Is the alarming rise in Covid cases a result of testing quirks?

The huge rise in coronavirus cases this week makes for bleak reading, and brought fears that even the toughest restrictions are failing to bring numbers under control.
More than 33,000 infections were recorded in Britain on Thursday – the highest figure on record, and a jump of more than 10,000 in one day.
Yet delving into the data suggests that the headline figures published on the Government's dashboard each day are not a good measure of the pandemic, and much of the alarming rise may be a result of testing quirks dating back weeks.
In September and October, Professor Jim Naismith, director of the Rosalind Franklin Institute at Oxford University, noticed something startling about the percentage of people testing positive for coronavirus.
Results from Pillar 2, which is testing the wider population, showed that positivity was between five and 10 per cent, and on some days, even rose above 10 per cent.
It was clearly way too high – the World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates a prevalence of less than five per cent – so it indicated that testing was being carried out on groups who were not representative of the wider population.
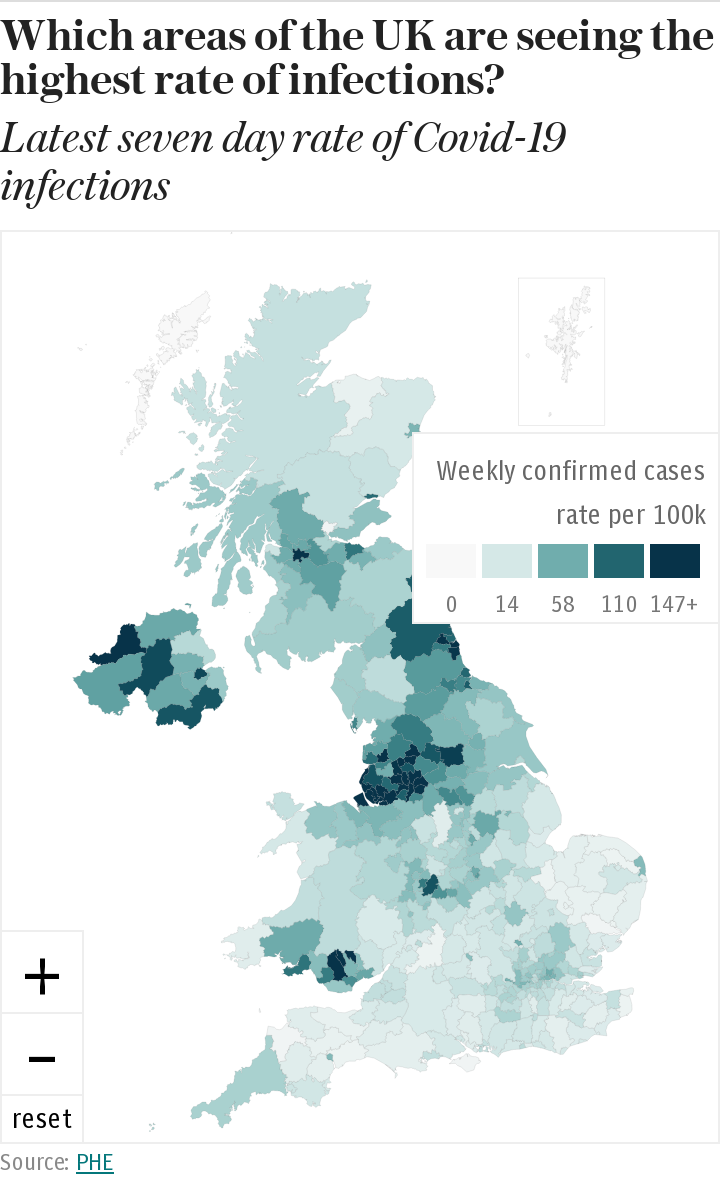
It was around the time that NHS Test and Trace began picking up huge numbers of cases in university students, but it may have meant that community cases were being missed, which are only now being represented in the figures.
Prof Naismith said: “When you have high positivity rates, you can miss a growth in infections. The positive test data missed the growth in September and early October.
“Thursday’s number of Pillar 2 tests processed showed a significant increase and I think the increase in cases reflects a more accurate measurement of the pandemic, not a surge in infections.
“The high level of positivity in Pillar 2 seen over the last weeks meant testing was no longer accurately measuring the pandemic.”
There have also been ongoing problems with tests coming back late, which can skew the figures. Just 52 per cent of cases reported on Thursday related to the previous two days, meaning thousands were from an earlier date.
Looking at the pandemic trajectory based on when tests were taken – rather than reported – shows a much more gentle upwards curve.
And a seven to 10 day lag needs to be factored into the case data, because there is a delay in catching coronavirus and testing positive.
Many of the most recent cases would have been acquired in the days leading up to new measures on November 5, and we should start seeing a fall next week as the benefits of lockdown start to feed into the test results.
Cases fell to 27,301 on Friday, a drop of 18 per cent from Thursday. The number of tests carried out rose to nearly 380,000.
Elsewhere, Office for National Statistics (ONS) surveillance numbers data suggests that the pandemic is decelerating. At the end of October, cases were rising by around 30 per cent a week, but now that increase has fallen to just under six per cent.
Likewise, new results from the React survey by Imperial College suggest the R-rate in the last half of October was 0.85 per cent, although a rise was detected towards the end of their study period, which may have been caused by a pre-lockdown rush to the pub.
King’s College, which has been monitoring symptoms through its tracker app since the first wave, also believes the R-rate is now 0.9 for Britain.
“We aren’t out of trouble yet, but with numbers falling and the news of a vaccine, it feels like the end is in sight,” said Tim Spector, Professor of Genetic Epidemiology at King's.
Government scientists also now believe that the figures are heading in the right direction, even if the daily dashboard appears to be saying something different. The R-rate is now between one and 1.2, and is expected to fall below one within the fortnight.
“There’s no doubt things are coming down,” said a Government source. “In some places they may be below one across the UK now, particular in Wales and maybe in Scotland and one or two places across England.”
Some of the Thursday rise has also been caused by increased testing. The number of tests carried out on November 12 was nearly 378,000 – the highest ever carried out on a single day, and city-wide testing is now taking place throughout Liverpool.
Commenting on the jump in cases, Prof Deborah Dunn-Walters, Immunology Section Lead, at University of Surrey, said: “I suspect that what we are seeing are some of the asymptomatic cases that were previously hidden to us when we only tested people with symptoms.
“It would be interesting to see what proportion of the cases were asymptomatic.”

