Everything to Know About the Winter Solstice, Including When and Why It Happens

Matt Cardy/Getty
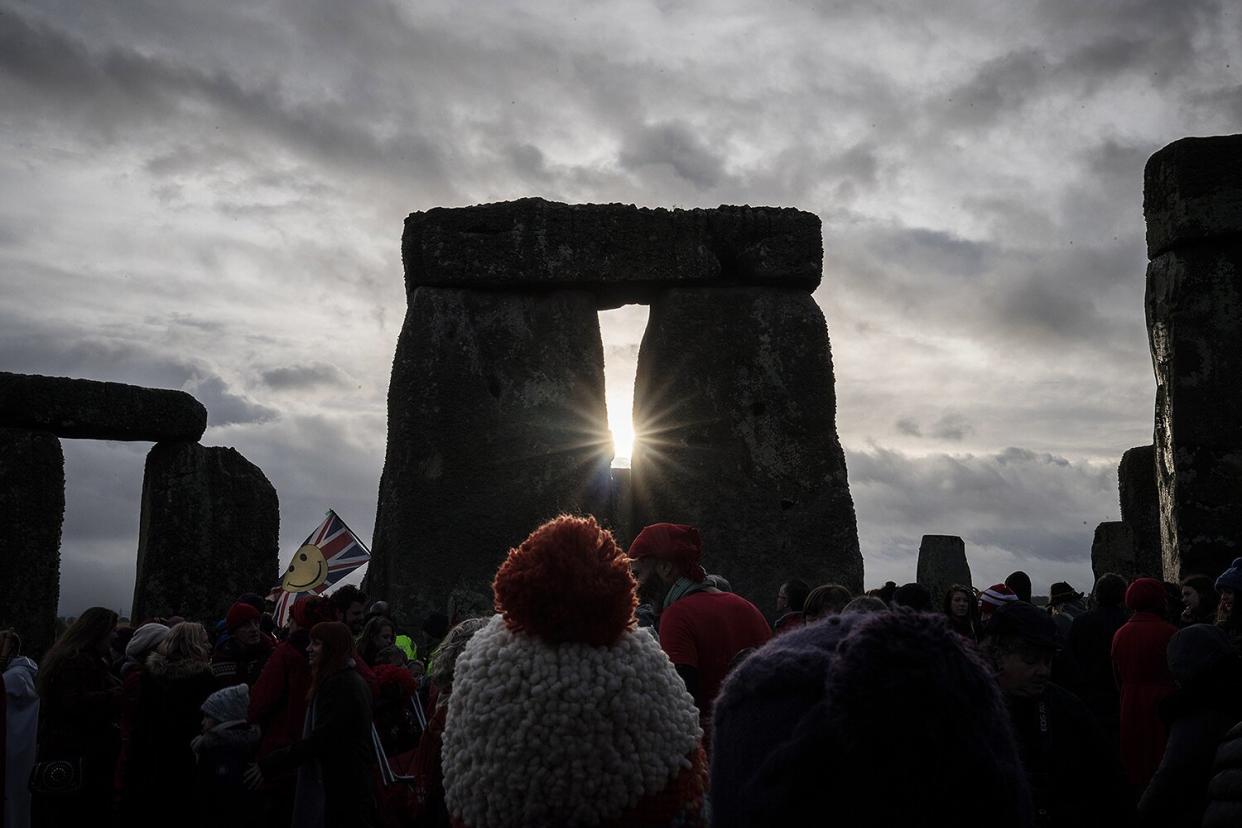
The winter solstice marks the shortest day and longest, darkest night of the year.
Also known as the December solstice, the astronomical occurrence happens due to Earth's tilted axis of rotation in relation to the sun. So while the Northern Hemisphere experiences the start of the winter season, the Southern Hemisphere experiences the first day of summer.
But have no fear, freezing earthlings north of the equator — there is a bright side! Every day that follows the winter solstice gradually gets longer. Simply put, the hours of daylight increase and mark one more day closer to summer.
Don't think we forgot about the other two seasons! While the solstices signify the start of winter and summer, planetary scientists also use equinoxes to define the beginning of the autumn and spring seasons.
RELATED: Everything to Know About the Ursid Meteor Shower, Including When It Peaks and How to Watch
The word equinox derives from Latin words "aequi" (meaning equal) and "nox" (meaning night). Taking place annually in March and September, equinoxes mark the time when the day and night are approximately equal in length.
Although the solstices and equinoxes traditionally define the start of the astronomical seasons (based on the Earth's position in relation to the Sun), meteorological seasons define the temperature and climatological patterns on Earth.
Keep scrolling for everything to know about the winter solstice, including when and why it takes place.
When is the winter solstice?

