Taylor Swift, the All Blacks, Japanese nukes and the gathering crisis in capitalism
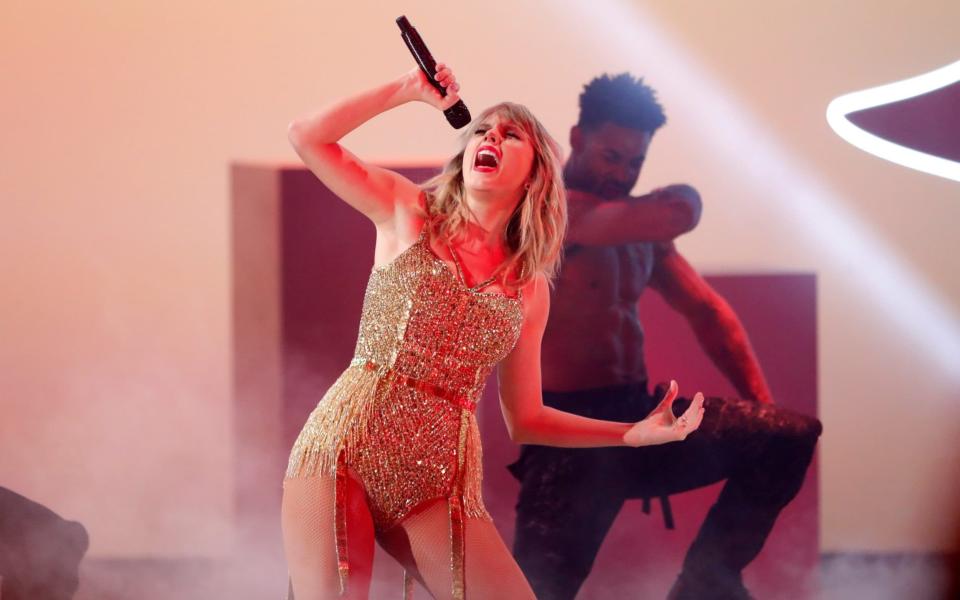

In the past week Taylor Swift released a re-recording of her 2008 album Fearless, several All Black rugby players have been involved in an acrimonious standoff with their sport’s governing body and the company that controls dozens of Japan’s nuclear reactors has lost its boss.
These seemingly unrelated events are among the latest dispatches from the ever-advancing frontier of private equity investment. Once an obscure corner of the financial industry, private equity is now the source of funding for an increasingly bewildering array of assets, including some where the primacy of the bottom line is rubbing up against questions of culture, heritage and national security.
Private equity’s advance has been accelerated by two trends in particular. One is the incredible shrinking public markets. Between 2000 and 2018 the number of publicly listed companies in the US fell from 7,000 to about 4,000 while the number of private equity-backed companies climbed from fewer than 2,000 to nearly 8,000, according to the Milken Institute.
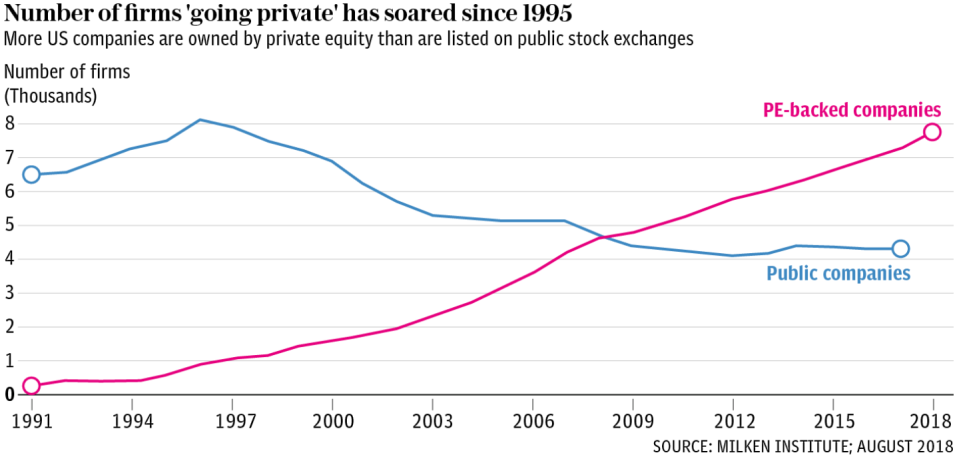
The other is the global yield famine. Central banks have kept interest rates close to zero for over a decade now, prompting an increasingly desperate search by investors for returns in ever-more remote nooks and crannies of the global economy.
Private equity is in the vanguard of this hunt and expected to be the fastest-growing asset class over the next five years, according to research by Preqin. The industry controlled $4.4 trillion last year but this is forecast to rise to $9.1 trillion by 2025.
Firms are sitting on almost $1.5 trillion of “dry powder”- unallocated capital that’s ready to be invested, according to a recent report by McKinsey. This tidal wave of money is already creating some weird eddies and currents.
The rights to Taylor Swift’s first six albums were bought by the music mogul Scooter Braun in 2019 with the backing of the private equity firm Carlyle among others. Swift has been fighting a guerilla war ever since, including blocking her songs from being used in films and adverts.
