Likely 2020 Voters Support Parts Of Green New Deal, Despite Reservations Over The Cost

A majority of likely 2020 voters supports key aspects of a Green New Deal even when faced with potential costs and downsides, but strict regulations to decarbonize the nation’s top polluters could trigger a backlash, according to a new poll from proponents of the policy.
The survey, released by the think tank Data for Progress and shared with HuffPost, found net support for a range of policies, including improving drinking water infrastructure, reforesting land, providing job training and insurance to displaced workers and guaranteeing clean-energy jobs.
“At the core, the Green New Deal is about a moral imperative to transform our economy and improve people’s lives for the better,” said Greg Carlock, the researcher at Data for Progress and architect of the first Green New Deal blueprint published last September. “You can’t put a price on that, but even when you do, people still support it.”
But faced with a range of possible price tags, voters’ support varied, suggesting costs could factor high into the Green New Deal’s political viability. The results showed a majority of voters would likely oppose policies with stringent mandates ― rules requiring all cars be electric by 2030 and every fossil fuel power plant close by 2035.
To test the support, Data for Progress commissioned the Democratic pollster Civis Analytics to survey 3,496 likely voters between Jan. 4 - 26 on 11 policies expected to be included a Green New Deal. The poll tested four different cost scenarios on each question, randomly alternating between zero, low, medium and high prices to test how the cost of a policy weighed on one-quarter of respondents’ opinions.
The green jobs guarantee, considered by Green New Deal proponents to be the heart of the suite of policies, proved one of the tricker components. In a lengthy prompt, the survey asked respondents if they support or oppose a policy that Democrats promised would “guarantee an environmentally friendly job to every American adult, with the government providing jobs for people who can’t find employment in the private sector.”
The question described the job as a position that would pay “at least $15 an hour, included healthcare benefits, and collective bargaining rights.” The surveyors added that Republicans warned the policy “would increase the national debt, endanger the long term health of our economy, and this policy will end up paying people who can’t contribute in the job market to perform pointless busy work.”
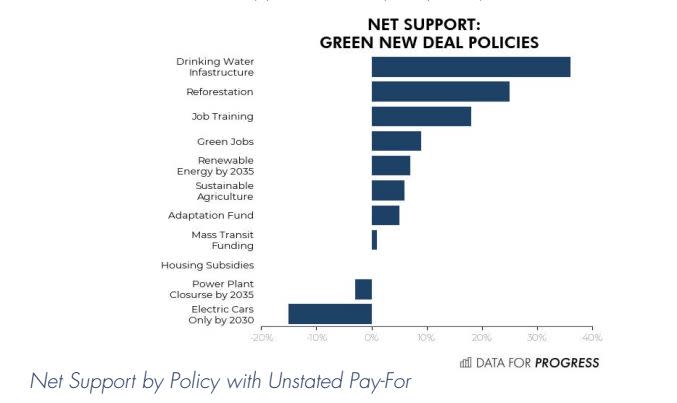
Thirty-nine percent supported the green jobs guarantee, 33 percent opposed and 27 didn’t know. Without a price, voters were 9 percentage points likelier to support than oppose the policy. At a low of $100 billion, support hit 2 percentage points. Voters were about evenly divided on policies costing $500 billion or $1 trillion.
Mandates requiring the country to generate 100 percent of its electricity from renewables by 2050 enjoyed sweeping support. The question noted that Democrats believed such a policy would “kickstart the renewable energy sector, creating jobs for many Americans and ensuring that America leads the world in green technology,” while Republicans said, “this would take away freedom from American consumers, put people out of work, and raise prices for everything from transportation to consumer goods.”
Thirty-eight percent supported the proposal, 33 percent opposed and 30 percent didn’t know. Without a price, voters backed the policy by 7 percentage points. At a low of $25 billion, that figure fell to 2 percentage points. Support held steady at 1 percentage point for both a medium cost of $37.5 billion and a high of $50 billion. Age impacted support at the unstated price level. Voters aged 18 to 34 supported the policy by 15 percentage points, while those 65 and older opposed the policy by 11 percentage points.
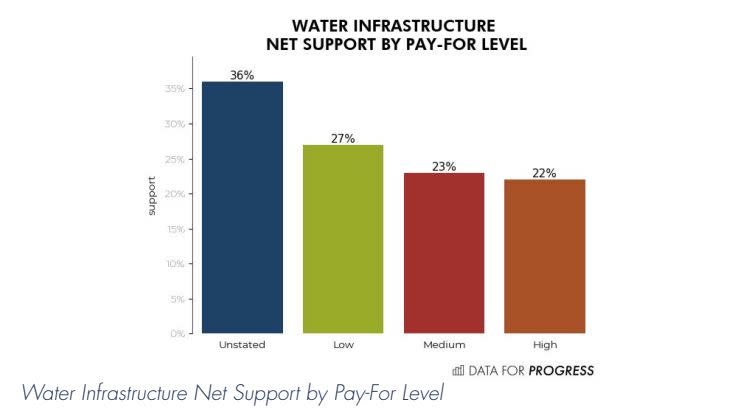
Policies improving drinking water infrastructure proved to be the most popular. The survey outlined a proposal to improve infrastructure “and replace lead pipes,” considering that Republicans “say that our drinking infrastructure is in good shape already, and this represents a wasteful use of resources that will burden our children with debt.”