Getty
The winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere (the Earth's half north of the equator) occurs at 4:48 p.m. ET on Wednesday, Dec. 21, 2022. It also coincides with the Ursid meteor shower this year!
RELATED: Everything to Know About December's Cold Moon, the Last Full Moon of the Year
Why does the winter solstice happen?
Getty
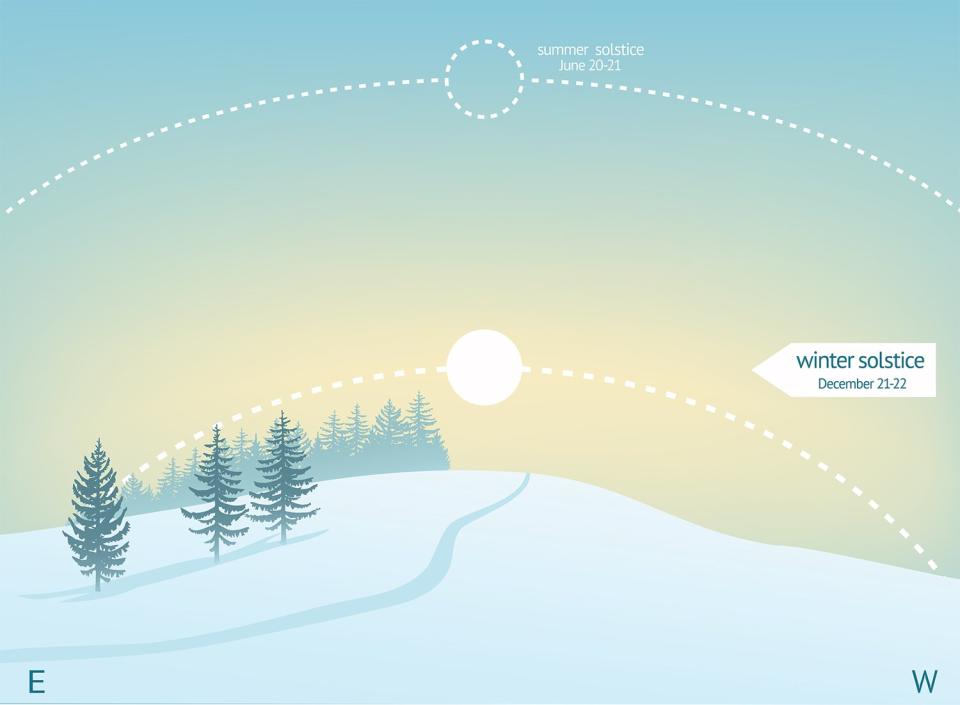
The winter solstice occurs two times each year because Earth's axis of rotation is tilted 23.4 degrees in relation to the Earth's orbit around the Sun, according to NASA. When the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth faces the sun and experiences summer, the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter — and visa versa.
The tilt drives the Earth's seasons, therefore causing the Northern and Southern Hemispheres to get unequal amounts of sunlight over the course of a year. From March to September, the Northern Hemisphere experiences more daylight, driving the spring and summer seasons — while September to March experience longer nights, driving the autumn and winter seasons.
Does the winter solstice mark the official start of winter?

Getty
While the winter and summer solstices have become synonymous with representing the official starts of their respective seasons, their starts technically depend on which definition is being used. Seasons can be defined in two ways: astronomically or meteorologically.
Astronomical seasons are based on Earth's position as it rotates around the sun, while meteorological seasons are based on annual temperature cycles. Therefore, the four seasons have different start and end dates depending on the calendar method utilized.
Although exact start times vary between the two methods, they generally fall within the same time frames. The astronomical method pinpoints a specific date across four months to signify the start of each season, while the meteorological method breaks the seasons down into groupings of three months.
Astronomically, winter in the Northern Hemisphere stars in December, spring starts in March, summer starts in June and autumn starts in September. Meteorologically, winter in the Northern Hemisphere includes December, January, and February; spring includes March, April, and May; summer includes June, July, and August; and fall includes September, October, and November.
The Old Farmer's Almanac, regarded as the "calendar of the heavens," uses the astronomical definition to define each of the four seasons.
RELATED: Everything to Know About the Geminid Meteor Shower, Including When It Peaks and How to Watch
When's the summer solstice?

The summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere is likely to fall on June 20 or June 21, 2023 — meaning days will only get longer and brighter from here. Let the countdown begin!