The re-recording is a full frontal attack. Swift hopes her fans will download the new versions of her songs on streaming services like Spotify and thus diminish the value of her original master recordings, which are (were?) reportedly valued at $300m.
In the past Swift had railed against “the unregulated world of private equity” which is “buying up our music as if it is real estate”. It has been amusing watching her give the moneymen a business masterclass, but also suggests that private equity firms looking to deploy ever larger quantities of loot may be snapping up assets they don’t fully understand.
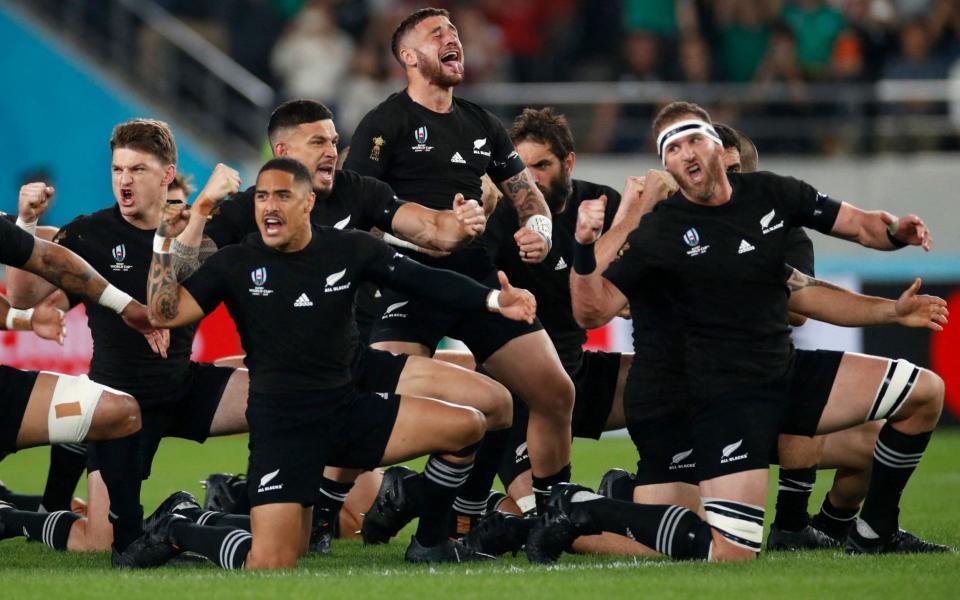
Similar tensions have been generated by private equity’s push into the world of sport and especially rugby. Earlier this year, Silver Lake, a US private equity firm that mostly invests in tech companies, made a £235m bid for a 15pc stake in the All Blacks commercial rights.
But in a letter sent to New Zealand Rugby, the body that represents the country’s players said it will not grant approval for the sale.
“New Zealand’s rugby players play for themselves, their family and their country with a commitment to success that is demanded by history and required by legacy,” it read. “New Zealand’s rugby fans understand this commitment and see in it the essence of what, from one perspective, it means to be a New Zealander. This, above all, is what NZR is selling and Silver Lake are buying.” Even the most red-blooded capitalist might struggle to argue with this.

Earlier this week, a similar attempt to rebuff private equity advances resulted in the chief executive of Toshiba stepping down as members of the company’s board attempted to block a $20bn buyout offer by CVC. Rival private equity group KKR is said to be waiting in the wings with an even richer bid, which, if successful, would easily be the largest leveraged buyout in Japanese corporate history.
But any attempted takeover will be extraordinarily sensitive given the importance of Toshiba to Japan’s nuclear and defence industries. It’s one thing having barbarians at the gates; it’s quite another if those gates are guarding a nuclear reactor.
Private equity has an important role to play in the economy. Many failing companies have been bought, restructured and revived away from the glare of the public markets, with their onerous, box-ticking disclosure requirements (although others have been sucked dry or broken up for parts).
But there is a danger that the balance is getting out of whack. Despite their flaws, public markets are the most democratic and inclusive form of capitalism we’ve yet devised. As more high-profile assets (especially ones to which people have a visceral attachment) are snapped up by private equity firms and a greater number of companies delist, ordinary people will understandably feel they have less of a stake in the whole jamboree.
Unfortunately the authorities appear intent on making things worse, not better. The UK Government is looking to introduce a range of measures that, in an attempt to introduce much-needed audit reform, will also add to the burden on public companies. And the Biden administration is expected to follow Europe’s lead by ushering in new rules around corporate disclosure especially with regards to environmental, social and governance investing.
Hester Peirce, an influential Republican commissioner at the US Securities Exchange Commission, the country’s main financial watchdog, has repeatedly warned that this could be a slippery slope. Just this week Peirce said the position of ESG advocates, who argue that prosperity alone is an insufficient measure of progress, was “unassailable”.
However, she expressed concern that a single set of ESG metrics could constrain decision making and impede creative thinking. Peirce added: “Such a regime would likely expand the jurisdictional reach of the [SEC], impose new costs on public companies, decrease the attractiveness of our capital markets, distort the allocation of capital, and undermine the role of shareholders in corporate governance.” Apart from that, great idea.
It would certainly be ironic if ESG advocates and those arguing for ever greater corporate disclosure ended up forcing even more companies off the public markets and into the arms of investors whose only measure of progress is prosperity.
