AVX-512 Works Surprisingly Well on Ryzen 7040 Series Phoenix CPUs

Phoronix recently benchmarked AMD's most sophisticated Ryzen mobile architecture, the 7040 mobile series, in AVX-512 workloads to see how performant it is compared to Intel's last two generations of AVX-512-supported CPUs in the mobile space. Turns out, AMD's Phoenix series CPUs are incredibly effective AVX-512 chips, easily beating out the competition in power efficiency and performance.
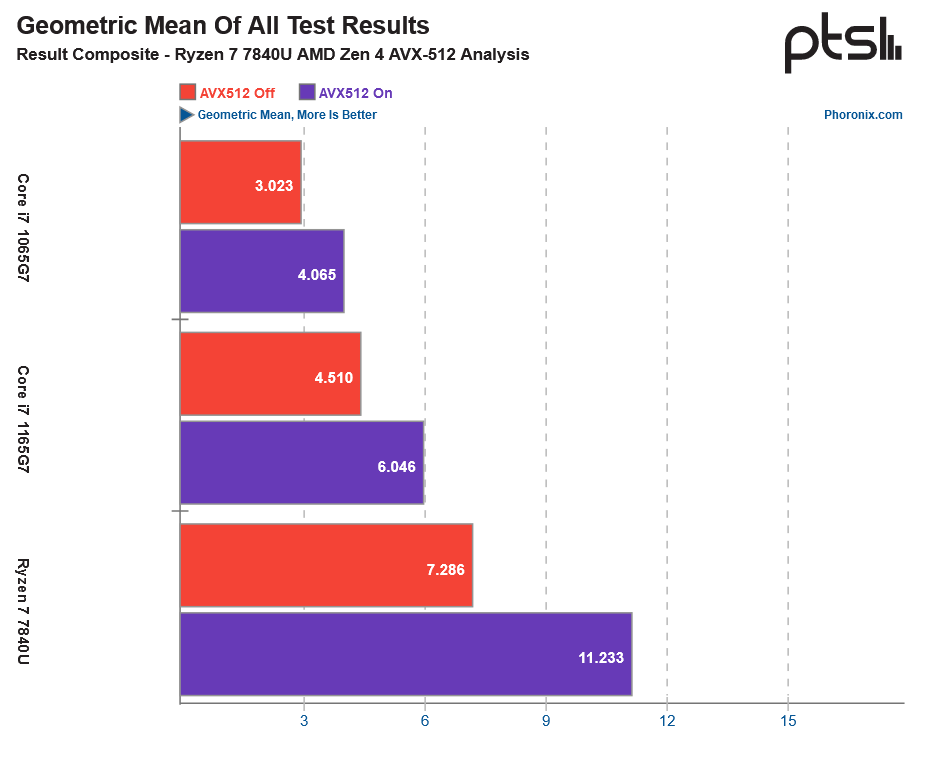
The CPUs Phoronix tested included a Ryzen 7 7840U, as well as Intel's older i7-1165G7, and i7-1065G7 — which were the last mobile CPUs to support AVX-512. The AMD chip blew past the older Intel CPUs outperforming the 1165G7 by 46% and outperformed the older 1065G7 by a whopping 63%. The Ryzen 7 chip also saw the highest performance gain when enabling AVX-512, with a 54% performance margin when enabling or disabling AVX-512. The Intel chips weren't even close, with a performance margin of 35%.
AMD's performance gains with AVX-512 are impressive, especially given that Zen 4 — the CPU architecture the 7840U utilizes — is the very first architecture from team red to adopt the new instruction set. Intel, conversely, has had years of experience developing AVX-512-capable architectures but has failed to pull off the same performance margins as AMD. Intel also had to deal with other architectural oddities found in Rocket Lake and Alder Lake regarding AVX-512 performance and capability, that AMD's Zen 4 architecture does not have.
AVX-512 is a relatively new instruction set that was first developed by Intel in the mid-2010s. The instruction set offers more efficient data processing compared to other AVX standards and is capable of boosting highly complex computation workloads, such as scientific simulation, 3D modeling, analytics, data compression, deep learning, and more.
The instruction set was first seen in desktop consumer chips in 2017, starting with Intel's Skylake-X CPU lineup of HEDT processors. Since then, the instruction set has made its way to desktop and mobile consumer chips, including Rocket Lake, Tiger Lake, and Ice Lake.
But, unexpectedly, Intel dropped AVX-512 support altogether when Alder Lake launched, even though the architecture featured improved AVX-512 capabilities over Rocket Lake. The problem was that Intel couldn't get AVX-512 to work in conjunction with its E-cores, which did not support AVX-512 at all. Though oddly, AVX-512 was actually functional on the P cores for a little while, as long as you disabled the E-cores from the BIOS.
The ironic part is that AMD was busy integrating AVX-512 into its Zen 4 CPU architecture when Alder Lake dropped, making 2022 one of the worst years to drop AVX-512 support on the consumer side for Intel.
So, not only do AMD's Zen 4 mobile CPUs feature AVX-512 support, but they are also the only players in the space until Intel decides to reintroduce it in its consumer mobile chips in the future. This will give AMD-powered notebooks a huge performance advantage for users that can take advantage of AVX-512's faster processing capabilities.