Half of the respondents supported the proposal, 21 percent opposed and 29 percent didn’t know. At no stated price, voters supported the proposal by 36 percentage points. Faced with a low cost of $25 billion, support sank to 27 percentage points. At a medium cost of $37.5 billion, the percentage dropped to 23. At a high of $50 billion, it fell to 22 percentage points.
The least popular policy was one “proposing requiring that all new cars sold be electric by 2030.” The question said, “Democrats say this would help stop climate change, save thousands of lives by reducing pollution, and make the U.S. the definitive leader in the electric car industry.”
Republicans say this would take away freedom from American consumers, put people making cars out of work, and make new cars unaffordable for the average American. Do you support or oppose this policy?”
Just 26 percent supported the policy, with 44 percent opposed and 33 percent unsure. Without even seeing a price, voters opposed the electric car mandate by 15 percentage points.
The second-least popular was a proposal “requiring that all fossil fuel plants (coal, natural gas and oil) cease operating by 2035” in an effort to “help stop climate change” that Republicans say “would put many Americans out of work, and could lead to an energy crisis as energy prices soar.”
Voters opposed the measure by 3 percentage points, again without seeing a price.
The findings come just weeks before the Senate is expected to hold a vote on the Green New Deal resolution Sen. Ed Markey (D-Mass.) and Rep. Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez (D-N.Y.) released last week. The measure, essentially a political statement outlining the scope of what’s needed to prepare the U.S. for a rapidly warming climate, staked out an ambitious list of policies to protect vulnerable communities already suffering from pollution.
In what Green New Deal supporters called a cynical ploy to up halt their movement’s growing momentum, Senate Majority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.), a veteran climate change denier who’s taken millions from the fossil fuel industry, vowed this week to hold a vote, forcing swing-state senators to take positions on a policy Republicans are aggressively working to vilify.
The vast majority of Americans understand climate change is happening and human-caused emissions are the primary cause. In December, 81 percent of registered voters supported the goals of the Green New Deal, including 64 percent of Republicans and 57 percent of conservative Republicans, according to a poll from Yale and George Mason universities. But the pollsters warned that the overwhelming bipartisan support could erode as the Green New Deal became more closely associated with individual politicians.
The Sunrise Movement, the grassroots climate advocacy group whose thousands of volunteers helped propel the Green New Deal into the national stage in November with a series of protests against top Democrats, said Wednesday it would ramp up actions confronting both Democrats and swing-state Republicans, urging them to support the policy. Groups like Justice Democrats, the left-wing organization that helped run Ocasio-Cortez’s campaign, and Data for Progress vowed to aid efforts to primary any Democrats who oppose the Green New Deal.
“The Green New Deal won’t hurt Democrats politically,” said Sean McElwee, the co-founder of Data for Progress. “But failing to take aggressive action on climate change could demoralize the millennial base who demand immediate action on climate change.”
Related Coverage
McConnell Trolls Democrats By Pledging A Vote On The Green New Deal
Green New Deal Activists Shift Focus To Vulnerable Republicans Ahead Of Senate Vote
EPA Vows To Regulate Cancer-Causing 'Forever Chemicals' Polluting Drinking Water
Also on HuffPost
Love HuffPost? Become a founding member of HuffPost Plus today.
Alaska

Venice

Antarctica

The Great Barrier Reef

The Himalayas

The Maldives

The Alps

The Arctic

Micronesia and Polynesia

This article originally appeared on HuffPost.

