That one's in it's last larvae stages, so that one's pretty big. It's probably about the size of a golf ball when it's all curled up. I have another one that's in a second stage that's a little smaller and another beetle that's super tiny.
Shannon Lee:
What species of beetle do you have?
Joe Sutton:
One is the eastern Hercules beetle, and the second one is a rainbow stag. I also have another Hercules Lichyi and one Japanese rhinoceros beetle. The place that I order the exotic beetles from is really weird -- it's not like a normal online store. You have to email the breeder and list off all the stuff you're interested in.
Shannon Lee:
I know this is a pretty recent hobby for you. I remember a pre-beetle Joe. How did this hobby begin?
Joe Sutton:
I kind of wanted to get a really cheap, low-maintenance pet. Something that I could just observe or maybe handle, even though I can't do that with the larvae. Fish would be nice, but you can't touch them or do anything that fun. I used to have a hamster growing up, but the problem with rodents is that they smell and I didn't want to deal with that. I was just Googling things for ideas and someone on some message board mentioned bugs as pets. That hadn't ever really occurred to me before, even though I did know that in other countries like Japan, having beetles for pets is a really popular thing.
I don't know if that's still true today, but I remember reading that one of the things that inspired the creator of Pokémon (and I'm a huge Pokémon fan) was going out and trying to find and catch beetles. Kids would apparently catch them and fight them. So there was this weird connection to this thing that I do really like already. I was also really interested in their life stages, the fact that they go from a larva to a pupa to an adult. Bugs were such a great, weird world amalgamation of all these other things that I was interested in. I got into beetles in particular because there are so many diverse species. I also like that you can get a pretty big beetle. I don't like the idea of having something tiny that could just get lost and be scuttling around anywhere.
As Sunny's heart finally slowed to a stop, the vet handed us a small, fluffy patch of her fur (it had been shaved off of her front forearm to administer the IV) before lifting her peaceful-looking body into the back of her car. In two weeks, a package containing her ashes arrived in the mail. I opened the package in the kitchen, sighing heavily before swiftly clapping my hands around another moth, letting its papery body float to the ground without consequence, and without ceremony.
It's been four months since I arranged that initial hit on my pantry moths. Since then, I've spent more than a hundred dollars on mason jars and other clear, airtight containers to store my moth-prone groceries, and I've developed the totally normal habit of taking them out of the pantry, bringing them to eye level and slowly shaking them back and forth, sifting through the grains to scope out any signs of life. Wilson has stripped the wallpaper and repainted the kitchen under the suspicion that the moths were laying their eggs between peeling corners. Amazon sends me emails regularly alerting me when there's a deal on my favorite consumer-grade moth-pheromone trap, Dr. Killigan's Killing Them Softly. And Danny has been to our house two more times to administer silica-infused cedar oil. He stopped charging after the second visit. True to his word, pantry moths are in fact, "hard to get rid of."
As I finish documenting this experience, there are still a handful of plodia interpunctella fluttering around the house, searching for a food source that I'll be damned if they find. I can almost always count on seeing a few in the bathroom on one of my late-night trips to the toilet, a consequence of having accidentally left the light on.
In a recent conversation I had with conceptual, sometimes environmental artist Mel Chin, I asked about the difference between ecology and the environment.
"Ecology," he explained, "is essentially about relationships." I think about this as I browse the website of yet another New York-based eco-friendly extermination company, Ecological Pest Control in Smithtown, New York. While household efforts have not completely eradicated the moths from existence within our domicile, they are at least manageable now. Perhaps it's enough that I now have a healthy relationship with my pantry moths, one where we are able to cohabitate in relative harmony (punctuated by an occasional swat).
Moving my fingers over the mouse pad to close out of the website's tab, I spot something small, dark and shiny scuttling on the floor out of the corner of my eye -- a fast and disconcertingly large black ant, undoubtedly leaving a strong pheromone trail that may one day lead another colony to my food and water.